This biomolecule contains only Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen.
What are carbohydrates?
Bananas can provide athletes with immediate energy because they are high in this macromolecule.
What are carbohydrates?
This polymer functions as energy storage in plants. We enjoy it when we eat foods like rice and potatoes!
What is starch?
This is the monosaccharide in table sugar.
What is glucose?
The process shown here.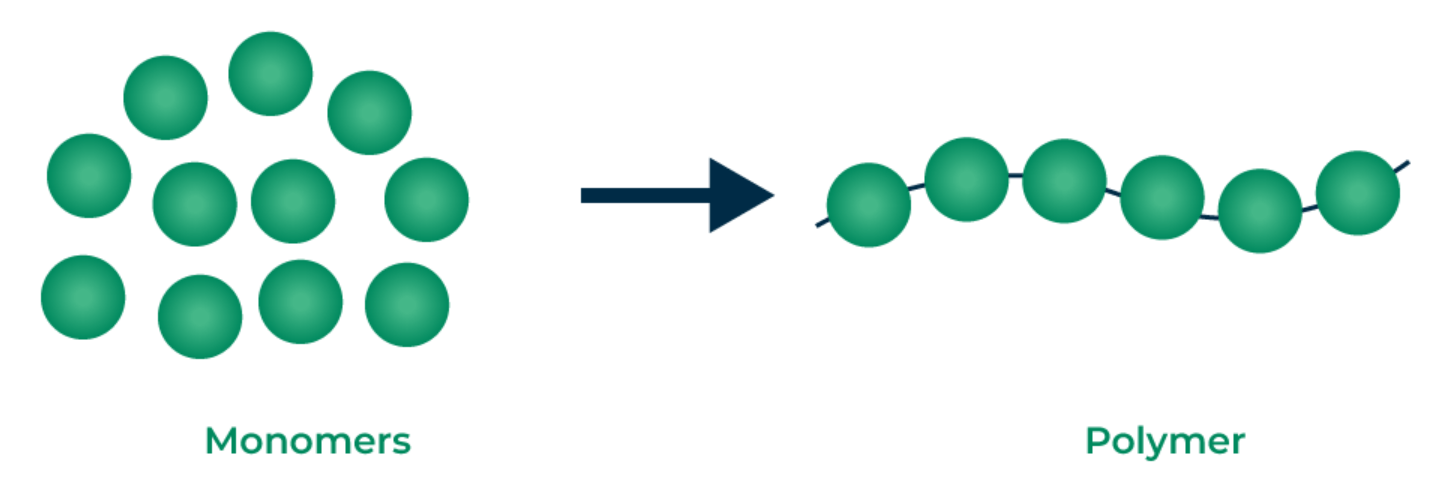
What is polymerization OR dehydration synthesis?
This process breaks down polymers into monomers.
What is hydrolysis?
This group of macromolecules has MANY functions including transporting molecules, building muscle, and protecting against disease.
What are proteins?
