Construction
of a Problem
Organizational
Context
Assessment
The goal of macro practice is “to bring about _______
________ (two words).
(Netting, Kettner, McMurty, & Thomas, 2011)
What is planned changed?
The act of making the assertion of presenting the argument that a condition is a problem.
What is claimsmaking?
This stakeholder is most directly impacted by the problem or condition.
Who is the primary stakeholder?
_______ and _______are sites of (arena) and drivers for intervention.
What are communities and organizations?
Fill in the blank:
Problems are translated to needs. Needs are translated to ________________.
What are interventions?
According to Meenaghan, Gibbons, and McNutt (2005), __________ involves intervention with organizations, communities, and groups of people).
What is macro practice?
In the traditionalist (rationalist) approach to the construction of social problems, a social problem is a condition that is harmful to society and ______________________ (3 words)
In the traditionalist (rationalist) approach to the construction of social problems, a social problem is a condition that is harmful to society and ______________________ (3 words)
Stakeholders who have no interest or involvement in an issue, but possess the power to influence are known as ______.
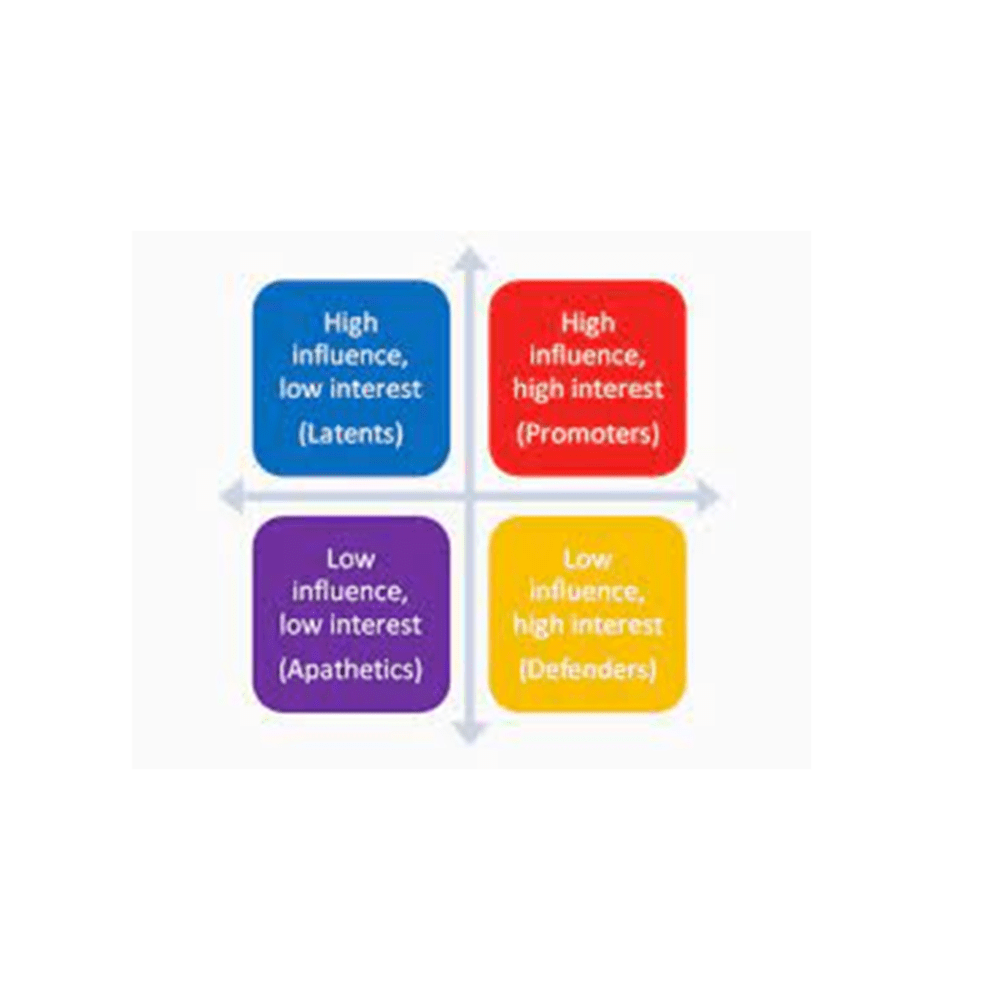
Who are latents?
According to The Community Tool Box, understanding this foundational aspect, which includes history, demographics, and power structures, is essential for macro social workers to effectively design interventions and address community issues.
