Surgical
Surgical
Diet encouraged for patients post-operatively to help prevent constipation.
What is a high fiber diet
Bone loss due to the softening of bone tissue
What is osteoporosis
It is important to assess this in a client, post bronchoscopy, to prevent aspiration when eating.
What is the gag reflex
This is the first intervention to be performed for a client exhibiting a myocardial infarction.
What is apply oxygen
Clients with hypothyroidism have an intolerance to this and may require warm clothing or blankets
What is cold intolerance
Lab value with has an expected reference range of 5,000-10,000.
What is white blood cells (WBC's)
Measures the intraocular pressure of the eye, in a client with glaucoma.
What is Tonometry
This nursing intervention is the priority action should the nurse discover any complication or reaction with a blood product or blood transfusion.
What is stop the infusion
DOUBLE POINTS
2 types of diagnostic procedure that help to determine the best course of antibiotic treatment for an infected wound.
What is a wound culture and blood culture.
what is a foam wedge or abductor pillow
This is a priority assessment prior to the administration of morphine.
What is a client's respiratory rate
Expected findings expected in a client with right-sided heart failure?
What is:
peripheral edema
high blood pressure
JVD
When low levels of the hormone vasopressin or ADH is produced it can cause this disorder to occur.
What is Diabetes Insipidus
When a patient has few neutrophils due to an autoimmune disease, infection, or radiation therapy
What is neutropenia
An opacity in the lens of an eye that impairs vision, causing blurred vision or impaired color vision.
What is cataracts
generalized urticaria or itching, bronchospasms, laryngeal edema, or hypotension
What is an anaphylactic transfusion reaction
This is known as the leading cause of non-melanoma skin cancer.
What is sun exposure
This type of bone fracture involves fragments of bone or splintered bone into several pieces.
What is a comminuted bone fracture
Expiratory wheezes are the most common lung sound noted in a patient with this acute, respiratory exacerbation.
What is asthma
Frothy sputum or Hemoptysis is an expected finding in this type of cardiac complication.
What is left-sided heartfailure.
Clients with a fruity odor to their breath and/or urine are most likely exhibiting this endocrine disorder.
What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis.
This conductive hearing loss test requires the provider to place a tuning fork on the mastoid bone of the client's head.
What is the Rinne test
A blood transfusion reaction that is mild or life-threatening. The manifestations usually occur immediately after the transfusion or within the first 15 minutes. This can occur due to the transfusion of blood products incompatible with the client's blood type or Rh factor. Common assessment findings are chills and lower back pain.
What is an acute hemolytic transfusion reaction.
The priority risk or complication for clients with partial-thickness to full-thickness burns of the head and chest.
What is airway obstruction
TRIPLE POINTS!
Client's with gout or a history of gout are educated to avoid these kinds of foods. (name 3 to triple point value)
What is shellfish or foods high in purines
- sardines -mackerel
- salmon - anchovies
- alcohol - organ meats
This type of breathing technique is useful for clients with emphysema and COPD, because it increases the pressure in the airway with exhalation and lengthens the expiratory phase of respiration, decreasing trapped air in their lungs.
What is pursed-lip breathing
This electrolyte can cause arrhythmias if abnormal, less than 3.5 mEq/L or greater than 5 mEq/L.
What is potassium
Clients with Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH) and a sodium level of 120 mEq/L, should do this with their fluid intake.
ideally 800-1,000 mL/day due to excess fluid volume diluting sodium levels.
This lab has an expected reference range of 150,000 to 400,000 mm³
What are platelets
Vision impairment that affects the patient's peripheral vision, causing a gradual loss in vision, potentially blindness.
What is open-angle glaucoma
A transfusion reaction that commonly occurs within 2 hours of starting the transfusion and findings include chills with a body temperature increase of 1° F or greater.
