What is the function of lipids?
energy storage & insulation
What is the function of carbs?
quick energy
What elements do proteins contain?
CHON (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen)
What is the main functions of nucleic acids?
storage and expression of genetic information
Enzymes ________ a reaction.
Speed up
Lipids make up biological ___________ around the cell.
Biological membranes
How old/what year in school did Ms. Jacobson get a cell phone?
13 / 8th grade after my mom forgot me at soccer practice and I didn't have her number memorized so I sat with my coach waiting for her to remember
What elements do lipids contain?
CHO
What elements do carbs contain?
CHO
What is the monomer of proteins?
amino acids
What elements do nucleic acids contain?
CHONP
What building block are enzymes are made of? (hint: what is the monomer of the macromolecule?)
Amino Acids
What molecule is this?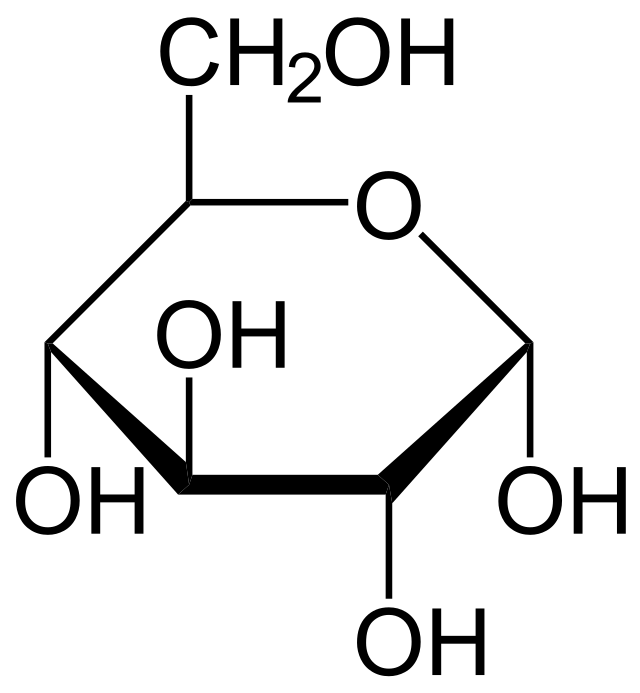
Glucose
If you run out of short term/accessible energy, what macromolecule will your body use next?
E
Carbohydrates contain a ______ structure.
Ring
What structural clues on a macromolecule tells us that a macromolecule is a protein?
R/Variable Group, CHON elements
What are 2 examples of nucleic acids
DNA, RNA, and ATP
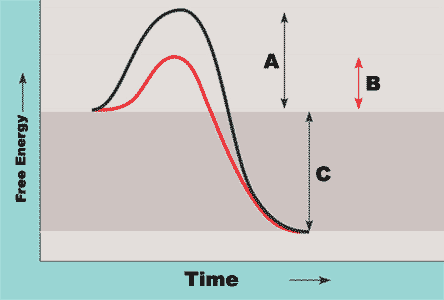 Which line shows a reaction where an enzyme is present?
Which line shows a reaction where an enzyme is present?
The red line because it has lower activation energy.
pink = enzyme amylase; green = substrate
How could you increase the reaction rate?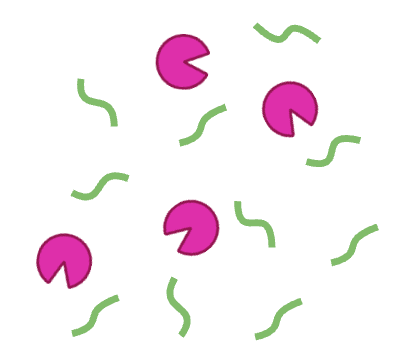
Add more enzymes to react with the substrates
Draw or describe a dehydration synthesis reaction.
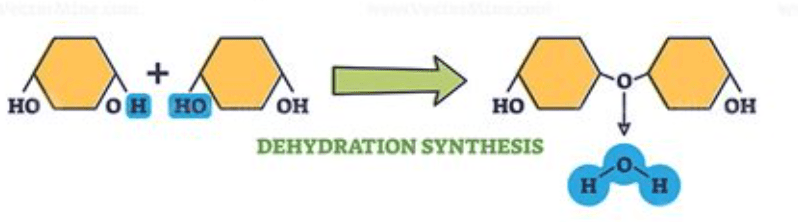
What are the monomers of lipids?
fatty acids & glycerol
What are examples of carbs?
glucose
starch
glycogen
What are the functions of proteins? (2+ correct examples to get this question correct)
coordinate signaling pathways
regulate transport across membranes
catalyze chemical rxns (enzymes)
What is the monomer of nucleic acids?
