This chamber normally rises and falls with breathing
What is water-seal chamber?
This position helps a patient with ARDS to re-expand the collapsed posterior alveolar units
What is the prone position?
Of sterile or clean, this is the proper way to perform trach care on a patient in the hospital.
What is sterile?
The length markings in this picture are on the ETT to ensure this doesn't happen.
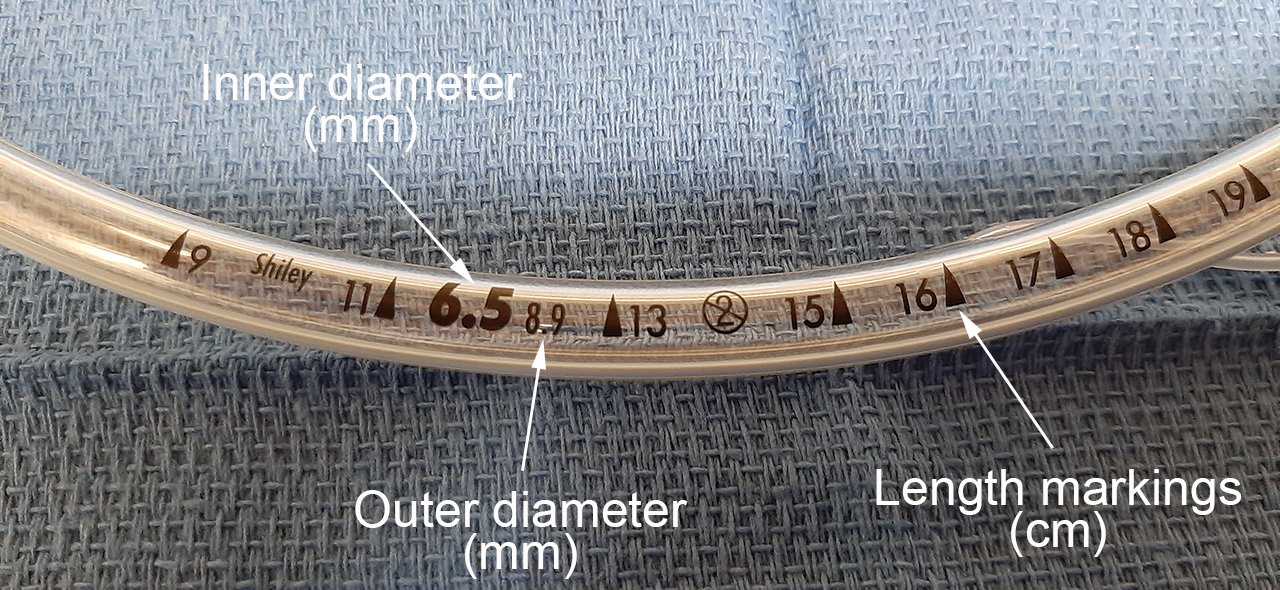
What is get dislodged?
This occurs when 2 or more ribs are broken in 2 or more places.
What is a flail chest?
This chamber is where the fluid drains into
What is the collection chamber?
Of these 3, this is the simple definition of ARDS:
Refractory hypoxemia
Insufficient fluid in the lungs
Pink frothy sputum
What is refractory hypoxemia?
A person with copious secretions needs suctioning. Name 3 rules for suctioning.
What is:
no longer than 10 seconds
hyperoxygenate first
suction on the way out
Hand hygiene and good oral hygiene is the best prevention for this complication of mechanical ventilation
What is ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP)?
This is where the trachea deviates toward when there is a collapsed lung.
What is the "good" lung?
Continuous bubbling in the water seal chamber is a sign of this
What is a leak in the system?
ARF can be classified as these 2 types.
What are hypoxemic and hypercapnic?
This is what the nurse is doing in this picture
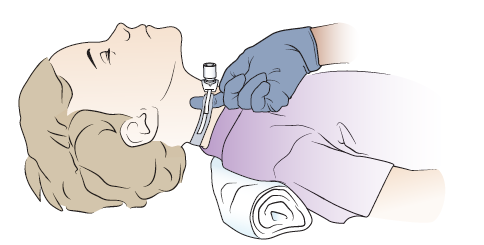
What is checking to make sure the trach ties are not too tight?
Priority nursing action when endotracheal tube becomes dislodged
What is manually ventilate the patient?
These are 2 modifiable risk factors for head and neck cancer.
What is using tobacco and drinking alcohol?
3 nurses have the following 3 different ideas about what to do if there is no tidaling in the water seal chamber.
Clamp the tubing
Strip the tubing
Have the patient TCDB
This is the correct choice.
What is Have the patient TCDB?
Of these 3, this is the setting on the ventilator that helps the ARDS patient:
High PEEP
No PEEP
High tidal volume
What is High PEEP?
This is a complication of the cuff being over-inflated.
What is tracheal necrosis?
This alarm sounds when the patient is coughing or has copious secretions
What is the high pressure alarm?
Acute rejection of a lung transplant usually happens in the first 5-10 days. Name 2 signs to watch for.
What are fever, fatigue, dyspnea, cough, and low O2 sats?
Your patient had his chest tube removed this morning. He now complains of severe shortness of breath. This is the most likely reason.
What is the patient has re-developed a pneumothorax?
This acid-base imbalance is found EARLY in ARDS, due to increased respiratory rate.
What is respiratory alkalosis?
This piece needs to be in the trach patient's room, in case the trach tube becomes dislodged.
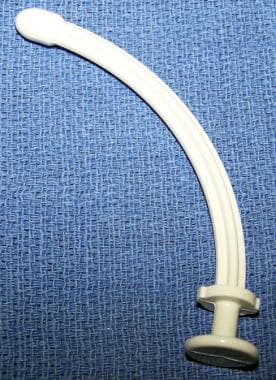
What is an obturator?
The priority action the nurse should take when suctioning a patient and notices cardiac dysrhythmia.
What is stop suctioning and give oxygen?
This is the best position for a patient who has recently had their whole lung removed.
What is lay on the affected side, AKA "good lung up"?