The word for when two magnets push away from each other.
Repel 
Where on the magnet is the magnetic field the strongest?
The magnet's ends or poles
The name of the device that can break a circuit and stop the flow of electricity.
A switch

The function of the D- Cell.
Source of energy

When we wrapped the wire in this place it became much stronger.
At the end.
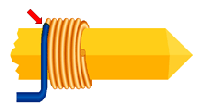
The word for when two magnets pull toward each other.
Attract

The name of the device that uses a magnet to indicate direction, that is commonly used for navigation.
A compass

This is the component in a circuit where the electrical energy comes from.
Battery or power source
The name of the device that is used to protect an electrical circuit from overloading or short-circuiting.
Circuit breaker
The two colors of the wires we used when we created the electromagnet.
Red and Yellow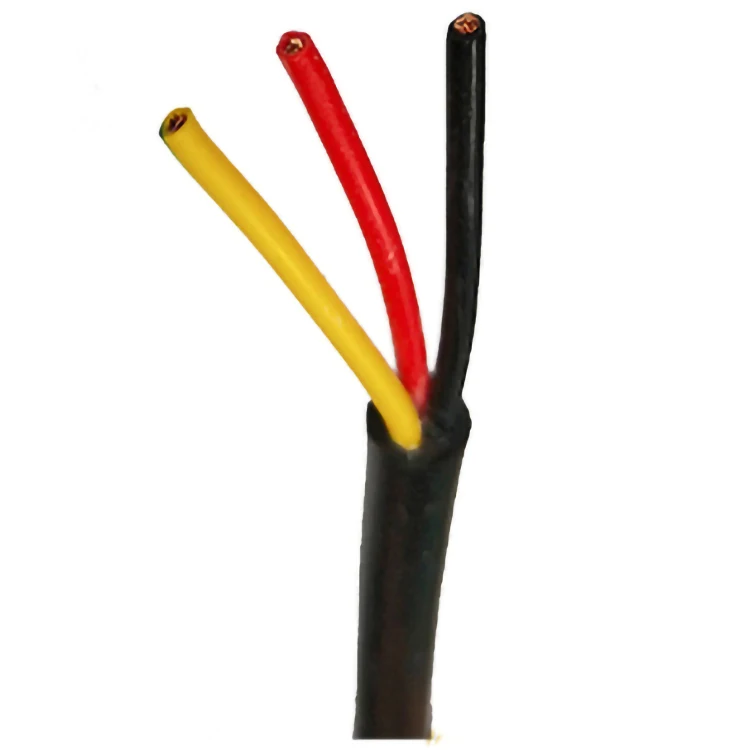 
The name of the metal that magnets are often made of.
Magnetic strength or magnetic field strength 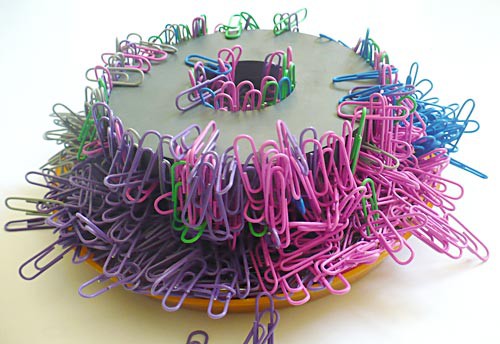
The name of the metal that magnets are often made of.
Iron
The name of the type of circuit in which there are multiple paths for the electric current to flow.
