When both species benefit from the relationship?
What is a mutualistic relationship?
Are located in extreme abiotic conditions, including toxins, temperature, ph, hydrostatic pressure, and lack of light, and have tubeworms as early pioneer species.
What are hydrothermal vents?
Herbivores occupy this feeding level.
What is the 2nd trophic level/primary consumer.
When many different species live within one ecosystem
What is high biodiversity?
An organism that can produce its own food energy through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Provides food for the next trophic level.
What is a producer?
Place where organisms live.
What is its habitat?
The relationship between Remora & Manta ray.
What is Commensalism?
Example of a stable and non-extreme environment.
What are coral reefs?
(also rocky shores)
A producer that uses light energy to produce its own food energy. Ex. seagrass, seaweed, mangroves, and kelp.
What is a photoautotroph?
Organisms that exploit a wide range of habitats and food sources are said to have this ecological niche.
What are generalized ecological niches?
The mass of living material in an area, can be measured as dry mass (without the water) or wet mass.
What is biomass?
All the individuals of the same species that live at the same place and time
What is the population?
Image is an example of....
What are ectoparasites?
A process that occurs in hydrothermal vents, which transfers inorganic to organic substances, and uses the energy from bacteria to transfer energy.
What is chemosynthesis?
Arrows in a food web are pointing in this direction?
What is the direction of energy transfer?
Competition that occurs between individuals of the same species
What is intraspecific competition?
Primary source of energy for this food web?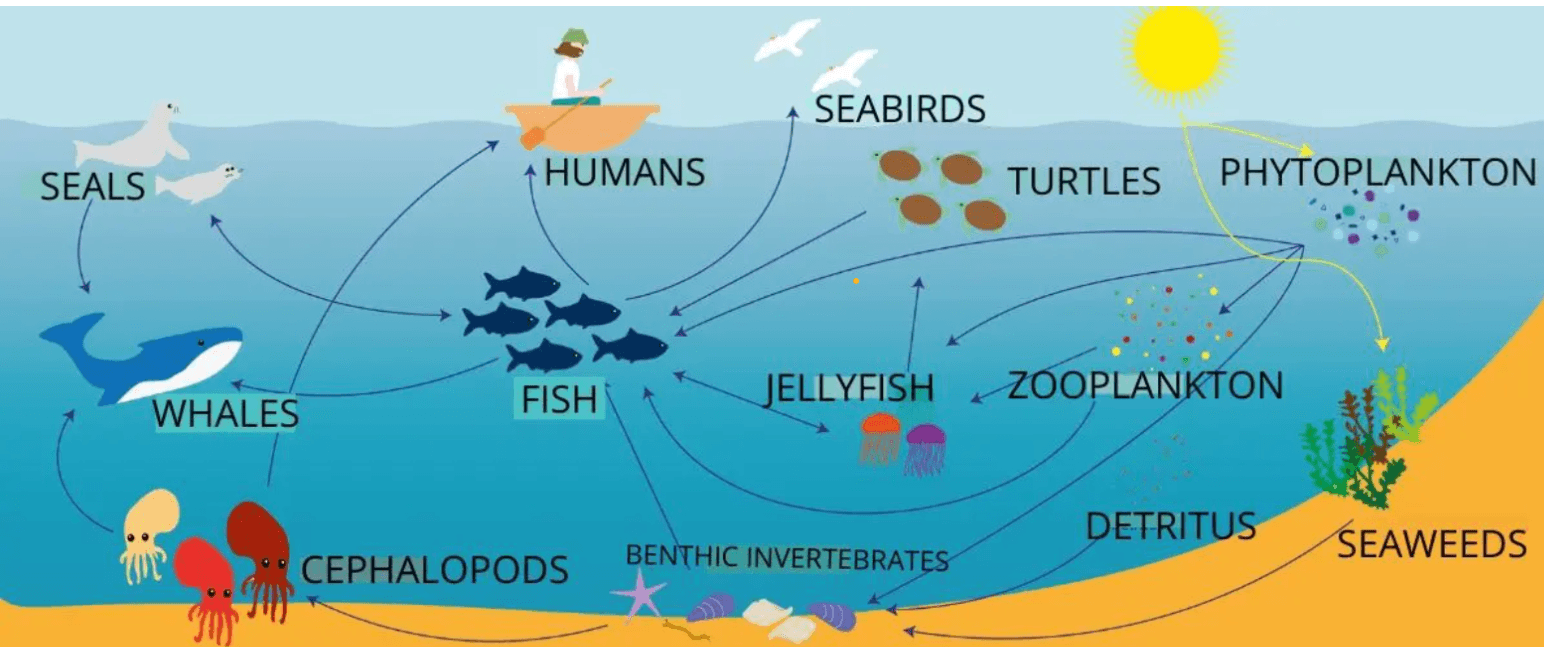
What is the sun?