What is community context?
Need defined as falling below a standard or criterion established by custom, authority, or general consensus
What is normative need?
What is this framework and what do the three interlocking circles represent?
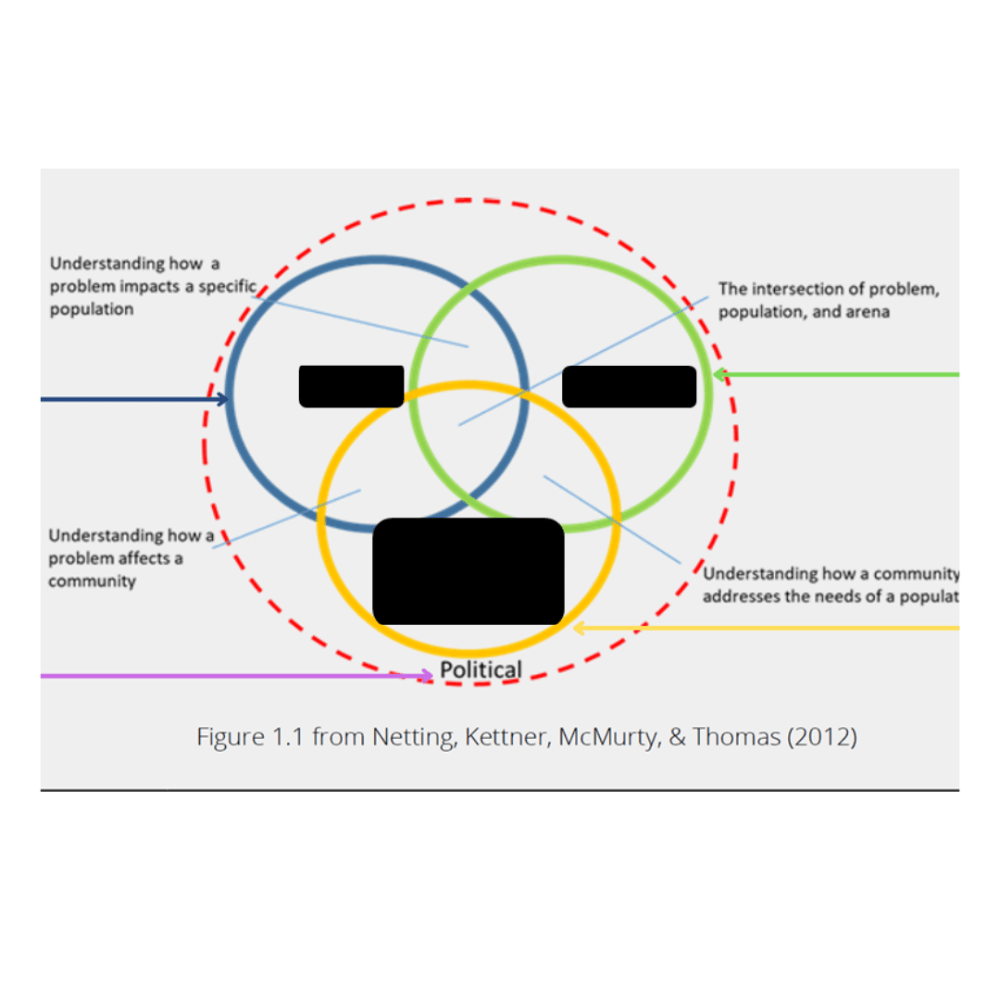
Macro Practice Framework; Problem, Population, and Arena
Practicing _______, allows us to see how our identities, values, worldviews, and experiences shape what we see as problems, how we frame problems, and our motivation and ability to address them.
What is reflexivity?
Stakeholder interests vary according to _________.
What is motivation?
The Community Tool Box, Chapter 3, Section 2 emphasizes the importance of identifying this specific type of community member as a crucial step in building effective partnerships for social change.
What is an informal leader?
_______ ________ are conducted with the purpose of:
Gathering information to understand community or problem
Plan a program or intervention
Understand community needs, assets, and resources
What are community assessments?
Use the following table.