Parallel circuit
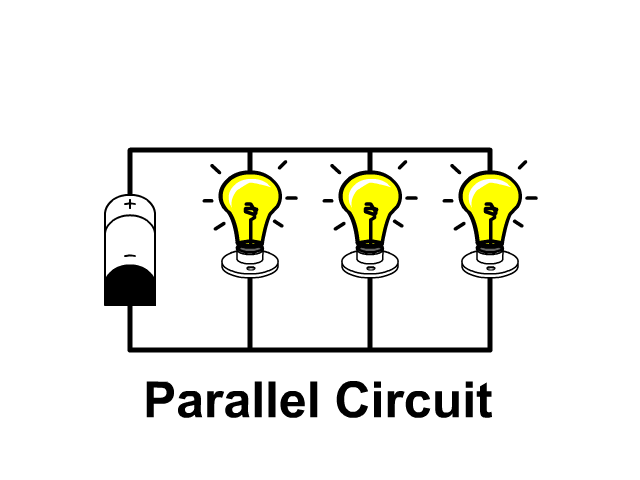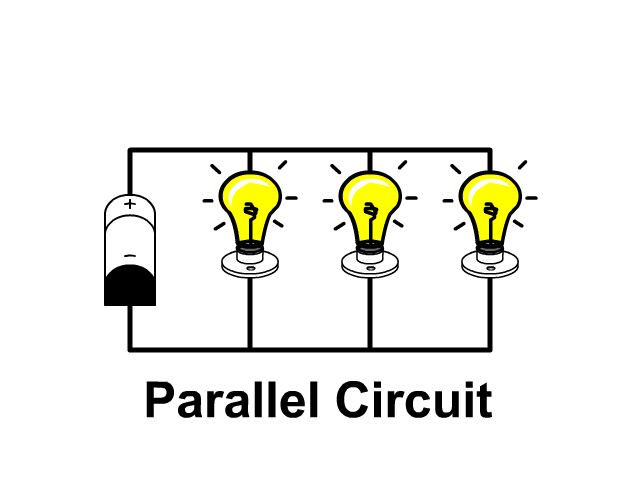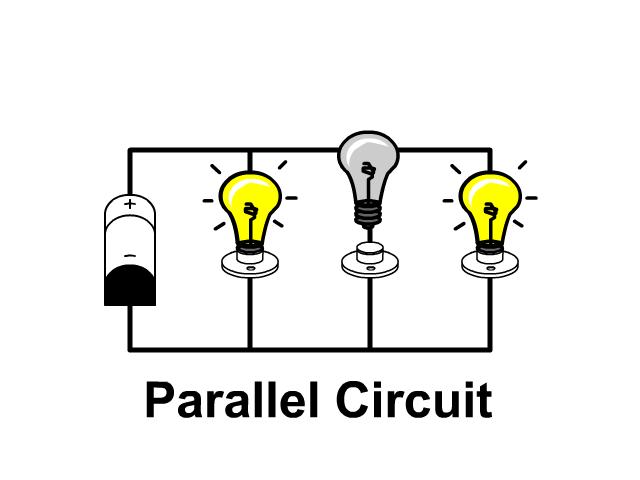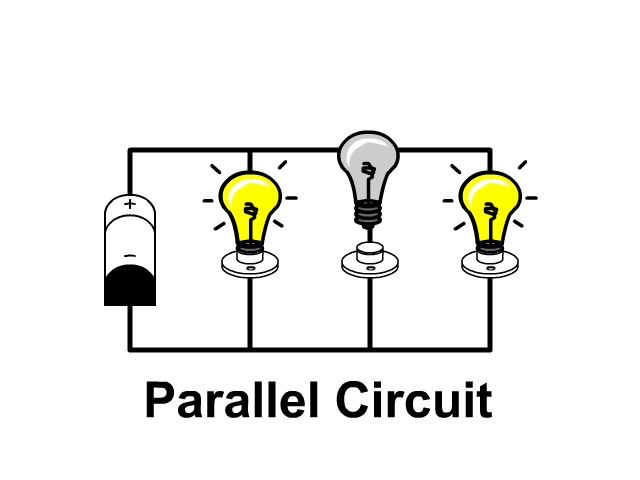
The space around electrically charged objects.
An Electric Field
When designing our electromagnets we used this to pick up the washers.
A steel rivet
This term describes a material that allows electricity to flow through it easily.
Conductor
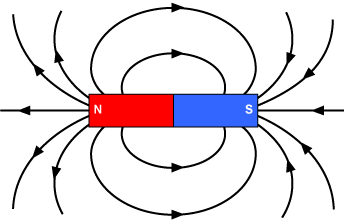
This term describes the area around a magnet where its magnetic force can be detected.
