A quadratic equation always has this highest exponent.
2
In direct variation, when one quantity increases, the other does this.
increase
Any number raised to the power of zero equals this.
1
The term used for a number inside a radical symbol.
radicand
The general form of a quadratic equation.
ax2+bx+c=0
What variation when one quantity increases, the other decreases?
inverse variation
The expression (xa)(xb) simplifies to this.
xa+b
Two radicals can only be added or subtracted if they have this in common.
index and radicand
The formula used to find the solutions of a quadratic equation.
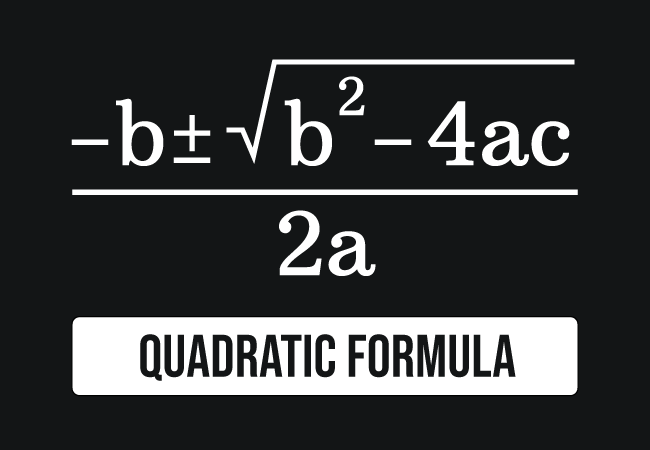
What is k called from the formula y=kx of direct variation?
constant variation
The negative exponent rule states that x-n is equal to this.
1/xn
The result of 3 square root of 2 + 5 square root 2.
8 square root 2.
If a quadratic equation has one solution, the discriminant is equal to this number.
0
The general equation for inverse variation.
y=k/x
The expression x5/x2 simplifies to this.
x3
The mathematical process used to eliminate a radical from the denominator.
rationalization
If x2−9=0, what are the values of x?
x = 3 x = -3
If y varies directly with x and y = 10 when x = 2, what is the constant of variation k?
5
mThe general rule for rewriting xm/n as a radical expression.
nth root of xm
The simplified form of square root of 18/square root of 2
3