Nucleotides
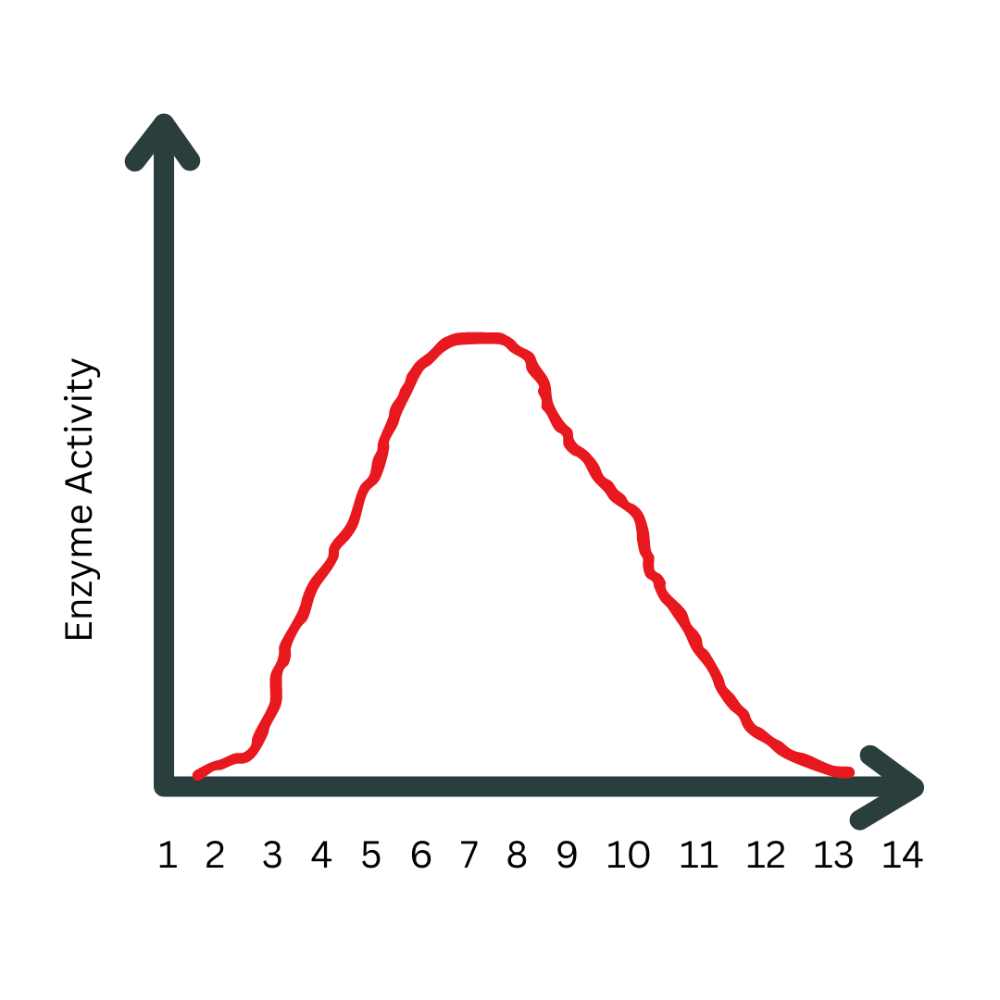 What is the optimal pH for this enzyme?
What is the optimal pH for this enzyme?
7
Enzyme X breaks down Substrate Y into Product Z. Enzyme X stops working. Will there be a build up of X, Y, or Z?
A build up of Substrate Y.
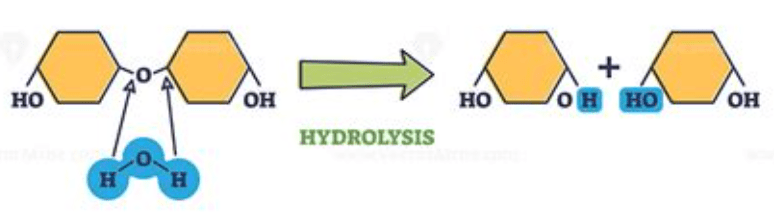
Describe or draw a hydrolysis reaction.
What is the structural difference between saturated vs. unsaturated fatty acids?
Unsaturated fatty acids have a DOUBLE carbon bond
Saturated fatty acids only have single carbon bonds
What is the monomer of carbs?
monosaccharide
What are examples of proteins? (2+ for correct answer)
Enzymes, antibodies, protein channels
What 3 things are essential in the structure of a nucleic acid?
