These are the three types of manufacturing costs.
What is Direct Labor, Direct Material, and Manufacturing Overhead?
Direct Labor -
Cost of salaries, wages, and fringe benefits for personnel who work directly on the product.
Direct Material -
Cost of raw material that is used to make, and can be conveniently traced, to the finished product.
Manufacturing Overhead
All other manufacturing costs – 3 Types
This method for estimating costs uses a scatter diagram of past observations with a visually fitted line.
What is a scattergraph plot?
The journal entry to purchase raw materials on account.
What is a debit to raw material inventory and a credit to accounts payable?
What is Estimated (budgeted) manufacturing overhead costs / Estimated (budgeted) amount of cost driver activity?
Steps include:
1.Estimate manufacturing overhead at the beginning of the period.
2.Identify appropriate volume based cost driver.
3.Calculate predetermined overhead rate (POhR) using the formula above
4. Apply to individual jobs or batches
Cost Driver Activity (Job i) * POhR = Manufacturing Overhead for Job i.
Cost Volume Profit analysis is the relationship between Sales Volume, Revenue, ________ and profit.
What is expenses?
• It is a means that management may use to estimate profit for any given volume.
• It allows for comparisons of management strategies such as automation, advertising, price changes, and outsourcing.
_______________ costing is the traditional way to measure net income. Variable costing is just another way to measure net income.
What is absorption costing?
These are the three types of manufacturing overhead.
What is indirect material, indirect labor, and other costs?
Indirect Material
Materials used to support the production process. Examples: lubricants and cleaning supplies used in an automobile assembly plant.
Indirect Labor
Cost of personnel who do not work directly on the product. Examples: maintenance workers, janitors and security guards.
Other Costs
Examples: depreciation on plant and equipment, property taxes, insurance, utilities, overtime premium, and unavoidable idle time.
This method for estimating costs is an estimate based on highest and lowest (past) activity levels.
What is the high-low method?
1. Identify the period with the highest & lowest level of activity
2. The period with the lowest activity is selected as the first point in the formula. The period with the highest activity is selected as the second point.
3. Variable cost = slope of line = Y2 – Y1 / X2 – X1
4. Find fixed cost by taking the total cost at either the high or low activity level and plug it into the formula:
Fixed cost element = total cost – variable cost element
The high-low method is simple to apply but its major defect is that it only utilizes 2 data points, which are usually not enough to accurate estimate costs.
The journal entry when raw materials are selected from storage to be used in production.
What is a debit to work in process inventory and a credit to raw materials?
Entry to record disposition of over-applied overhead.
What is a debit to manufacturing overhead and a credit to cost of goods sold?
NOTE: The entry to record disposition of under-applied overhead is the opposite (debit cost of goods sold and credit manufacturing overhead).
CVP is all about contribution margin. How do you calculate unit contribution margin?
Sales Price per unit
-Variable Cost per unit
= Contribution margin per unit
Note: Contribution margin is the amount that each unit of sales contributes to the fixed costs and profit of the organization.
Once fixed costs are covered, contribution margin measures the profit from each additional sale.
This costing system uses more than one predetermined overhead rate.
What is Activity Based Costing?
Why ABC: ABC can produce more precise measures of product cost and thereby better management decisions.
Stage 1: Identify the activities involved in your production process and assign overhead costs ($) to an activity cost pool.
Stage 2: Identify appropriate activity measures (i.e. cost drivers) for each activity cost pool and assign costs to products based on the quantity of cost driver it consumes.
Direct material, direct labor and manufacturing overhead are all examples of __________ costs, which are debits to inventories when incurred and expensed when sold.
What are product costs?
This method for estimating costs is based on all available (past) activity levels.
What is Least Squares Regression?
Regression is a statistical procedure used to determine the relationship between variables such as activity and cost. It fits a line to data that minimizes variance from the line.
The objective of the regression method is the general cost equation: TC = F + V(X).
This is the most accurate way to estimate costs but is the most complex to calculate.
The journal entry when employees working directly on the product are paid in cash.
What is a debit to work in process inventory and a credit to cash.
