Can be life threatening, with symptoms of rapid heart rate, low blood pressure, dyspnea, bronchial edema, and angioedema.
What is anaphylaxis?
The disease process that this photo represents.
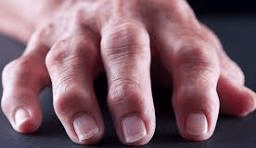
What is osteoarthritis?
The most common disorder of the vein.
What is a venous thrombosis?
Name two risks for decreased wound healing.
Name the three burn phases of recovery.
What is emergent, acute, and rehabilitation phases.
The physical manifestations of a transient wheal (pink, raised, edematous, that vary in size and shape hat may occur on the body in response to a systemic allergen.
What is urticaria?
The disease process that this photo represents.
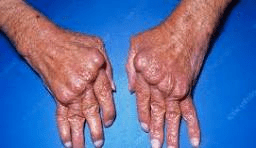
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
Name four signs and symptoms of DVT.
What are unilateral leg edema, pain, tenderness, with palpation, dilated superficial veins, a sense of fullness to the calf, parensthesia, warm skin, erythema, or systemic temperature above 8c.
Identify the skin lesion.
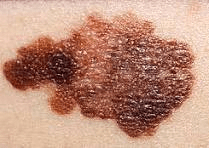
What is Melanoma?
Name two criteria that meets the diagnosis for major burn.
What is 10% of BSA of full thickness burns and 25% of partial thickness burn, over age 60, presence of chronic cardiac or pulmonary disorder, and endocrine disorder, presence of electrical burn, presence of inhalation burn, or burn to eyes, ears, face, hands, feet or perineum.
The type of isolation is used to prevent the spread of organisms by cough, talking, and sneezing.
What is droplet precautions?
RA is systemic. Name three other structures that can have their connective tissue affected.
What is blood vessels, pleura, pericardium, iris, and sclera.
Name four nursing measures to prevent DVT.
What is turn and reposition every two hours, passive range of motion with flex and extension of the feet, early ambulation, graduated compression socks, anticoagulants.
Name the test that comprises of the isolation of a pathogen on a plate and the testing of the effects of antimicrobial agents on the noted organism.
What is culture and sensitivity?
The name for continuous leakage of plasma from the vascular space into the interstitial space, which results in electrolyte imbalance and hypotension.
What is third spacing or capillary leak syndrome.
Presenting signs include abdominal pain, rebound tenderness, muscle rigidity, shallow breaths, fever, tachycardia, tachypnea, nausea/vomiting, and altered bowel habits?
What is peritonitis?
The procedure of aspiration of synovial fluid with a needle from the effected joint that is evaluated for WBC and sent for culture.
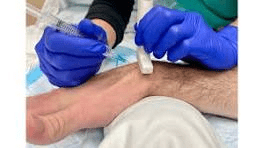
What is arthrocentesis?
A low molecular weight weight heparin (LMWH) used subcutaneously that does not require routine blood testing and has an antidote of protamine sulfate.
What is enoxaparin (Lovenox).
This name of this condition.
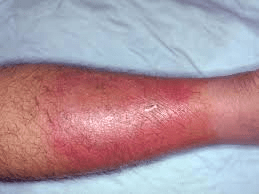
What is cellulitis?
Name four signs of burn shock or hypovolemic shock in burn patients.
Confusion, increased capillary refill time, decreaed urine output <0.5mg/kg/hr, rapid increase in temperature, decreased bowel sounds, low blood pressure, increased heart rate.
The blood protein made in response to an antigen.
What is an antibody?
A medication that is commonly given to patients with arthritis. However, they are not given long term dosing secondary to risk of osteoarthritis, hyperglycemia, immunosuppression, and cataract formation.
What is a corticosteroid or prednisone.
The word embolism is derived from the Greek word meaning this.
What is plug or stopper?
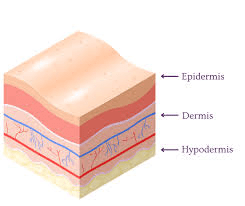
Name the three layers of skin in the correct order from superficial to deep.
What is the epidermis, dermis, and hypo-dermis.
This procedure is the incision that relieves pressure from the constricting forces of fluid buildup under the circumferential burns on the extremities or chest and improves circulation.
What is escarotomy?