This polymer is responsible for storing information that will be passed onto future generations.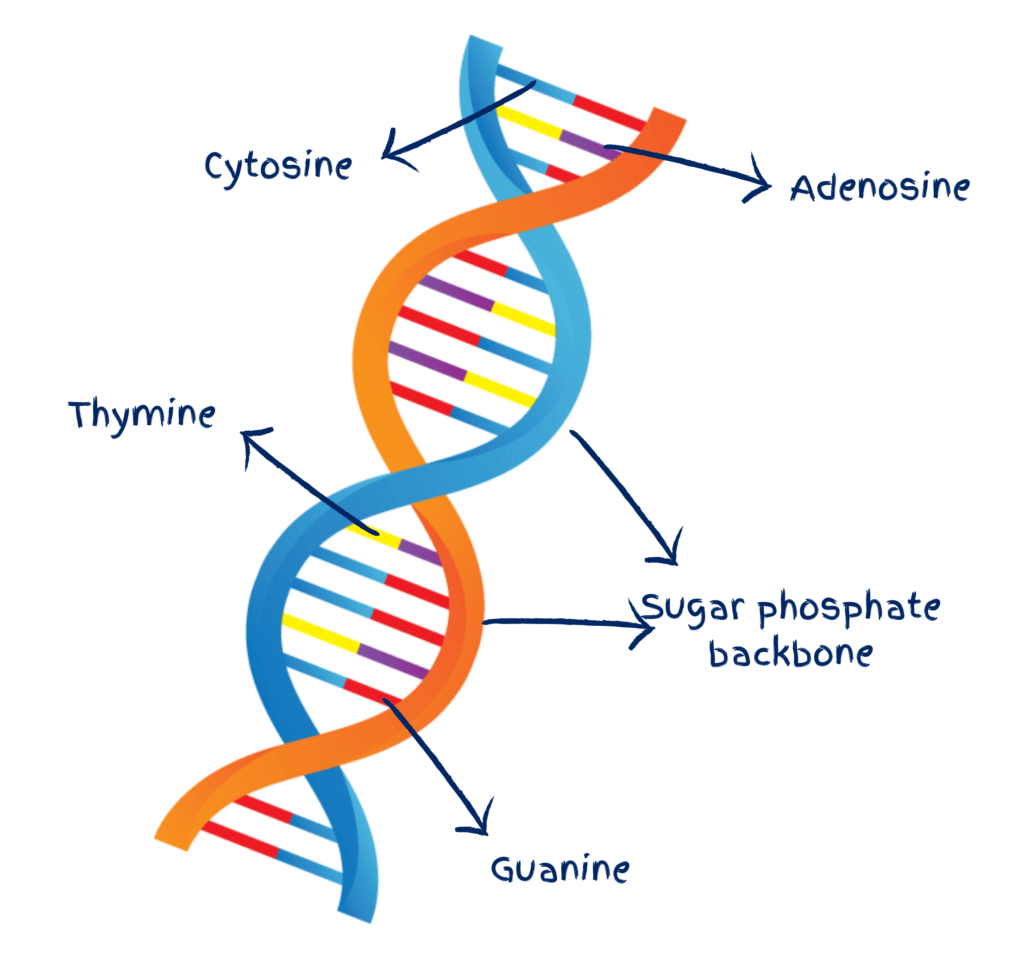
What is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)?
This part of the amino acid gives the molecule its unique properties.
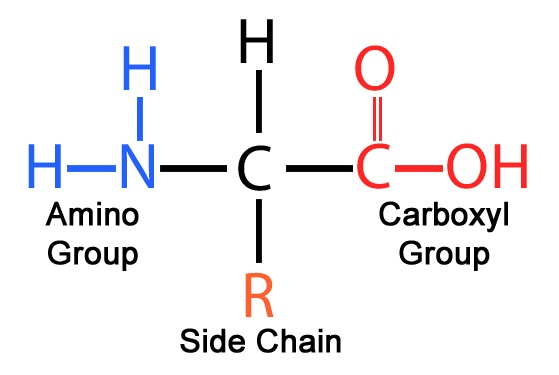
What is the R group OR side chain?
This class of biomolecule folds into complex three-dimensional structures. The folding process is modeled here.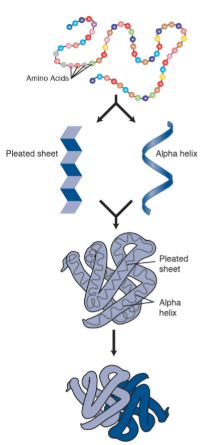
What are proteins?
The monomer of carbohydrates.
What are monosaccharides?
Triglycerides, an example of this macromolecule, provides long term energy.
What are lipids?
This lipid polymer makes up the main fabric of the cell membrane.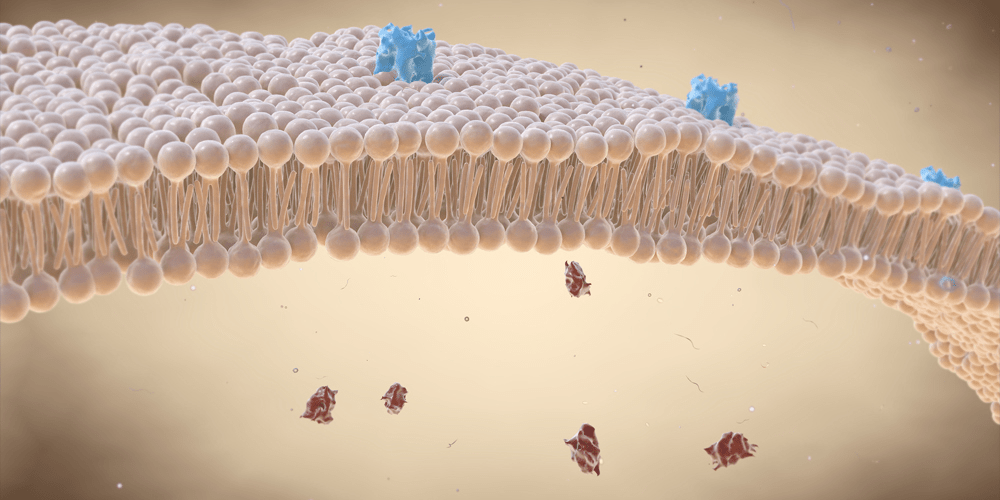
What is a phospholipid?