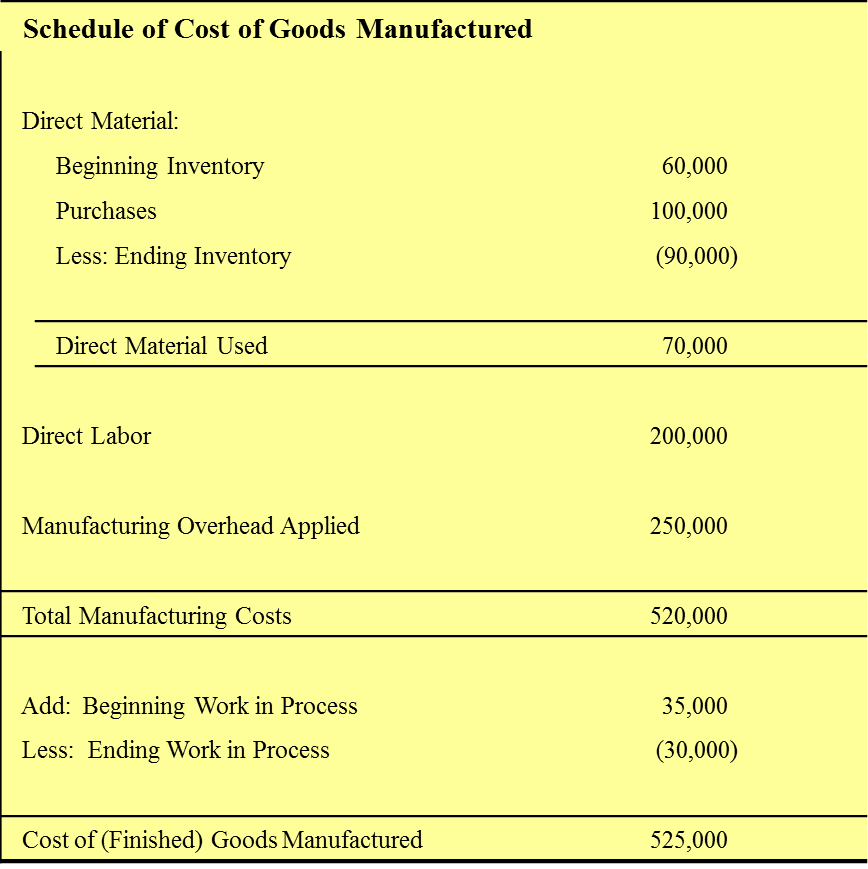
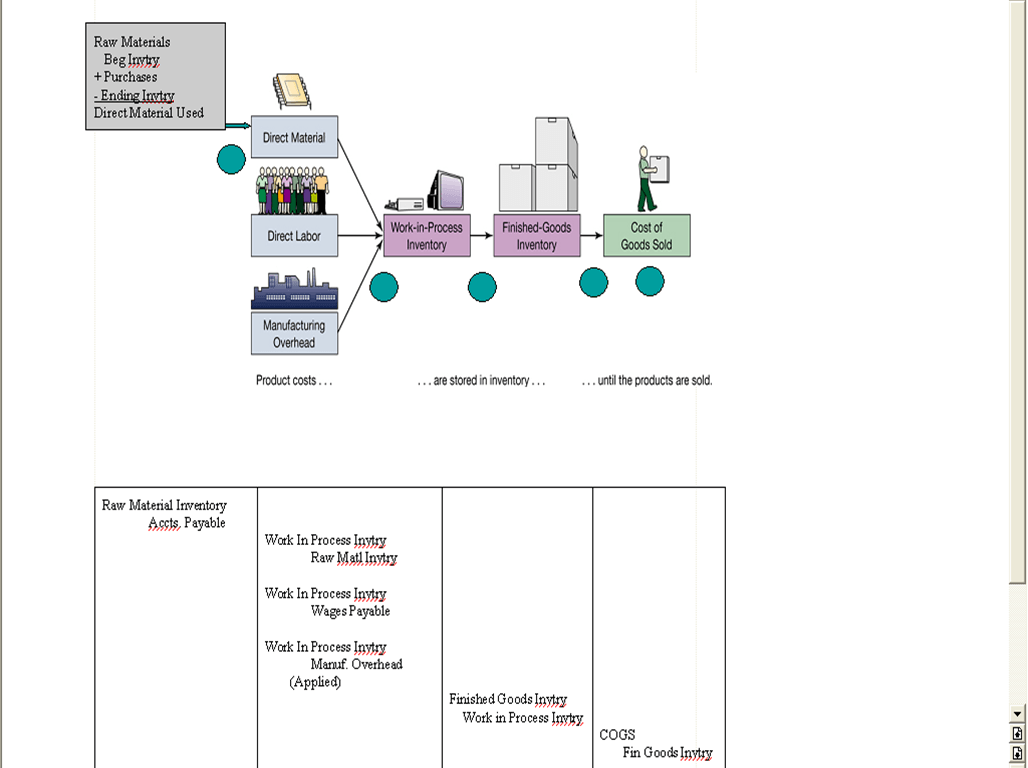
Draw out the schedule of cost of goods manufactured.