Direct Practice = treatment plan + intervention
AS
Macro Practice = 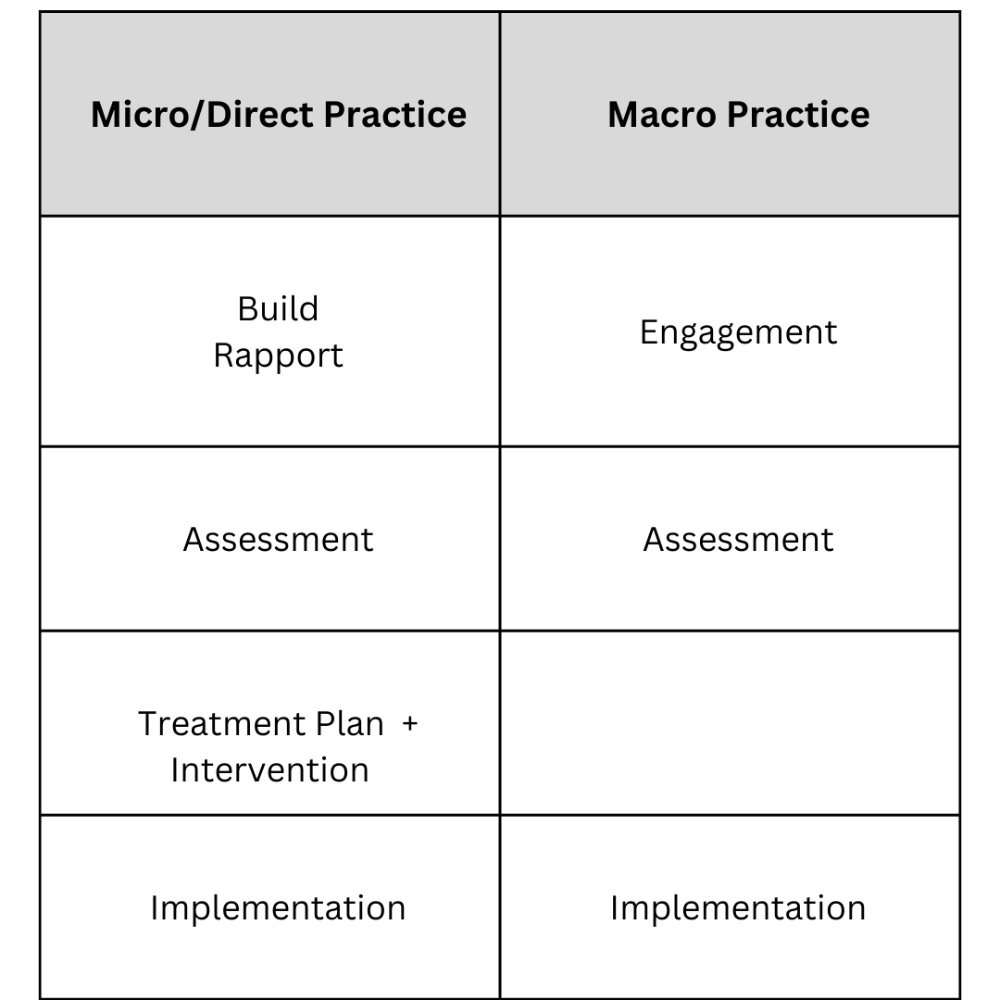
What are logic models and interventions
True or false. Not all conditions that are harmful to society and affect lots of people rise to the level of a social problem that spurs intervention and policy change.
True
Meet & greets, tabling, public forums, walking tours, and cultural events are all strategies used to __________ ___________ (two words).
What is engage stakeholders?
Shared norms, beliefs, and behavioral expectations that drive behavior and communicate what is valued in organizations”
Ex. “the way we do things around here.”
What is organizational culture?
The US Census is an example of this type of data that is collected by researchers directly from the main sources through interviews, surveys, and experiments.
What is primary data?
In "Poverty, by America," Matthew Desmond explains that this systemic issue, often addressed in macro social work, is not simply an individual failing but a societal condition maintained by policies that prioritize the interests of the wealthy over the needs of low-income individuals.
What is structural inequality?
_______ __________ (two words) requires asking: Who is labeling this a problem? What response is being suggested? Why now? How was this handled in the past?
What is problem analysis?
There are many considerations for engaging with stakeholders. If engaging with a group of K-12 teachers around improving student coping and resilience. What considerations might be important here?
What is:
Who is leading or facilitating?
Time?
Resources?
How will emotions be handled?
Who is with the children while this is happening?
Communication techniques?
Psychological safety?
Cultural considerations?
“Employee’s perception of psychologic impact of the work environment on well-being”
What is organizational climate?
A serious exploration of need should account for all four dimensions (types of need). List all 4 types.
What is:
Normative Need
Perceived Need
Expressed Need
Relative Need