What is the empirical formula for carbohydrates?
CH₂O
The macromolecule shown belowis: 
lipid (triglyceride)
Name the monomer of a protein.
amino acids
Name the monomer of a nucleic acid.
nucleotide
What term describes water's ability to stick to other molecules?
adhesion
Name the monomer of a carbohydrate.
monosaccharide
What type of fatty acid contains one or more double bonds?
unsaturated fatty acid
What is the primary structure of a protein?
amino acid sequence of a polypeptide
What are the two polymers of nucleic acids?
DNA and RNA
The partial negative charge at one end of a water molecule is attracted to a partial positive charge of another water molecule.
What is this type of attraction called?
hydrogen bonds
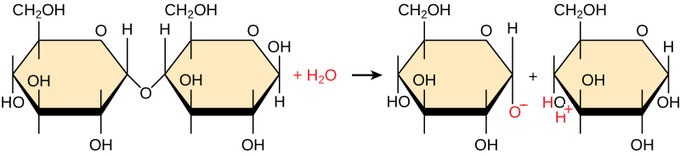
This is a ______________ reaction
Hydrolysis
What is the structure of a phospholipid?
glycerol, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate head
What type of bond forms between amino acids during dehydration synthesis
peptide bonds
What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide?
sugar, phosphate, Nitrogen base
Fall Foliage Triple
Which type of bonds form between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms of WITHIN a water molecule?
covalent
What is the primary storage carbohydrate in animals
glycogen
DAILY DOUBLE:

Name a type of lipid that has fused carbon rings
steroids, cholesterol
The macromolecule monomer shown below is:
amino acid
What are the 4 nucleotides for RNA?
Guanine
Uracil
Adenine
Cytosine
What do we call molecules that do not dissolve in water?
hydrophobic
What type of bond connects the monomers in a carbohydrate?
glycosidic
How do phospholipids behave in aqueous solutions?
they orient their hydrophobic tails away from water and hydrophilic heads toward water, forming a bilayer
What are proteins that assist in the proper folding of other proteins?
chaperonins
What type of bond links nucleotides in a nucleic acid?
phosphodiester bond
Why does ice float on water?
What is the expansion of hydrogen bonds at lower temperatures?