At what level of hemoglobin do you usually transfuse blood?
7g/dL
How many thoracic vertebrae are there?
12
Type 1 diabetics typically have the following clinical characteristics:
A. Thin, young with ketones present in the urine
B. Overweight, young with no ketones present in the urine
C. Thin, older adult with glycosuria
D. Overweight, adult-aged with ketones present in the urine
A: Thin, young with ketones present in the urine
A patient is being admitted with Folic acid deficiency anemia. Which would be the most appropriate referral?
A.Alcoholics anonymous
B.Leukemia society of America
C.A hematologist
D.A social worker
Alcoholics Anonymous
Chronic alcohol consumption leads to deficiency of folic acid due to their dietary inadequacy, intestinal malabsorption, decreased hepatic uptake and increased body excretion, mainly via urine. The decreased concentration of serum folic acid may occur in 80% of alcoholics.
What is the definition of orthostatic hypotension?
Orthostatic hypotension is defined as a decrease in systolic blood pressure of 20 mm Hg or a decrease in diastolic blood pressure of 10 mm Hg within three minutes of standing when compared with blood pressure from the sitting or supine position.
**It results from an inadequate physiologic response to postural changes in blood pressure. Orthostatic hypotension may be acute or chronic, as well as symptomatic or asymptomatic.**
3. A patient with diabetes has a morning glucose of 50. The patient is sweaty, cold, and clammy. Which of the following nursing interventions is the MOST important?
A. Recheck the glucose level
B. Give the patient ½ cup (4 oz) of fruit juice
C. Call the doctor
D. Keep the patient nothing by mouth
B. Give the patient ½ cup (4 oz) of fruit juice
A patient is admitted with iron- deficiency anemia and has been receiving iron supplementation. The patient voices concern about how their stool is dark black. As the nurse, you would?
Reassure the patient this is a normal side effect of iron supplementation
What joints are commonly affected by osteoarthritis?
Hands
Knees
Hips
A nurse is preparing a plan of care for a client with diabetes mellitus who has hyperglycemia. The priority nursing diagnosis would be:
A. High risk for deficient fluid volume
B. Deficient knowledge: disease process and treatment
C. Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements
D. Disabled family coping: compromised
A. High risk for deficient fluid volume
Why?
Increased blood glucose will cause the kidneys to excrete the glucose on the urine. This glucose is accompanied by fluids and electrolytes, causing osmotic diuresis leading to dehydration. This fluid loss must be replaced when it becomes severe.
You are providing diet teaching to a patient with low iron levels. Name some foods you would encourage the patient to eat regularly?
Egg yolks
Beef
Legumes
Shellfish
Spinach
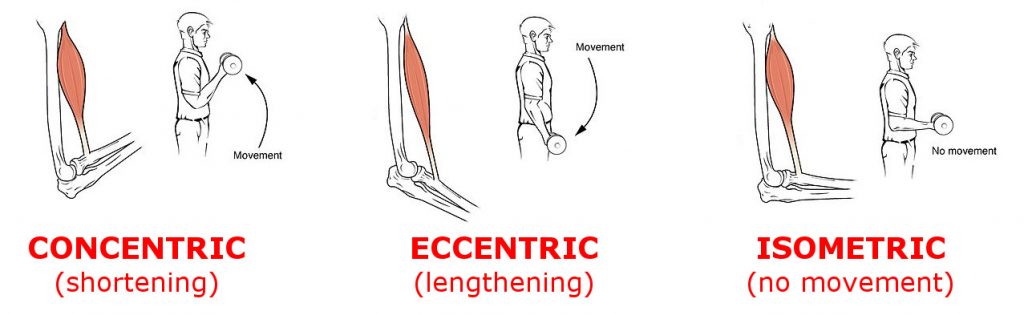
Explain the difference between concentric and eccentric movements.
A nurse is caring for a client admitted to the ER with DKA. In the acute phase the priority nursing action is to prepare to:
A. Administer regular insulin intravenously
B. Administer 5% dextrose intravenously
C. Correct the acidosis
D. Apply an electrocardiogram monitor
Administer regular insulin intravenously
Lack (absolute or relative) of insulin is the primary cause of DK1. Intravenous insulin by continuous infusion is the standard of care. A more recent prospective randomized trial demonstrated that a bolus is not necessary if patients are given hourly insulin infusion at 0.14 U/kg/hr.
Fe is absorbed in the
Stomach
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
Duodenum
What are the three posterior hip precautions a patient has to follow post THA (posterior approach)?
1. Don't bend your hip more than 90 degrees
2. Don't cross your legs
3. Don't point toes or knees inward
**Pt should do this for 90 days post-op**
7. Which of the following statements are true regarding Type 2 diabetes treatment?
A. Insulin and oral diabetic medications are administered routinely in the treatment of Type 2 diabetes.
B. Insulin may be needed during times of surgery or illness.
C. Insulin is never taken by the Type 2 diabetic.
D. Oral medications are the first line of treatment for newly diagnosed Type 2 diabetics.
B. Insulin may be needed during times of surgery or illness.