(aka Doppler Effect)
What is mass?
In fact, all of the other aspects of a star such as its luminosity, temperature, size, density, etc., can be explained using its mass.
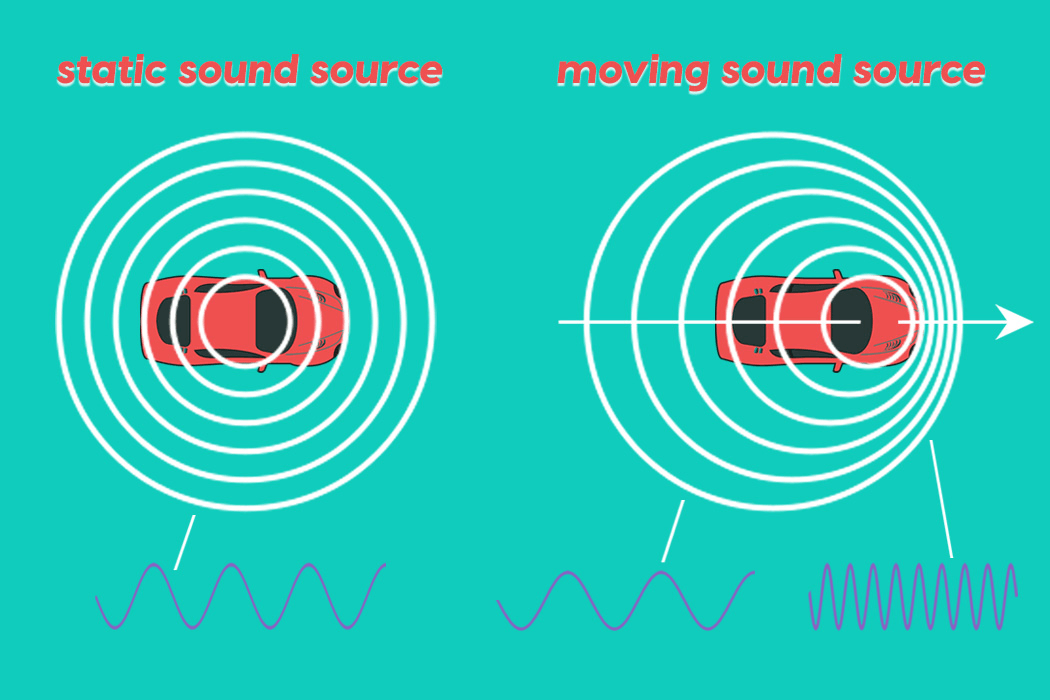
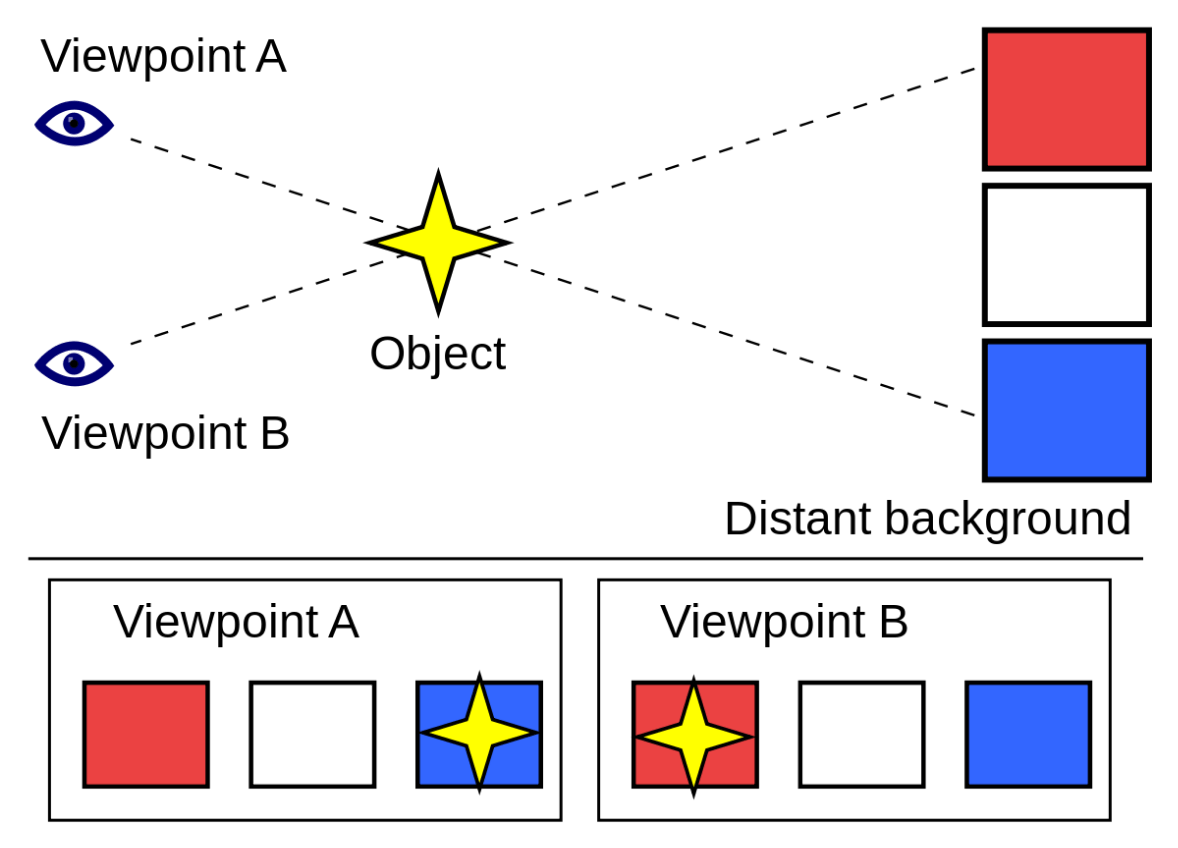
This phenomenon indicates that the observer & the source are moving towards each other.
This property describes how bright a star appears to an observer on Earth.
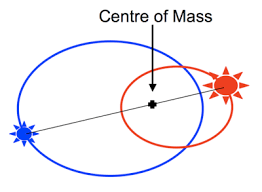
Bonus: do you know a third?
This property accounts for a star's distance from Earth.
What is Absolute Magnitude?
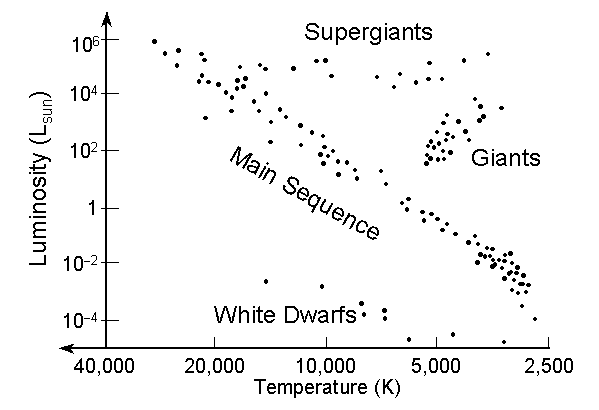
This property describes a star's energy output per second.
What is Luminosity?
Bonus: Do you know the units?

What is the more massive a star is, the greater the gravity pressing inward, and the hotter and denser the star must be inside to balance its own gravity?

What are Eclipsing Binary and Spectroscopic Binary?