Magnetic Field
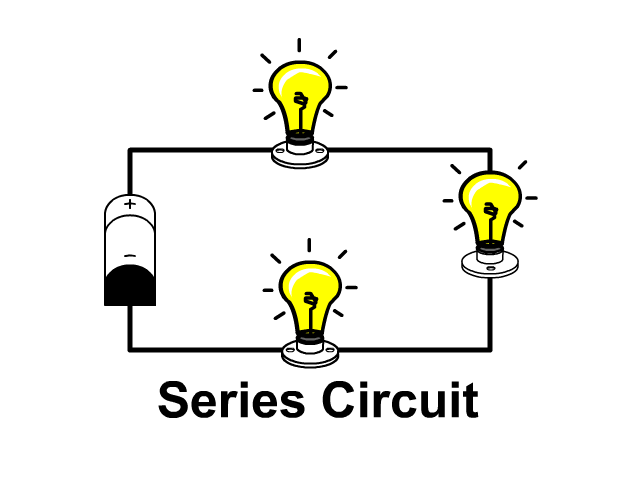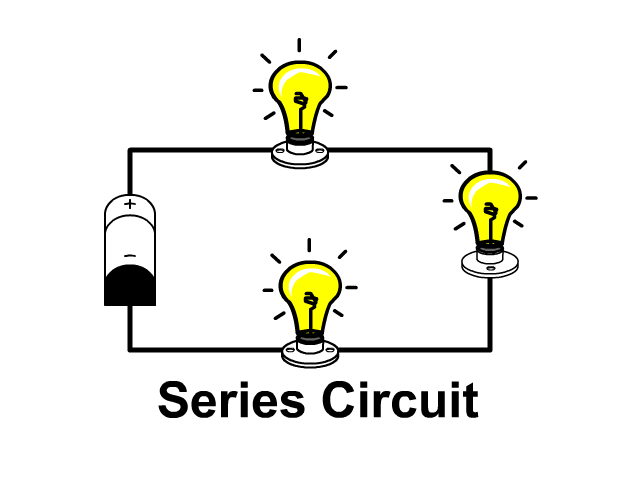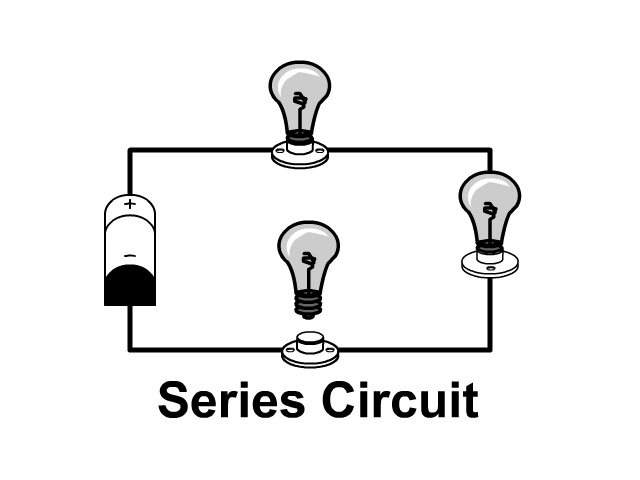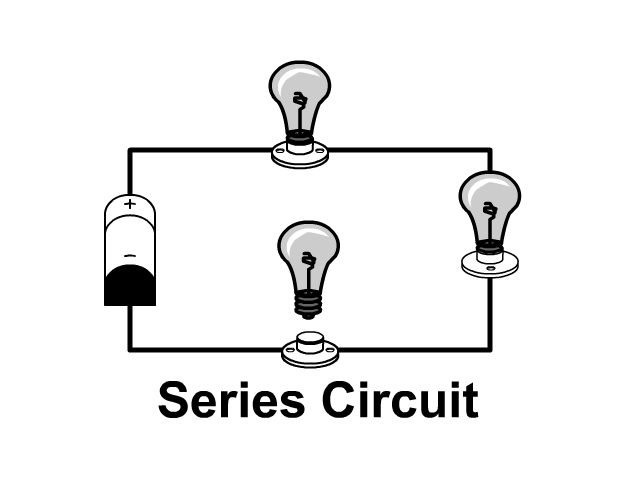
The name of the type of circuit in which there is only one path for the electric current to flow.
Series Circuit
The name of the material that does not conduct electricity.
Insulator 
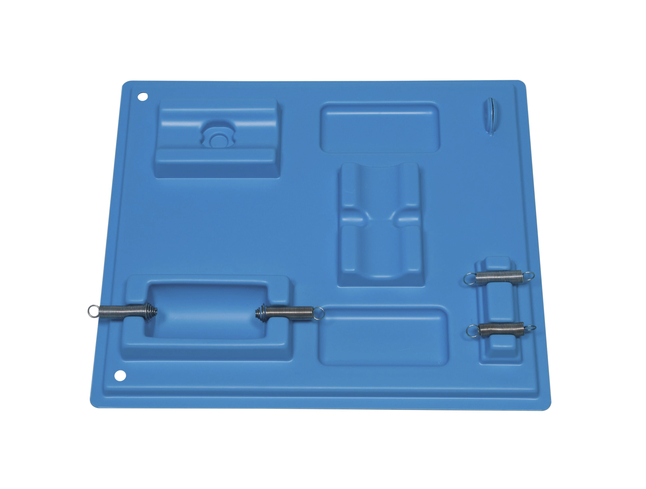
The object's name that we set up our experiment on.
Circuit Base