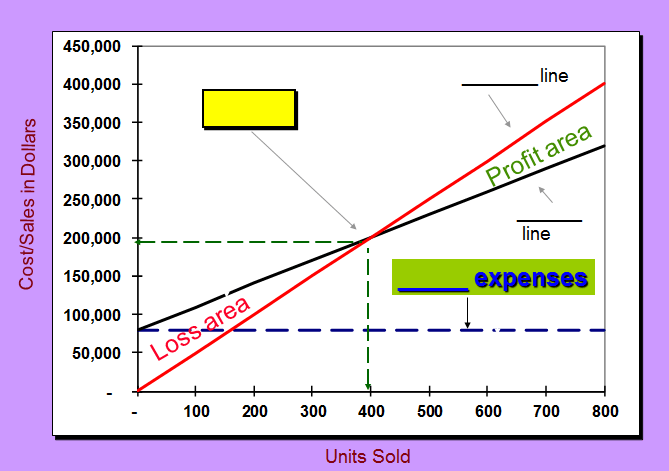
Identify the following: Revenue line, Total Cost Line, Fixed Costs, Break Even Point.
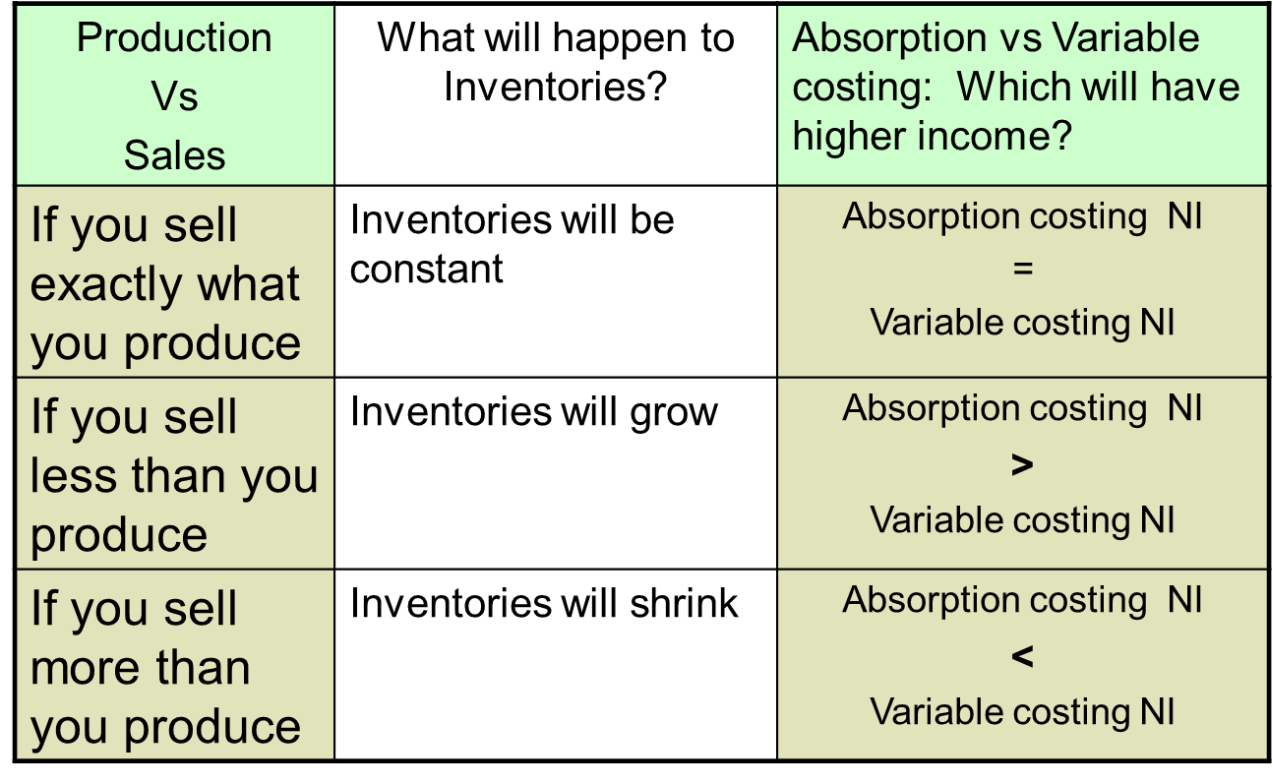
This costing method (between variable and absorption) will produce a higher net income if you sell less than you produce.
