Medication given after childbirth.
What is Oxytocin?
Dose: 10 Units IM
First line of defense medication for bronchospasm.
What is albuterol/duoneb?
We do not want to raise the head of patients with suspected head trauma no more than this.
What is 30 degrees?
In a hypoglycemic emergency, and an IV is unavailable, you administer this.
What is glucagon?
Dose:
patients 20kg or higher: 1mg IM
patients 20kg or less: 0.5mg IM
The 5 H's of potential causes of cardiac arrest.
What is:
Hypothermia
Hypovolemia
Hypoxia
Hypo/Hyperkalemia
H+ (acidosis)
Administered for suspected croup.
What is Dexamethasone?
Dose: 0.6mg/kg PO/IV/IM/IO
Normal range for capnography.
What is 35-45mmHg?
The patients hand is this percentage of patients body surface area (BSA)
What is 1% BSA?
Your differential diagnosis' of Altered Mental Status.
A: alcohol (other drugs), acidosis (hyperglycemia/DKA)
E: electrolyte abnormality, endocrine problem, epilepsy
I: insulin, diabetes (hypoglycemia)
O: oxygen (hypoxia), overdose (poisoning)
U: uremia (renal failure/insufficiency)
T: trauma, temperature (hypothermia/ heat stroke)
I: infection (meningitis, sepsis)
P: psychogenic
S: stroke, seizure, shock
Identify this rhythm and tx.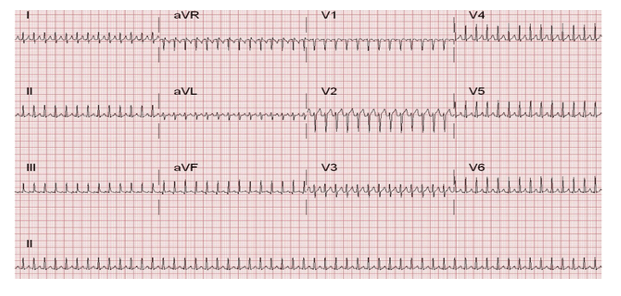
What is SVT?
Treatments:
- Valsalva maneuvers
- Adenosine
- Synchronized Cardioversion
Administered for open fractures.
What is ceftriaxone?
Dose: 2g IV in 100mL NS or D5W over 10 minutes
Name the adventitious lung sounds.
What is wheezing, stridor, crackles, & rhonchi ?
This intercostal space is preferred for needle decompression over the second & third intercostal space of the mid-clavicular line because of significant failure rates.
What is the fourth & fifth intercostal space on the anterior axillary line?
What are: migraine, hypoglycemia, seizures, intoxication, & sepsis?
Identify rhythm and tx.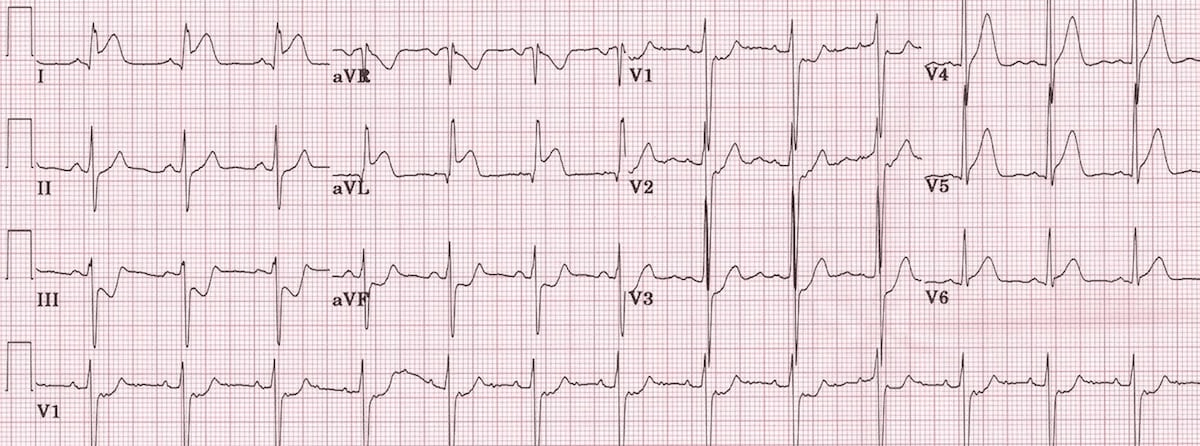
What is lateral wall MI?
Tx:
- oxygen as needed
- aspirin/ nitro as appropriate
- IV access
- pain management as needed
- repeat 12-leads
- activate Cath Lab
A person, 16 years and older, with multi-trauma and hemorrhagic shock are given this:
What is TXA?
Dose: 1g IV in 250mL NS over 10 minutes
Defined as two (2) unsuccessful intubation attempts by the most proficient technician on scene OR anatomy inconsistent with intubation attempts.
What is "Failed" intubation?
Before administering pain management for the following:
isolated head trauma, back Pain, non-traumatic extremities pain, any patient with mental health changes, any patient with unstable vitals, & coincident drug use (including alcohol)
What is contact OLMC?