This lipid is part of the cell membrane and it is the basis for many hormones.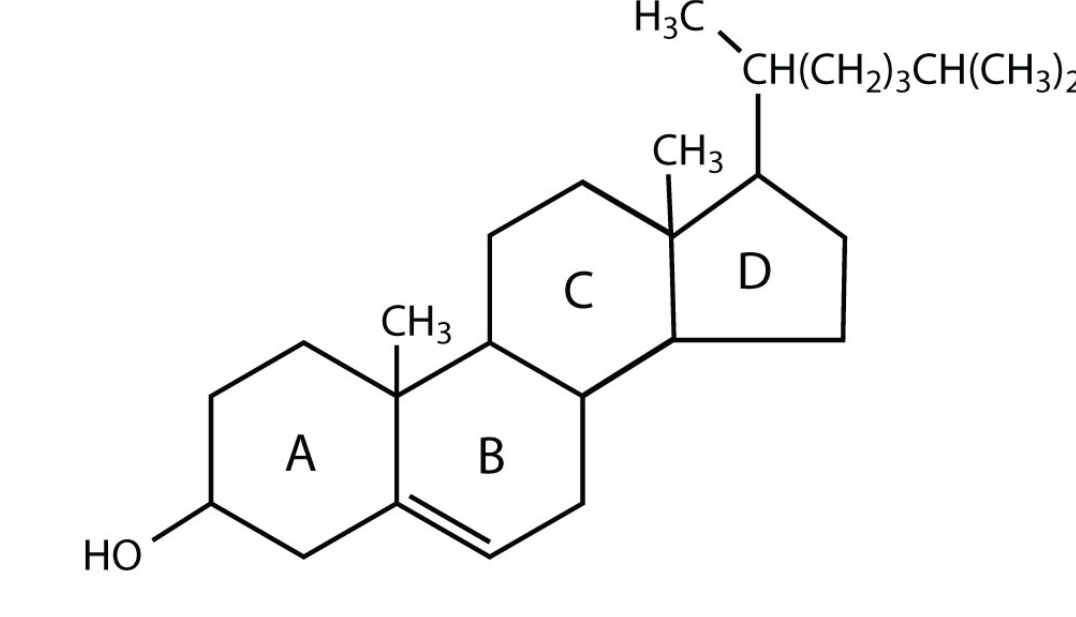
What is cholesterol?
This many water molecules is needed to break down a polysaccharide made of 897 glucose molecules.
What is 896 water molecules?
The monomer of proteins.
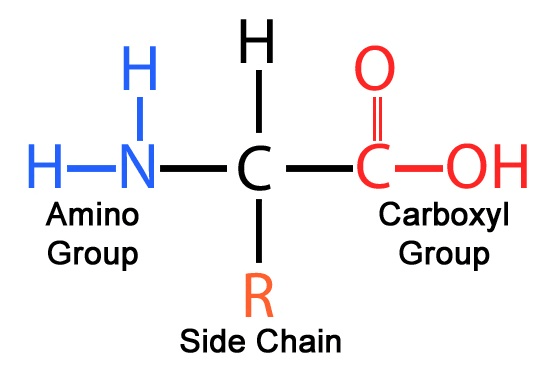
What are amino acids?
These macromolecules store and express genetic information.
What are nucleic acids?
This polysaccharide functions as reserve energy for animals.
What is glycogen?
Identify this molecule (notice the double bond).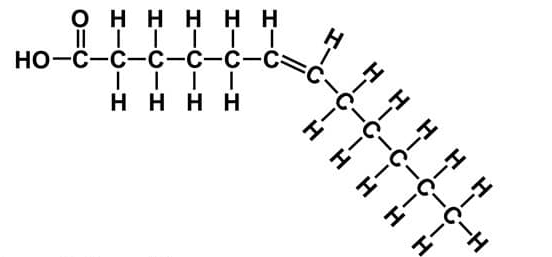
What is an unsaturated fatty acid?
OR unsaturated fat
The process of a protein unfolding due to changes in temperature or pH.
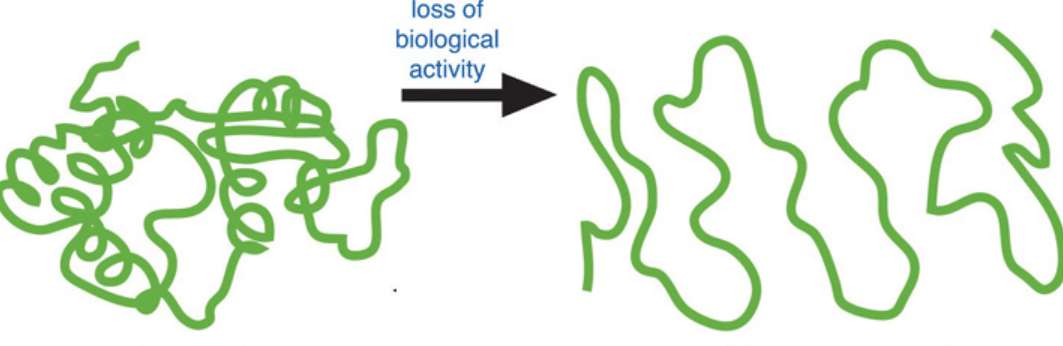
What is denaturation?
