By this gestation, organ systems, fetal circulation, & placental development are complete
What is 12 weeks?
What is False?
Preterm labor occurs during this period
What is 20-37 weeks gestation?
Normal value is 40-60 mg/dL
What is newborn blood glucose?
Milia, Mongolian spots, stork bite rash
What are normal newborn skin findings?
The recommended dose of folic acid
What is 400 mcg?
S&S of this postpartum complication include sore, red, warm area on breast
What is mastitis?
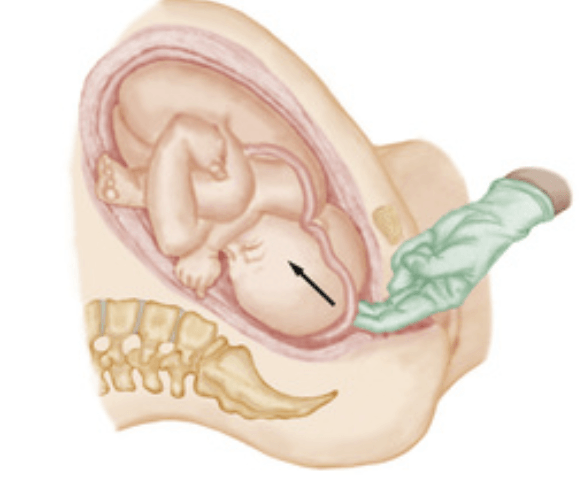
What is Prolapsed umbilical cord?
Bilirubin reaches excess levels, often caused by Rh incompatibility; occurs within 1st 24 hours after birth
What is pathologic (AKA non-physiologic) jaundice?
Medication given to accelerate fetal lung maturity
What are corticosteroids dexamethasone or betamethasone?
The pregnant woman may have an increase of 40% - 50% of this
What is blood volume?
normal fetal heart rate
What is 120-160 bpm
SBP ≥140 mm Hg, DBP ≥90 mm Hg, or significant BP increase occurring after 20 weeks + proteinuria
What is pre-eclampsia?
S&S: decreased skin temp, increased RR with periods of apnea, bradycardia, mottling of skin, & lethargy
What is cold stress?
S&S: fundus deviated to the right, decreased uterine tone, & increased bleeding
What is a full bladder?
S&S include faintness, lightheadedness, dizziness, nausea when laying on back
What is supine hypotension?
the length of each contraction from beginning to end
What is duration of contraction?
Deep tendon reflexes, respiratory rate, urine output
What are assessments required when administering magnesium sulfate?
weight >90%ile; can lead to low blood glucose
What is macrosomia?
inactivity, bedrest, prolonged labor, put the postpartum woman at risk for
What is DVT?
The 3 structures present only in fetal circulation
What are foramen ovale, ductus venosus, & ductus arteriosus?
Regular contractions accompanied by cervical change
What is true labor?
Rh sensitization that can lead to erythroblastosis fetalis occurs under what circumstances?
What is maternal Rh negative blood type & fetal Rh positive blood type?
Priority intervention for a newborn that is jittery
What is blood glucose check?
Complication when the placenta partially or completely detaches
What is placental abruption or abruptio placentae?