What is absorption costing?
___________ Costs are expensed when incurred.
What are period costs?
Examples include:
Selling, Administration, Research & Development, & Income Taxes
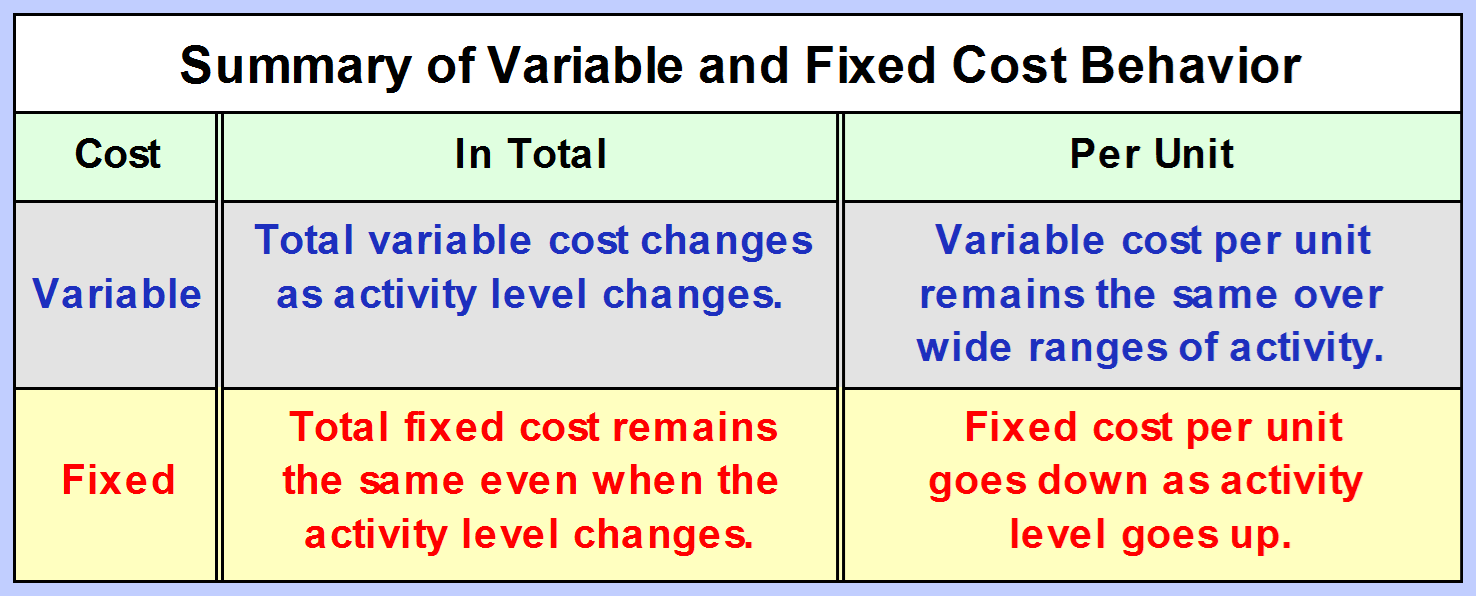
Total ____________ cost changes as activity level changes but the per unit remains the same over wide ranges of activity.
What are variable costs?