A patient that is less than 6 weeks post-partum having a seizure or postictal will be administered this.
What is magnesium sulfate?
Dose:
8gm IM (4gm in each buttocks)
4gm IV/IO over 15 minutes via med pump
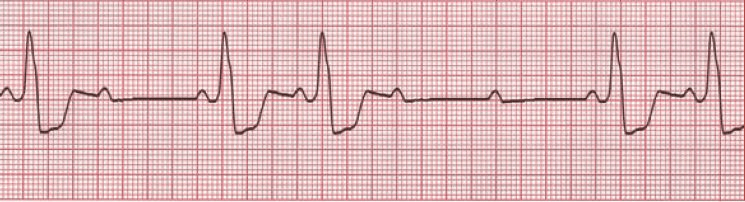
What is 2nd Degree Type 2 heart block?
Tx:
- Transcutaneous pacing
- IV access
- pre-medication if possible for TCP
For medical shock, this is administered to the patient.
What is Norepinephrine?
Prepare: Mix 8mg in 250mL NS
Dose: 0.03mcg/kg/min
Two methods to treat anxiolysis in post-intubation.
What is midazolam and Ketamine?
*Must contact OLMC for only one.
This is used to treat crush injuries?
What is sodium bicarbonate?
Dose:1 mEq/kg IV over 5 minutes
Identification of sepsis include suspected infection and includes two or more of the following:
- temperature less than 96.8 F or greater than 101 F
- HR greater than 90 BPM
- RR greater than 20
- New onset AMS
- and....
What is hypotension?
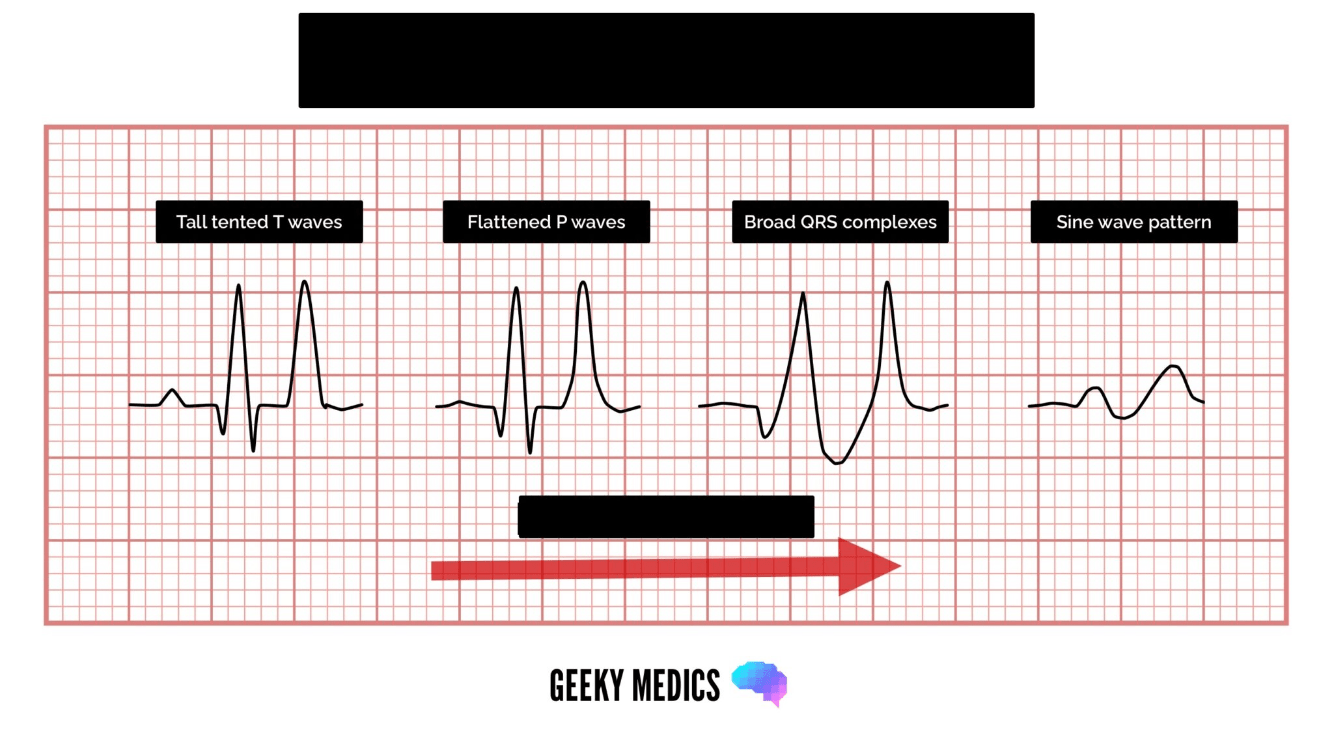
Patients with renal failure are at the highest risk for this cardiac consequence. The most common at-risk patients are those on dialysis who have missed appointments thus they have accumulated dangerously high levels of electrolytes.
What is Hyperkalemia?