All the different populations occupying a habitat at the same time
What is a community?
A small tapeworm that derives food and shelter by living in the guts of whales is an example of this.
What are endoparasites?
This occurs on sites that have previously supported a community that is now no longer there because of habitat destruction.
What is secondary succession?
Limiting factor that affects the location and number of predators in an ecosystem.
What is the availability of food?
Term used to describe an organism spends all their time shoaling or schooling and may become agitated when separated from the group.
What is an obligate?
They are crucial for keeping a healthy balance of populations within the ecosystem
What are predator-prey relationships?
A measure of the numbers of different species present
What is biodiversity?
Coral and Zooxanthellae
Tubeworms and chemosynthetic bacteria
Cleaner fish and shrimps and their hosts
What are the 3 marine examples of mutualism ?
They are likely to occur near the top of the food chain, although they are not necessarily the top predator; control the other species by means of predation and competition.
What are the Keystone species?
Number of different kinds of Primary consumers are present.
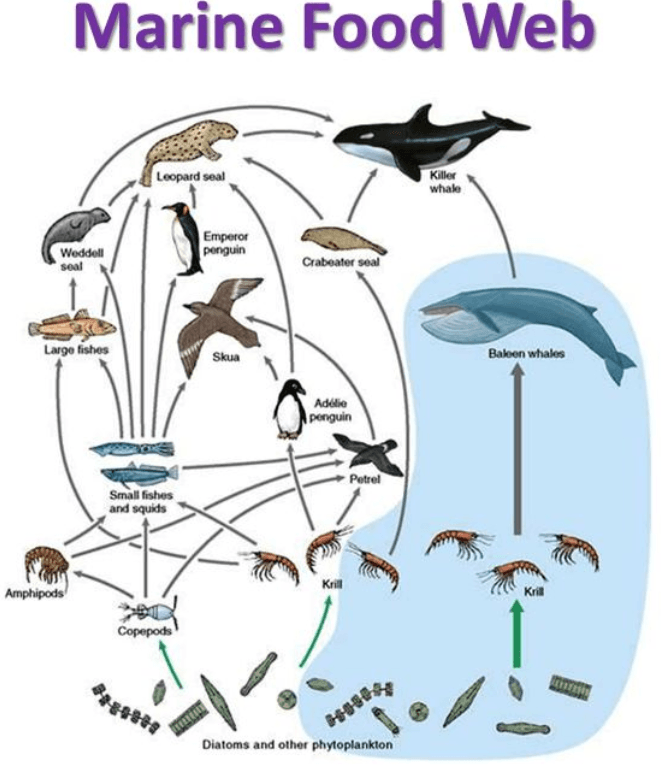
What are two primary consumers?
A bottlenose dolphin, whose diet includes a large variety of fish and squid species and whose habitat extends throughout the world's oceans except for polar regions is said to have this type of niche?
What is a generalized niche?
Some predators are more efficient at attacking shoals than individual fish; large numbers of fish swimming close together cause excretory waste to build up, while oxygen and food supplies are depleted.
What are the disadvantages of Shoals?
A relationship between two organisms where both species are negatively affected by trying to fill the same ecological niche
What is Competition?