Care of a patient who just underwent radiofrequecy catheter ablation is similar to that of a patient who just underwent ____
Recurring, regular saw tooth-shaped waves
Concerning symptoms: Can cause HF in pts with underlying heart disease, increased risk of stroke. Pts often on Coumadin to prevent clots
Name this rhythm and the tx
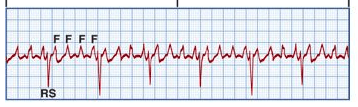
What is atrial flutter
Tx (if symptomatic):
1. CCB
2. BB
3. Surgical ablation
4. Electrical cardioversion for emergencies
Respiratory symptoms, labs requiring rapid response from nurse, and rapid notification of doc (3)
What are:
1. Low PaO2
2. Extreme acidosis or alkalosis
3. All the late signs of IWOB (discussed on another tab)
Calculate the MAP (mean arterial pressure):
BP = 83/50
What is SBP + 2(DBP) / 3
83 + 50(2) / 3
83 + 100 / 3
183/3
MAP = 61 mmHg
This is a type of VTach
Name this rhythm and the tx:
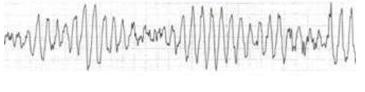
What is Torsades de pointes
Tx:
Treat like VTach, but also must give mag sulfate 4 gm
This is what defibrillation treats (2)
What are:
1. VFib
2. Pulseless VTach
Define defibrillation and how to perform (2)
What is:
1. Attempt to repolarize the heart and have the SA node resume the pacemaker role
2. Apply shock pads and ECG leads, turn OFF the sync button
This is used to treat adenosine OD (3)
What are:
1. Defibrillation
2. Vasopressor for hypotension
3. Theophylline
What is radiofrequency catheter ablation
Adenosine has drug interactions with these (5)
What are:
1. Caffeine
2. Carbamazepine
3. Dipyridamole
4. Guarana
5. Theophylline
Antiarrhythmic; used in PSVT; slows conduction thru the AV node and can interrupt reentry pathways thru AV node; decreases cardiac O2 demand, which decreases hypoxia
What is adenosine
Teach patients to report these symptoms when given adenosine (5; these symptoms are usually transient)
What are:
1. Facial flushing
2. Dizziness
3. Sweating
4. Palpitations
5. Chest pain
These are common side effects that are NOT emergent when given adenosine
What are:
1. Headache
2. Nausea
3. Vomiting
4. Tingling in arms
5. Numbness
No impulse from SA to AV node, complete heart block; both nodes contracting independently
Name this rhythm and the tx:
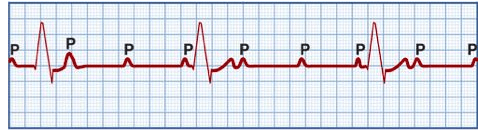
What is 3rd degree AV block
Tx:
1. Pacemaker
2. Dopamine
3. Epi
HR 150-220, normal or abnormal rhythm.