A Sugar, a Nitrogenous Base, and a Phosphate Group
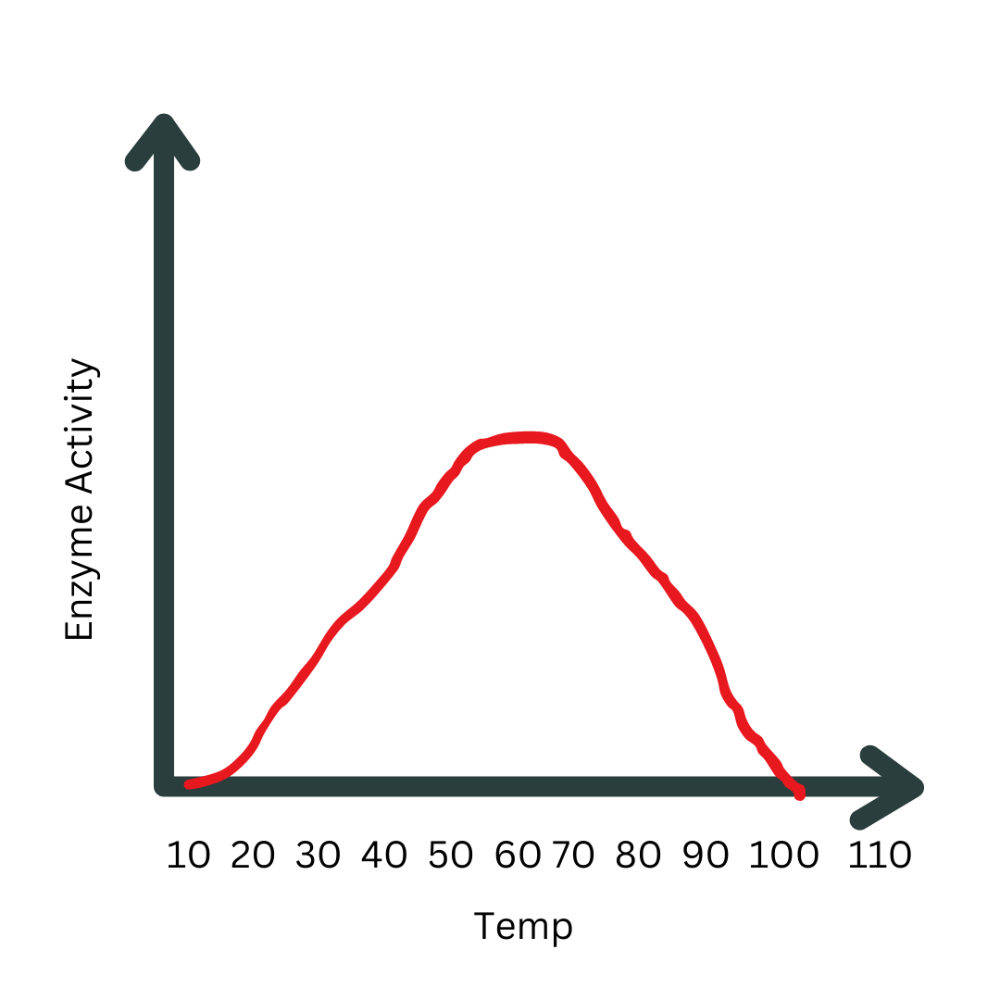
What is the optimal temperature for this enzyme? What temperature would you keep it at to slow down enzyme activity without denaturing the enzyme?
Optimal = between 60 degrees
Temperature to slow activity = ~30 degrees
Double Jeopardy:
Explain why the graph hits a plateau.
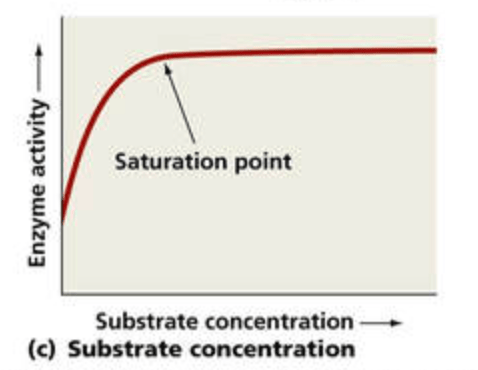
All enzymes are occupied so adding additional substrate (as measured by the X axis) does not increase the rate of react/enzyme activity (as measured by the Y axis). All enzymes being occupied means additional substrates does not yield additional enzyme activity/reactions.
The structure of cellulose is shown below. How does this structure relate to cellulose being in the cell wall?
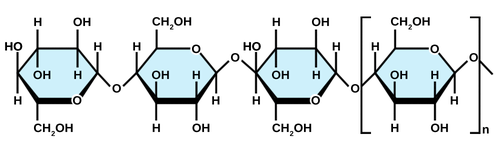
Cellulose has a rigid, line structure. This provides the rigid structure of the cell wall that provides structure for plant cells.