Which macromolecule contains Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen and Phosphorous?
Examples of this include DNA & RNA.
Nucleic Acids
This macromolecule is not water soluble -- meaning it cannot dissolve in water.
ex. putting oil in water
What are lipids?
Which two macromolecules serve as energy sources for cells?
DOUBLE POINTS: How are these energy sources different
Carbohydrates -- quick energy
Lipids -- long term energy storage
Which 3 elements are found in ALL macromolecules?
BONUS POINTS: All organic molecules contain which TWO elements.
Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen
BONUS: All organic molecules contain carbon and hydrogen.
Draw an enzymatic reaction. (HINT include: active site, enzyme-substrate complex, enzyme, substrates, products)
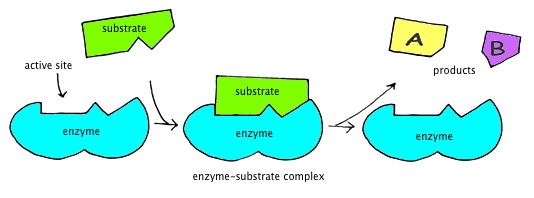 See board
See board
Name 2-3 functions of proteins.
What is... build muscle, help fight disease, and serve as enzymes to increase reaction rate.
Glycerol, starch, and glucose are all...
What are: carbohydrates
Describe what lock & key means for enzymes.
Enzymes fit their substrate very specifically, like a lot and key at their active site.
What does the term denatured mean? What are two causes of this? What effect does this have on enzyme activity.
If an enzyme is denatured, the enzyme will change shape. This can be caused by high temperature, extreme pH levels, presence of metals, etc. This will cause the enzyme to not work as well.
Take a look at this graph of the effect of temperature on enzyme activity.
What is the independent variable (CAUSE)?
What is the dependent variable (EFFECT)?
Where is the enzyme MOST optimal?

Independent Variable - temperature (it is causing a change in the enzyme activity)
Dependent Variable - enzyme activity (it is being affected by temperature)
Optimal - around 35-37 degrees C