Give an example of a food that is high in carbohydrates.
Bread, pasta, rice, fruit, vegetables
Fatty Acids
What is the monomer for proteins?
Amino Acids
DNA and RNA
Which major macromolecules makes enzymes?
Proteins
Monosaccharides
Sugars
What are two main jobs of lipids in the body?
1. Long term energy storage
2. Insulation
3. Cushioning
4. Make up cell membranes
How are proteins made in the body?
From DNA
What is the monomer of nucleic acids?
Nucleotides
What is the general role of an enzyme?
What is the main function of carbohydrates?
Short term energy
Lipids do not mix with water because they are.....
Hydrophobic
Non polar
Name three functions of proteins.
1. Transport
2. Support
3. Hormones
4. Genetic Presentation
5. Fight Disease
6. Control Cell Processes
Which elements make up nucleic acids?
CHNOP
What do you call the beginning and end of chemical reaction?
Reactant (substrate)
Product
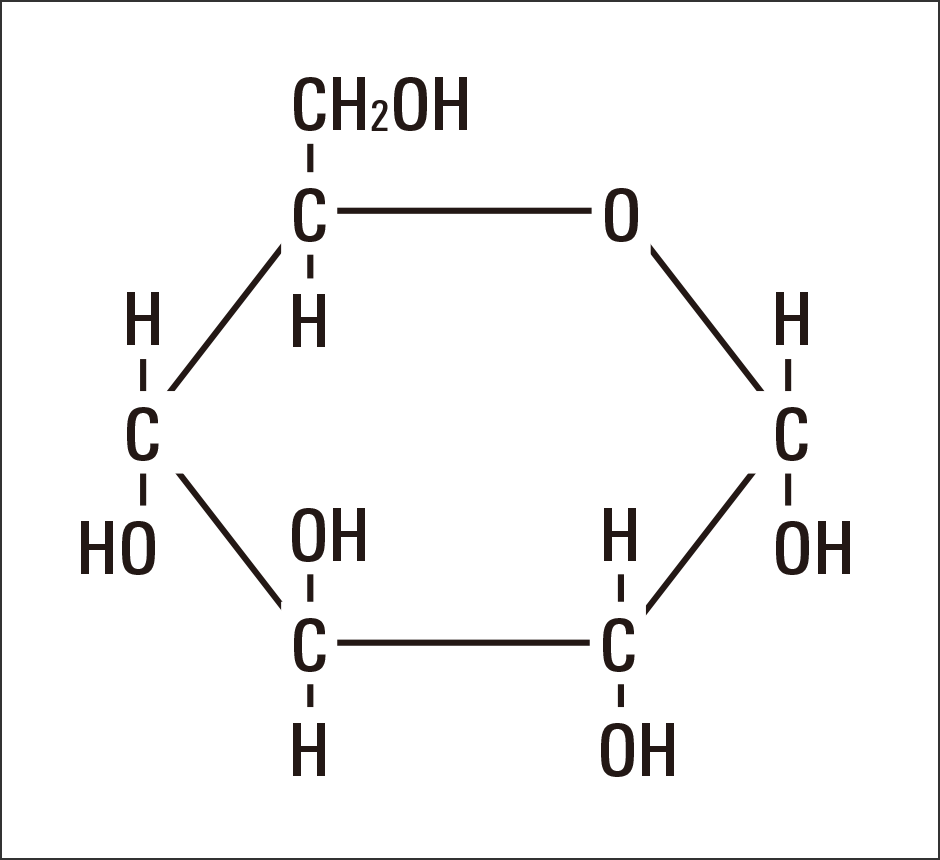
Draw a picture of a monosaccharide.
What are two of the kinds of fats that we see on a nutritional label?
Saturated
Unsaturated
Trans
What determines the function of a protein?
The structure and folding.
Anything that was alive.
How does an enzyme speed up a chemical reaction?
DAILY DOUBLE
What kind of sugar is lactose? And why is it hard for some people to process?
1. Disaccharide
2. They may not produce enough of the enzyme lactase.
Give one difference between saturated and unsaturated fats.
1. Saturated has all single bonds, unsaturated has at least one double bond.
2. Saturated are solid at room temperature, unsaturated are liquid.
3. Saturated fats are worse for you than unsaturated.
What are the 4 levels of structure to make a protein?
1. amino acid chain
2. folding (beta pleated, alpha helix)
3. 3-D Shape
4. Polypeptides join together
What three parts make up a nucleotide?
1. 5 Carbon Sugar
2. Nitrogenous Base (ATGC)
3. Phosphate Group
Mrs. Neduva put a stomach acid enzyme in milk. Milk is very basic and stomach acid is very acidic. What is going to happen to the enzyme?
It will become denatured.