The journal entry for APPLYING overhead.
What is a debit to work in process inventory and a credit to manufacturing overhead?
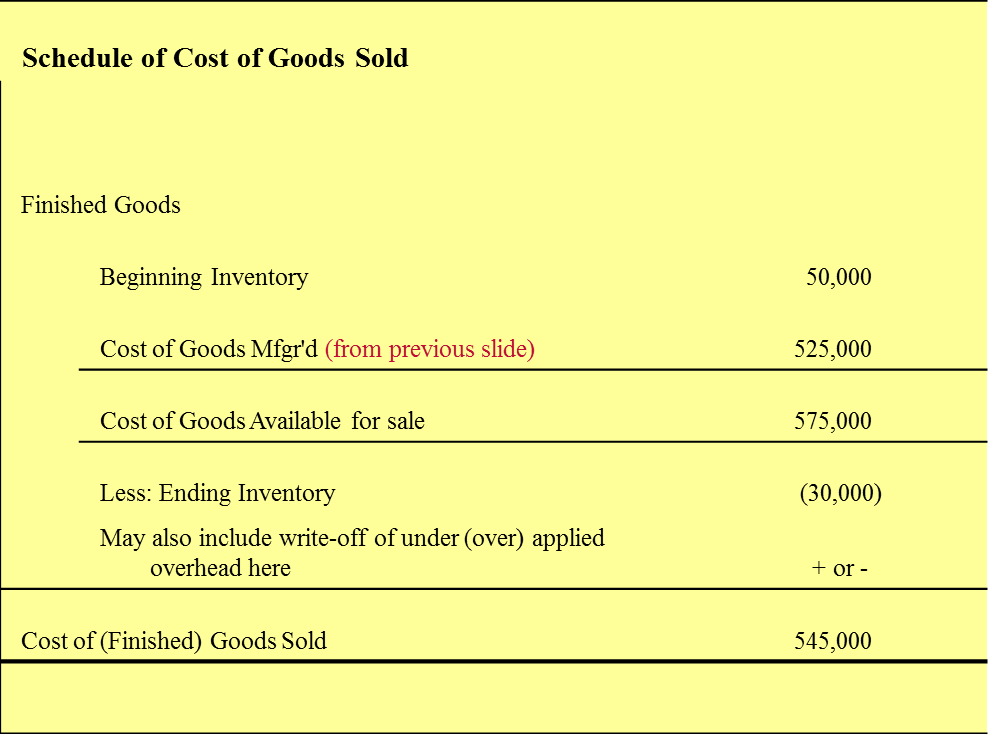
Draw out the Schedule of Cost of Goods Sold.
The break even formula (in units).
What is:
FIXED COSTS / CONTRIBUTION MARGIN PER UNIT
When does it matter which costing method you use?
What is it only matters if the company has inventory?
With ABC costing - it only matters if you have more than one product.
With Variable Costing - it only matters if you have inventory. This costing method removes management's incentives to produce more product than you can sell since fixed MOH is expensed and not assigned to inventory,
Define each part of the following equation:
TC = F + V(X)
What is:
TC - Total cost is the dependent variable.
F - The intercept term (F) is the estimate of the fixed cost.
V - The coefficient (V) is the estimate of variable cost per unit of activity, the slope of the cost line.
X - the activity (X) is the level of cost driver.
A __________________ fixed cost of a segment is a fixed cost that is incurred because of the existence of the segment and if the segment were eliminated it would go away.
What is a traceable fixed cost?
Examples include: product manager salary, equipment rental. These SHOULD be used in evaluating a profit center.
A common fixed cost supports the operations of more than one segment (Examples: CEO salary, office staff). These SHOULD NOT be used in evaluating a profit center.
The journal entry to account for indirect materials moved from storage into production.
What is a debit to manufacturing overhead and a credit to raw materials?
Two reasons why overhead may be over or under applied.
What is:
We did not accurately estimate the actual dollar amount of overhead or we did not accurately estimate the actual level of the cost driver (e.g. direct labor hours) used to apply overhead.
This is the Target profit formula (units).
What is:
Fixed Costs + Target Profit / Contribution Margin Per Unit
The formula to determine the difference in income between variable costing and absorption costing.
What is the change in inventories * unit fixed cost?