What is a febrile transfusion reaction
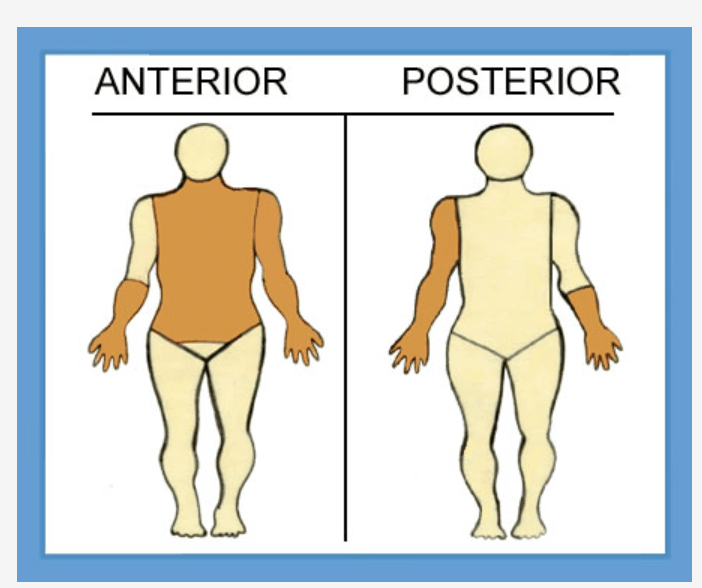
What is 31.5%
Left arm = 9%
½ of right arm = 4.5%
Front torso = 18%
Patients with osteoporosis who take this oral medication should sit upright for at least 30 minutes post-administration to prevent esophagitis.
What is Alendronate
This white coating of the mouth develops most commonly in clients who are taking a steroid inhaler/breathing treatment.
TRIPLE POINTS!!!
These 3 interventions are important for the post cardiac catheterization client.
check distal pulses in both legs
remain flat with used extremity straight for 4-6 hours, as tolerated
leave dressing in place for 24 hours
When the thyroid stimulating hormone is below normal levels (0.5 to 5.0 mIU/L)
What is Grave's disease or hyperthyroidism.
This antedote is given for patients with an elevated PTT to reverse the effects of heparin.
What is protamine sulfate
TRIPLE POINTS!
3 priority interventions or education provided for patients post glaucoma surgery
What is adhering to medications, avoiding activities that increase IOP, do not lie on the operative side.
A transfusion reaction that can occur during the transfusion or within 24 hours after the transfusion, as a result of a sensitivity to the components of the transfused blood product.
What is an allergic transfusion reaction.
Name this drain
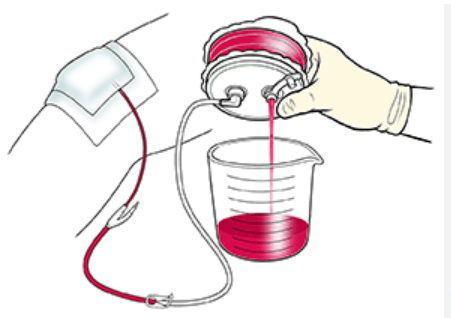
What is a hemovac
These pinpoint, unraised, round red spots under the skin caused by bleeding can develop from fat embolism syndrome as a result of a bone fracture.
What is respiratory acidosis
This is the normal lab value for Troponin T.
What is 0-0.04 ng/mL
What is Addison's disease
This type of cancer can lower platelet counts below 150,000/mm3 , increasing the client's risk of hemorrhage.
What is Leukemia
What is meclizine
DOUBLE POINTS!
The blood type that is the most needed for blood banks when donating blood because it is termed the universal donor.
What is O negative
Mr. Jones presents to the hospital with an infected wound to the right lower leg, caused by a diabetic ulcer. The lab results of his wound culture show he has developed MRSA of the wound. He has been hospitalized for 3 days. He is started on IV antibiotics, day 1. He begins to complain of hearing loss and the nurse notices he has had a significant decrease in urinary output throughout her shift, despite being on 0.9% normal saline at 75 mL/hr and drinking sufficient oral fluids. The nurse looks at the clients labs and sees that a blood draw for a trough is due 30 minutes prior to his next infusion, which is in 2 hours. The nurse suspects toxicity of this antibiotic.
What is Vancomycin