This molecule serves as the genetic blueprint for all living organisms and is composed of nucleotides.
What is DNA?
What is the component of amino acid structures that varies among different amino acids??
what is the components of the R group?
What is one characteristic that ALL lipids have in common?
none of them dissolves in water.
This simple sugar, also known as glucose, is a primary source of energy for cells.
What is a monosaccharide?
What is a reaction called where water molecules are produced as a polymer is formed from monomers?
What is dehydration synthesis?
This type of nucleic acid is single-stranded and plays a key role in protein synthesis.
What is RNA?
What are pyrimidines?
- Structure: Pyrimidines have a single six-membered ring structure.
- Nitrogenous Bases: The main pyrimidines are:
- Cytosine (C)
- Thymine (T) (found in DNA)
- Uracil (U) (found in RNA)
- Characteristics:
- Smaller than purines.
- Involved in base pairing (C pairs with G, T pairs with A in DNA; U pairs with A in RNA).
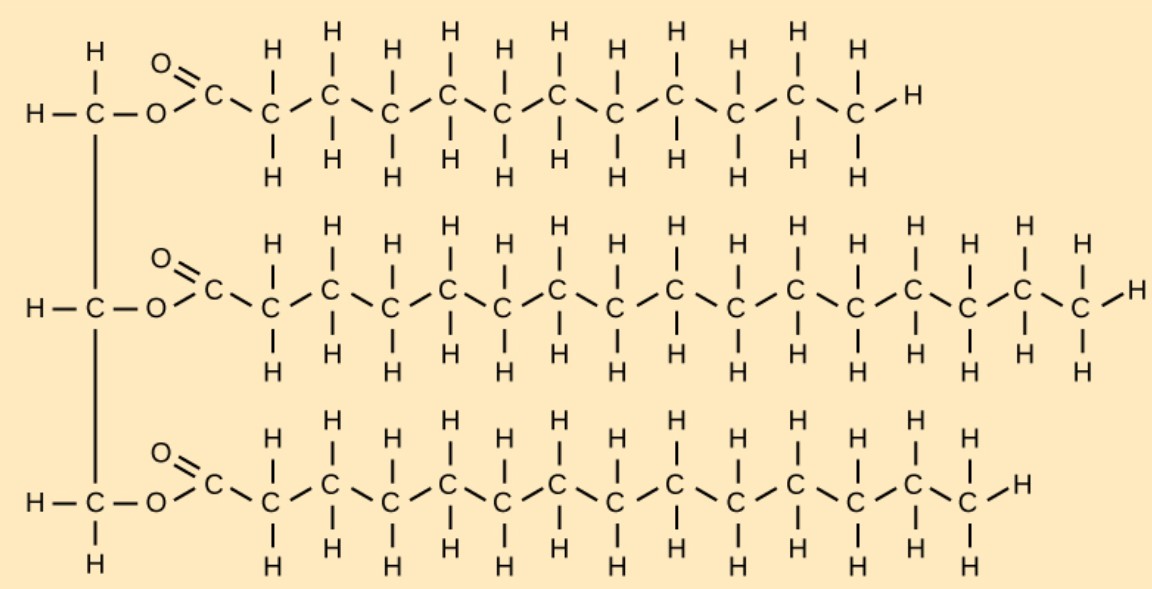
What is a triglyceride and saturated fat?
These complex carbohydrates are made up of long chains of monosaccharides and include starch and glycogen.
What are polysaccharides?
What are the monomers of nucleic acids called?
What is nucleotides?
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA and how do they pair together?
What is cytosine, guanine, adenine, thymine
C-G and A-T.
What are purines? Make a summary table with your team.
- Structure: Purines have a fused double-ring structure, consisting of a six-membered and a five-membered ring.
- Nitrogenous Bases: The main purines are:
- Adenine (A)
- Guanine (G)
- Characteristics:
- Larger than pyrimidines.
- Also involved in base pairing (A pairs with T in DNA; A pairs with U in RNA; G pairs with C in both DNA and RNA).
- Summary Table
Feature Pyrimidines Purines
Structure Single ring Double ring
Examples Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil (pyrimidine)
Adenine, Guanine (purines)
Size Smaller Larger
 What is this molecule?
What is this molecule?
What is a phospholipid?
This common carbohydrate is composed of two monosaccharides, specifically glucose and fructose, and is found in table sugar.
What is sucrose?
What are the two types of unsaturated fats?
What is? Monounsaturated Fats: One double bond (e.g., olive oil).
Polyunsaturated Fats: Two or more double bonds (e.g., fish oil, flaxseed oil).
This specific bond connects the sugar of one nucleotide to the phosphate group of the next in a DNA or RNA strand, forming the backbone of the molecule.
What is a phosphodiester bond?
This macromolecule is made up of long chains of amino acids and plays crucial roles in biological processes, including catalyzing reactions and providing structure.
What is protien?
How can you tell if a fatty acid is a saturated or unsaturated fatty acid?
Saturated= No double bonds
Unsaturated= Double bonds
This polysaccharide, found in plant cell walls, provides structural support and is not digestible by humans.
What is cellulose?
What are the three components that make up a nucleotide?
phosphate group, a sugar (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA.) and a nitrogenous base
Where does the sugar connect to the next nucleotide?
The sugar connects to the next nucleotide through its 3' carbon, where the next phosphate group attaches. This forms the sugar-phosphate backbone.
This type of bond forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another, linking them together in a protein chain.
What is a peptide bond?
This type of lipid consists of a glycerol backbone linked to three fatty acids, making it a major form of energy storage in animals, commonly found in adipose tissue.
What is a triglyceride?
This type of carbohydrate is known for its role in cell recognition and signaling, often found attached to proteins and lipids on cell surfaces.
What are glycoproteins (or glycolipids)?
where does the phosphate group attach to the sugar molecule, and what kind of bond does this create?
The phosphate group (PO₄) attaches to the 5' carbon of the sugar molecule. This creates a phosphodiester bond.