Mass
All Elements are made of basic particles called
Atoms (question #1 on study guide)
What measurement of matter is the amount of space an object takes up?
volume (#14 on study guide)
The SI unit for mass is…
grams (#8 on study guide)
Density is a basic physical property of __
A. All Matter
B. Gases
C. Liquids
D. Solids
A. All Matter (#6 on study guide)
Give an example of matter. List something that is not considered matter.
MATTER – DESK, BOOK, CHAIR, PAPER
NOT MATTER – ENERGY (#2 on study guide)
Matter is defined as…
anything that takes up space (volume) and has mass. (#7 on study guide)
How do you find the volume of a regular shaped object?
The beaker has a mass of 32.310 g. What is the mass of sodium bicarbonate in the beaker?
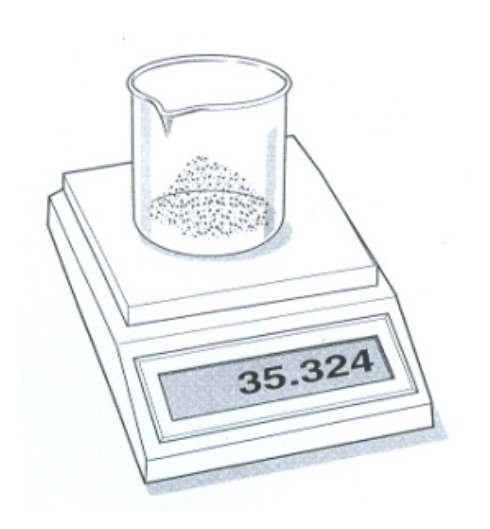

3.014G (#9 on study guide)
Which of the following could you use most easily to determine the density of a liquid?
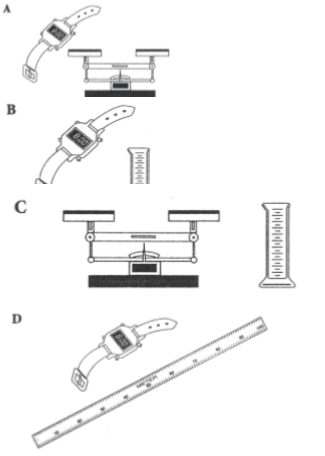
(#10 on study guide)
Part 1: How do you calculate the density of an object? Be able to find the density of an object when given the mass and volume.
Part 2: EX – Mass of object is 240 g and the volume is 36 mL. What is the density?
Part 1: Mass Divided by Volume
Part 2: 240/36 = 6.67 G/CM3
(#27 on study guide)
Give an example of a chemical formula....
h2o, co2, o2 (#24 on study guide)
Explain how to find the volume of an irregular object... (be able to do this)
DISPLACEMENT - RECORD THE STARTING WATER LEVEL. SUBMERGE THE OBJECT INTO THE WATER AND RECORD THE NEW WATER LEVEL. SUBTRACT AND YOU WILL BE LEFT WITH JUST THE VOLUME OF THE IRREGULAR OBJECT. (#22 on study guide)
What does the diagram below show about matter?
A. Matter has mass B. Matter takes up space.
C. Matter is a solid. D. Matter is made up of elements.
A. Matter has Mass (#21 on study guide)
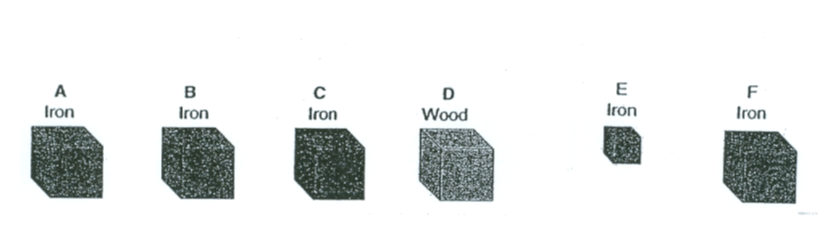
Part A - Which of the items pictured above would have the same densities?
Part B - Which of the objects shown above has a different density than all of the other objects?
Part A (#16 on study guide) - A, B, C, E AND F
Part B (#17 on study guide) - CUBE D
When you pour water from a graduated cylinder to a beaker, there is a change in the water’s…
a. density
b. mass
c. volume
d. shape
D. Shape
(#29 on study guide)
How can we change from one form of matter to another?
adding or removing thermal energy (heat) (#3 on study guide)
The diagram below shows one way to measure the volume of an irregular object. What is the volume of the rock sample?