Nucleic acids contain these five elements.
What are C, H, N, O, P?
carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus
What are enzymes?
This nucleic acid polymer is critical for protein synthesis. Provide the full name.
What is ribonucleic acid?
These are the three parts of a nucleotide.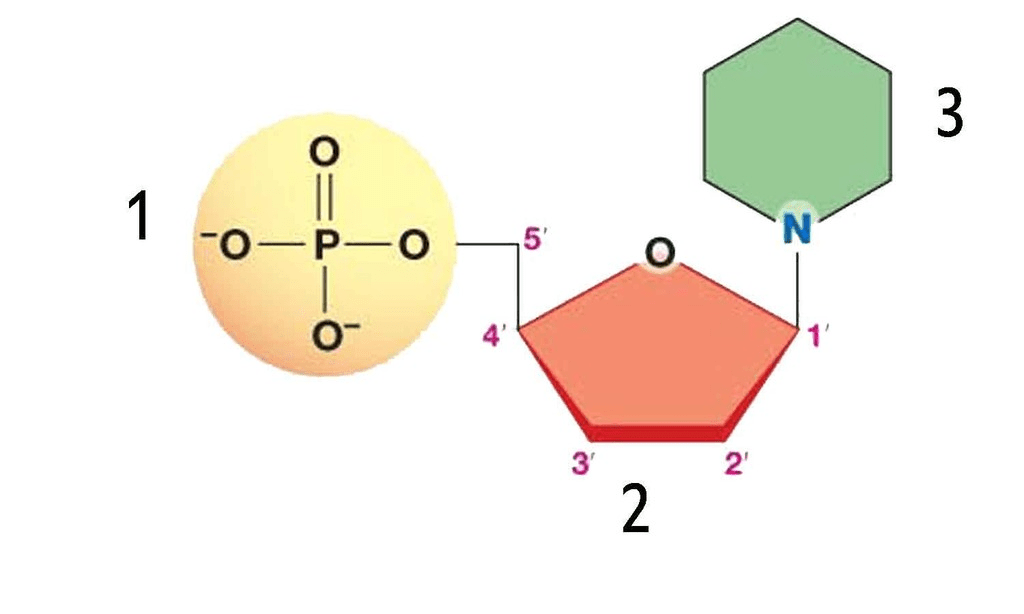
What are:
1 - phosphate group
2 - sugar (pentose sugar)
3 - nitrogen base
The cellular energy molecule shown here.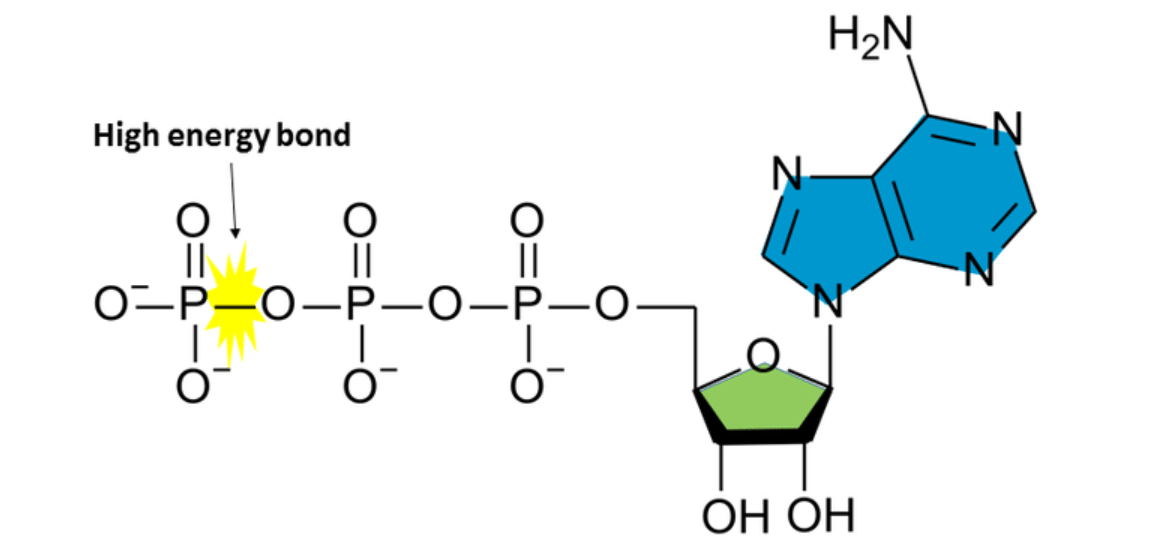
What is ATP?