Symptons: Prolonged HR > 180 causes decreased CO, hypotension, palpitations, dyspnea, angina
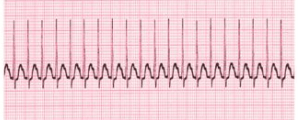
What is SVT
Tx:
1. Valsalva maneuver
2. Carotid massage
3. Coughing
4. Adenosine (regular rhythm)
5. If irregular, adenosine unsuccessful, or hemodynamically unstable, synchronized cardioversion
6. BB
7. CCB
Prolonged signal from SA to AV node; gradual lengthening of PR interval followed by a dropped QRS complex; P waves are normal; associated with ischemia; generally transient and well-tolerated
Name this rhythm and tx
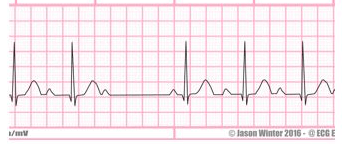
2nd degree AV block type I (Mobitz I or Wenckebach)
Tx (if pt symptomatic):
1. Atropine to increase HR
2. Temp pacemaker
Conduction from SA to AV node is prolonged; prolonged PR (> 0.20)
Name this rhythm and the tx
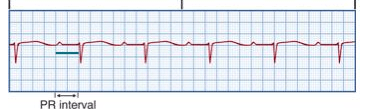
What is 1st degree AV block
Tx: None needed, just observe
Most common clinically significant dysrhythmia, not a medical emrg. Total disorgan. of atrial electrical activity because of multiple ectopic foci resulting in loss of effective atrial contraction. P waves barely discernible. Atrial = wavy or coarse baseline
Name the rhythm and the tx
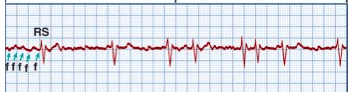
What is AFib
Tx:
1. Coumadin to reduce clot risk
2. CCBs
3. BBs
4. Dig to control rate
5. Dronaderone
6. If symptomatic but not responding to therapy - ablation
Dropped QRS complex WITHOUT PR lengthening; block in bundle branches; P waves are normal
Name the rhythm and the tx:
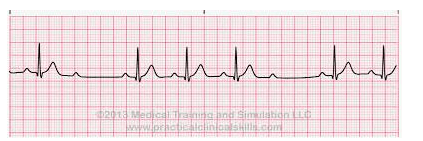
Tx: Pacemaker
3 or more PVCs; ventricle takes control as pacer; life-threatening dysrhythmia
Name these rhythms and the txs:
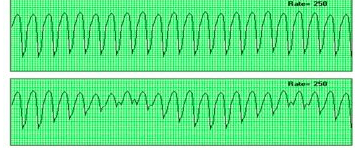
What is VTach:
1. Monomorphic
2. Polymorphic
Tx:
1. WITH a pulse = amiodarone and cardioversion
2. Pulseless = CPR and defibrillation
These are the late signs of IWOB (5)
1. Pursed-lip breathing
2. Pt. only able to speak 2-3 words, needing to take a breath (signs of dyspnea)
3. Chest retractions (inward moving of the intercostal spaces or supraclavicular area and accessory muscle use)
4. Paradoxical breathing indicates severe distress
5. If pt. has to sit up to breathe
HR < 60, normal rhythm
Symptoms of fatigue, dizziness, chest pain, syncope, pale/cool skin, hypotension, weakness, confusion, disorientation
Name the rhythm and the tx
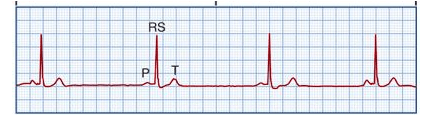
What is sinus brady; what is:
Tx:
1. Atropine
2. Pacemaker
3. Medication evaluation/discontinuation
HR > 100, normal rhythm
Symptoms include dizziness, dyspnea, hypotension (decreased CO), angina
Name this rhythm and the tx
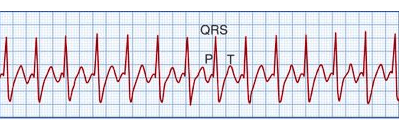
What is sinus tach
1. Treat cause
2. Vagal maneuvers
3. BBs
4. CCs
5. Adenosine
6. If clinically unstable use synchronized cardioversion
Distorted P wave, irregular rhythm, contraction starts from ectopic focus in atrium causing it to fire a 2nd time
Symptoms: Palpitations
Name this rhythm and tx
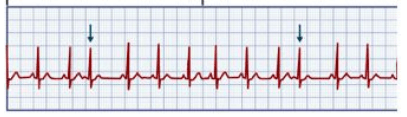
What are PACs
Palpitations - Isolated PACs are not concerning; repeated PACs could be problematic
Tx:
1. Withdrawal of stimulation source (caffeine, sympathomimetic drugs)
2. If severe, administer BB to decrease PACs