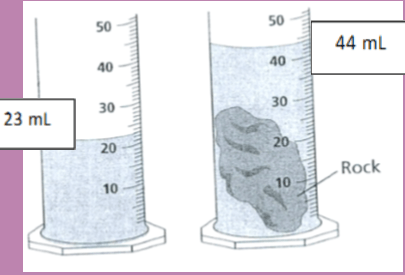
21 mL (#12 on study guide)
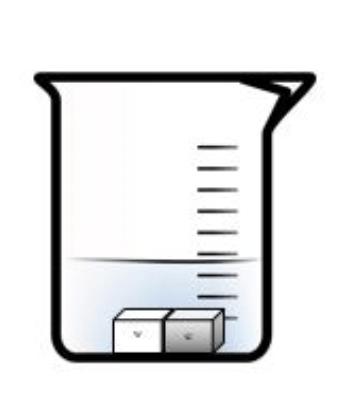
Find the mass of the sand that is inside the beaker in the picture below. Be sure you can read a triple beam balance (multiple questions on reading triple beam balance).
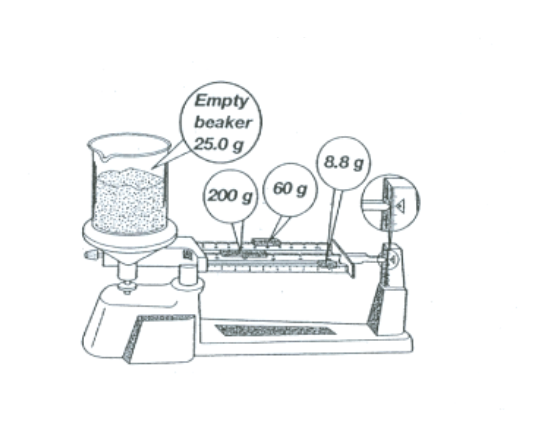
Mass = 243.8g (#28 on study guide)
What are the proper units for density?
g/cm3 or g/mL (#20 on study guide)
Why do substances separate when placed in the same container?
Think of oil and water. Think of the density column we created!
THE SUBSTANCES SEPARATE BECAUSE THEY HAVE DIFFERENT DENSITIES. THE OIL IS LESS DENSE THAN THE WATER. (#25 on study guide)
Draw a diagram of the molecules found in a solid, liquid and a gas.
(#13 on study guide)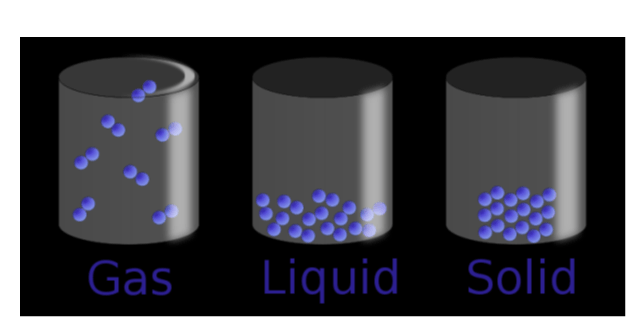
Study the illustration of the two graduated cylinders below. The two objects pictured have equal volumes. However, the objects have different masses and therefore different densities. Predict what will happen when Tanner puts the objects in the separate graduates.
THE WATER LEVEL IN EACH SHOULD RISE THE SAME SINCE THEY BOTH HAVE THE SAME VOLUME. (#15 on study guide)
Explain how to find the MASS of a liquid…
TO FIND THE MASS OF A LIQUID, YOU FIRST NEED TO FIND THE MASS OF AN EMPTY GRADUATED CYLINDER OR BEAKER. THEN ADD THE LIQUID YOU WANT TO FIND THE MASS OF. RECORD THE NEW MASS. SUBTRACT THE EMPTY CONTAINER FROM THE CONTAINER WITH THE LIQUID AND YOU WILL BE LEFT WITH THE MASS OF JUST THE LIQUID. (#23 on study guide)
Draw a diagram with a beaker of liquid that has a density that allows both a piece of wood and steel to have a greater density than that of the liquid.
(#30 on study guide)
Cindy has 2 cans of coke, one diet and one regular:
Part A: She notices that on both cans it is marked 355mL. This means that the can has _____.
a. mass of 355 mL b. weight of 355 mL
c. density of 355 mL d. volume of 355 mL
Part B: What should she expect to be true about the water displaced by each of the cans?
Part A: d. volume of 355 mL
Part B: THE AMOUNT OF WATER DISPLACED BY BOTH SHOULD BE THE EXACT SAME.
(#11 on study guide)