This term is used to describe the study of gametes and their development, fertilization, and the prenatal growth of embryos and fetuses.
What is embryology?
This joint allows the head to flex and extend, or nod up and down.
What is the atlanto-occipital joint?
Identify the structure indicated by the red dot.
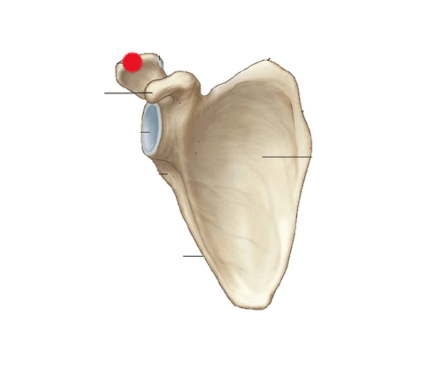
What is the acromion?
These structures ultimately separate the arm into anterior and posterior compartments.
What are the medial and lateral intermuscular septa of the arm?
During venipuncture of the median cubital vein, inserting the needle too deeply can result in the injury of this nerve that traverses the cubital fossa.
What is median nerve?
A patient describes they are experiencing muscular pain just to the lateral side of their shoulder. Anatomically, you would use this term to describe the position of these muscles relative to the arm muscles.
What is proximal?
These anatomical structures carry efferent information directly out of the spinal cord.
What are anterior rootlets?
This joint acts as the only bony articulation of the upper limb to the axial skeleton.
What is the sternoclavicular joint?
These two arm muscles (or parts of arm muscles) perform actions at more than one joint.
What are the biceps brachii muscle and the long head of the triceps brachii muscle?
This structure is responsible for providing innervation to the medial half of the flexor digitorum profundus muscle.
What is ulnar nerve?
To kick a soccer ball, one must use a number of muscles in their lower limb. You would use this phrase to describe the kicking movement made by the leg at the knee joint.
What is extension of the leg?
The nervous system is divided into functional parts. These functional components are responsible for the innervation of skeletal muscle.
What are general somatic efferent fibers?
Of the four rotator cuff muscles, this muscle holds the responsibility of medial rotation of the humerus.
What is the subscapularis muscle?
The upper limb is supplied with blood by several contributing arteries. These vessels of the third part of the axillary artery work together to supply blood to the surgical neck of the long bone in the upper extremity.
What are the anterior circumflex humeral and posterior circumflex humeral arteries?
The carpal tunnel acts as a passageway for several structures from the flexor compartment of the forearm into the hand. These three muscles traverse this space.
What are flexor pollicus longus, flexor digitorum superficialis, and flexor digitorum profundus muscles?
Creation of the three primary germ layers results in the formation of many specific collections of cells. This layer is known to form the skeletal, cardiac, and smooth visceral muscle, the skeleton, blood vessels, and other supporting connective tissue.
What is the mesoderm/mesodermal layer?
The sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) carries information to the prevertebral ganglia of visceral targets in the abdomen and pelvis by way of these nervous structures
What are splanchnic nerves?
The shoulder joint is supplied with blood by several contributing arteries. This vessel serves as one of the primary sources of blood to the posterior scapular region after passing through the most medial space in the shoulder.
What is the circumflex scapular artery?
This artery functions to supply blood to the anterior and posterior compartments of the arm. It is known to originate/begin from this specified location.
What is the inferior border of the teres major muscle and/or where the profunda brachii artery branches?
This arterial structure is primarily responsible for providing oxygenated blood to the superficial palmar surface of the hand. It is a continuation of this forearm artery?
What is the ulnar artery?
You are an X-Ray technician who works nights at a rural hospital. The doctor on call orders an MRI. You complete the order. Below is an image from the scan.
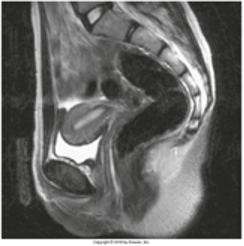
This anatomical plane divides the body into what structures?
What are right and left parts?
A 16-year-old male is brought to the Emergency Department from swim practice. He states that he has been experiencing frequent pain and tenderness along the posterolateral portion of his back. His pain becomes the most intense when trying to complete his 100-m butterfly relay. You expect this muscle to be the cause of his symptoms.
What is the latissimus dorsi muscle?
After surgical repair of a humeral neck fracture, a 34-year-old female patient presents with post-operative weakness in abduction of the arm and numbness in the proximal shoulder. The injured structure traverses this space in the shoulder.
What is the quadrangular space?
A 6-year-old male is brought to the Emergency Department by his mother. She expresses her concern as she has noticed her son frequently experiences progressive shortness of breath and weakness in his ability to flex his fingers, specifically his pinky. You suspect an injury to this cord of the brachial plexus.
What is medial cord?
A 16-year-old baseball player arrives at the emergency department after sustaining an injury to his right medial elbow. Upon physical examination, the physician notices that his right hand is in a fixed claw position. You suspect this structure is damaged.
What is the ulnar nerve?