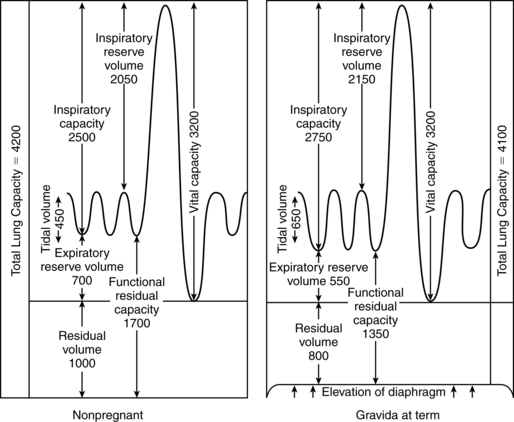
Functional residual capacity ______ during pregnancy due to what anatomical change?
Decreases, due to upward displacement of diaphragm (cannot counteract expansion of the rib cage).
Increase, decrease, no change?
1) GFR
2) Renal plasma blood flow
1. Increase up to 25% by 2nd week and 50% by 2nd trimester
2. Increase also by as much as 80%
This increases from 6-8 weeks gestation and peaks at a 45% increase above nonpregnant values, resulting in a physiologic hemodilution.
What is plasma volume. Red blood cell mass increases by 250-450cc. (only a 20-30% increase)
Increase, decrease, or no change: Thyroid binding globulin level.
What is increases.
What happens to the following? (Increase, Decrease, or no change)
1. Expiratory reserve volume
2. Residual volume
1. Decrease 2. Decrease
What creatinine level in pregnancy suggests underlying renal disease?
What is 0.9 mg/dL and greater (normal should be ~0/5 mg/dL).
Cardiac output increases by 30-50% by an increase in what? A. Stroke Volume B. Heart Rate C. Both
What is C. CO increases as early as 5 weeks gestation. Resting HR increases 10-15 bpm. SV also increases (increased venous return and decreased SVR), peaking at ~32 weeks.
Why do pregnant women get hemorrhoids? (2 reasons)
Constipation (progesterone) Elevated pressure in veins below level of enlarged uterus
What is the equation for minute ventilation?
Respiratory Rate x Tidal Volume
BP decreases during pregnancy, reaching a nadir at what gestational age? A. 16-20wga B. 24-28wga C. 32-36wga
What is B. 24-28wga. Decreased SVR as well as arterial stiffness; plateaus and then slightly increases.
Free T4 Increase, decrease, no change?
Rises at 6-9 weeks in response to increased BhCG, then declines to normal levels
Increase, decrease, or no change?
1. Tidal volume
2. Respiratory rate
True or False: Glucosuria can be common in pregnancy?
What is True. Due to and increased GFR and impaired tubular reabsorptive capacity for filtered glucose.
This hormone is responsible for decreased systemic vascular resistance and increased venous compliance.
What is Progesterone
The pituitary gland increases in size by ~135% due to estrogen stimulated hypertrophy and hyperplasia of what cell type?
What are lactotrophs? Prolactin levels are roughly 10-fold greater at term!
Which of the following represents a normal ABG for pregnancy?
1) 7.40/40/100/24
2) 7.45/30/105/20
3) 7.37/44/95/25
Answer: B-- Pregnancy causes a mild respiratory alkalosis. This results in a shift to the left of the O2 dissociation curve, increasing the affinity of maternal hemoglobin for oxygen (Bohr effect)
Free Candy!

Cardiac output increases by 60-80% immediately after delivery. Why? (2 reasons)
1. Release of venacaval obstruction 2. Autotransfusion of uteruoplacental blood
TSH Increase, decrease, no change
Decrease (BhCG and TSH have identical alpha subunits and similar beta subunits, which gives BhCG thyrotropic activity)