What type of force will the two bar magnets have with each other?

Attractive force
On a magnet, where is the magnetic force strongest at?
The north and south poles (either pole on the magnet)
What are these lines called?
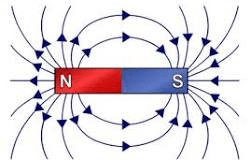
Magnetic Field Lines
Unit of measurement for an electric charge (q)?
Coulomb (C)
Loss or gain? Oxidation entails the ______ of electrons.
loss
The image below is an example of?
Magnetic domains
A magnetic force is created by the motion of a magnet OR by the motion of ______ ______.
Electric charges
What type of lines are depicted below?
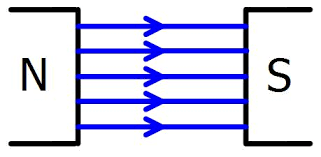
Uniform Magnetic Field
Unit of measurement for strength of a magnetic field (B)?
Tesla
Loss or gain? Reduction entails the ______ of electrons.
gain
Substances that are strongly attracted to magnets due to the alignment of their magnetic domains. Iron, cobalt and nickel are examples.
Ferromagnetic
In the formula F = BIL, what does the "I" stand for?
Current or Electric Current
Electric field lines which do not overlap indicate that the two charges are ?
Either both positive or both negative
Unit of measurement for magnetic force (F)?
Newton
Where does oxidation occur in a voltaic cell or standard battery?
At the anode
Conductive materials can generate opposing magnetic fields in the presence of magnets. This phenomenon is called _______ _______.

Eddy Currents
Perpendicular, parallel or random? How does the Magnetic Force move to the velocity of a charged particle and its magnetic field?
Perpendicular
Which electric field is strongest?

The electric field in "C". This is the case regardless of the negative or positive charge.
Unit of measurement for electromotive force (EMF)?
Volts
Where does reduction occur in a voltaic cell or standard battery?
At the cathode
Michael Faraday showed that moving a magnet through a magnetic field creates an electric current, a phenomenon known as __________ ___________.
Electromagnetic Induction
The strength of a magnetic force (F) depends on the magnitude of the charge (q), the strength of the magnetic field (B), and the ?
velocity of the charged particle (v)
What are the charges for particle A and for particle B?

A is negative and B is positive
What is this number known as "k" known as? 9.0 x 109 Nm2/C2
Coulomb's Constant
In addition to the flow of electrons in a voltaic cell or standard battery, what other "substance" flows?
Ions