Patients with chronic COPD usually have a higher level of this compound.
What is carbon dioxide?
f/u question
This is the dose of oxygen delivered via nasal cannula at 5 lpm.
What is 40%?
If it sounds like a seal…it’s this.
What is croup?
The heart’s ability to generate electrical impulses.
What is automaticity?
Left ventricular failure leads to left atrial enlargement, which leads to this sound.
What are rales?
Healthy people’s drive to breathe is called this.
What is the hypercarbic drive?
Paradoxical movement in the chest may indicate this.
What is a flail chest?
Aside from taking their meds, a pink puffer does these two things to help them breathe.
What are tripod position and pursed-lip breathing?
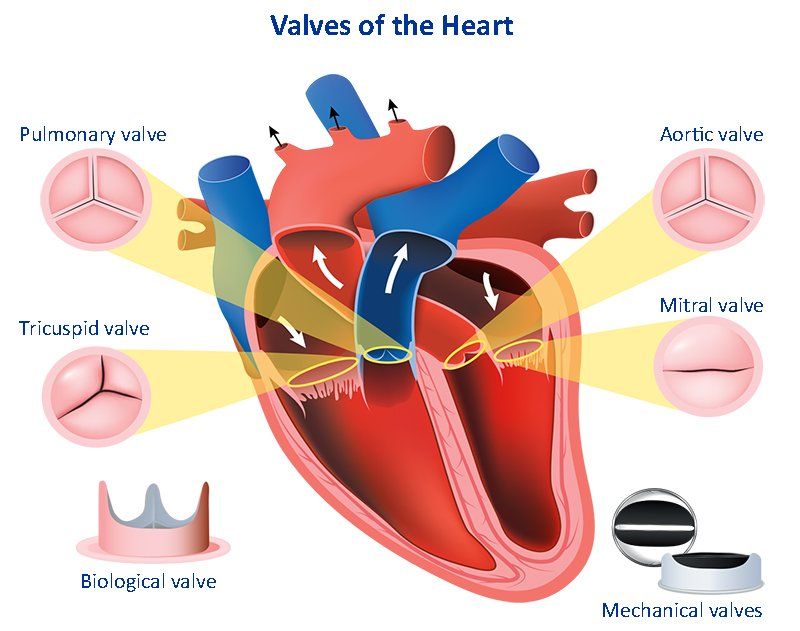
As blood leaves the right atrium, it passes through this valve.
What is the tricuspid valve?
This type of chest pain often occurs during periods of physical or emotional stress.
What is angina pectoris?
Set the O2 regulator to at least this when using a NRB on a patient breathing 500ml per breath and 16 breaths per minute.
What is 10 lpm?
16 x 500 = minute volume of 8,000 ml per min. Add some extra.
When suctioning the mouth of an infant, the strength of the device should not exceed this.
What is 80-120 mmHg?
A combination of fatigue, dizziness, SOB, chest tightness, numbness in hands / feet / around the mouth, tachypnea, tachycardia, carpopedal spasms are indicative of this condition.
What is hyperventilation syndrome?
f/u question
This is when there is a tear in the aorta’s tunica intima and blood separates the layers.
What is an aortic dissection?
Skill – determine someone’s BP using their popliteal artery.
Were they correct?
The best place to auscultate the right middle lobe is located here.
What is the mid-clavicular line at the level of the 4th or 5th ICS?
f/u question
Increased resistance while using a BVM may indicate this condition.
What is gastric insufflation?
A fairly rapid onset of severe dyspnea, drooling, high-pitched stridor, and decreased O2 sats are indicative of this condition which is usually found in children ages 3-6 years.
What is epiglottitis?
Pedal edema, ascites, and JVD can be caused by this.
What is right-sided heart failure?
The locations of the 3 main pacemakers in the heart are these (in order).
What are the SA node, the AV node and the Perkinje Fibers?
This device improves heart rate and BP, reduces the sympathetic tone, reduces afterload and myocardial workload.
What is CPAP?
These are 3 of the contraindications for using CPAP.
What are:
- Apnea
- Can’t follow commands
- Can’t maintain their own airway
- Unresponsiveness
- Only responds to verbal or painful stimuli
- Cardiac arrest
- Needs frequent suctioning
Symptoms include prolonged coughing sessions to yak out the phlegm, this can decrease O2 Sat, poor alveolar gas exchange, and promote bacterial pneumonia.
What is pertussis or whooping cough?
Skill – Find a skinny person and count their heartrate by feeling their abdominal aorta.
Were they correct?
The Bachmann bundle connects these two areas.
What are the right and left atria?