This organelle is responsible for generating ATP in eukaryotic cells
What is Mitochondria
What is Lead
He is known as the father of psychoanalysis, emphasizing the importance of unconscious motives and childhood experiences in shaping behavior
Who is Sigmund Freud
This type of transport is utilized by the sodium and glucose cotransporter
What is Secondary Active Transport
This term, derived from Latin, refers to the body's ability to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes
What is Homeostasis
This is the common name for a polymer composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
What is Protein
This is the common name for an aromatic ring compound with six carbons and a methyl substituent
What is Toluene
The phenomenon where individuals are less likely to offer help to a victim when others are present is known as this term coined by social psychologists
What is Bystander Effect
The term for when a membrane becomes more polarized than at resting potential
What is Hyperpolarized
This term, often used in genetics, refers to the complete set of genes or genetic material present in a cell or organism
What is Genome
This enzyme is responsible for unwinding the DNA double helix during replication
The weak base that makes up the bicarbonate buffer system found in blood
What is Carbonic Acid / H2CO3
This disorder is characterized by extreme mood swings, shifting from periods of euphoria and energy to episodes of depression and lethargy
What is Bipolar Disorder
The hormone produced by the pineal gland that regulates your circadian rhythm
What is melatonin
This term is commonly used to describe the condition of high blood pressure
This step of gene expression involves the action of helicase-like enzymes in eukaryotic cells.
This is the structure of this functional group
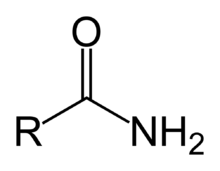
What is Amide.
The phenomenon of people tending to remember the first and last items in a series best
What is Serial Position Effect
This chamber of the heart pumps blood to the system circuit
What is Left Ventricle
The medical term for the inflammation of the liver, often caused by viral infections or excessive alcohol consumption
What is Hepatitis
This is a term for the specific sequence of nucleotides that serves as a recognition site for RNA polymerase during transcription, indicating where the process should initiate on the DNA template
What is Promoter
This kind of product is formed when protecting groups are added to ketones to protect them from undergoing reactions
What is Acetal
The part of the brain that is often called the "thinking center" and is responsible for decision-making, problem-solving, and planning
What is the Prefrontal Cortex
This is the name of the theory that governs muscle fiber movement
What is Sliding Filament Theory
In the context of prescription medications, this abbreviation is often used which translates to "as needed" in Latin.
What is PRN or "pro re nata"