A client with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome will be admitted to the medical unit. Which intervention will the nurse include in the client’s nursing plan of care?
a. Performing a urine test for ketones every morning before breakfast
b. Performing perineal care with warm water and applying a moisture barrier twice daily
c. Assessing the abdomen for fluid wave and shifting dullness every 8 hours and PRN
d. Keeping 2 units of packed red blood cells on hold, transfusing if hemoglobin <8 g/dL
ANS: B
Clients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome often experience severe diarrhea and steatorrhea, so the nurse should include careful perineal care in the plan of care. Abdominal fluid wave testing and shifting dullness checks for ascites, which is not seen with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. The client’s physician is responsible for ordering transfusion of blood, not the nurse.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Application
TOP: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity (Basic Care and Comfort)
MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Planning)
To promote self-care, the nurse is planning to teach a client in skeletal leg traction about measures to increase bed mobility. Which item is most helpful for this client for achievement of this goal?
A. Fracture bedpan
B. Overhead trapeze
C. Isometric exercises
D. Range-of-motion exercises
ANS: B
Rationale:
The use of an overhead trapeze is extremely helpful for assisting a client with moving about in bed and getting on and off the bedpan. This device has the greatest value for increasing overall bed mobility. A fracture bedpan is useful for reducing discomfort with elimination. Isometric exercises will not increase bed mobility and could be harmful for a client in skeletal traction. Range-of-motion exercises can also be harmful to a client in skeletal traction and should not be initiated unless there are specific prescriptions to do so.
Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance
Cognitive Ability: Applying
Content Area: Skills: Activity/Mobility
Health Problem: Adult Health: Musculoskeletal: Skeletal Injury
Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Planning
Priority Concepts: Mobility, Safety
Strategy(ies): Strategic Words, Subject
an invasive method used for intravenous therapies lasting from 1 to 4 weeks
What is a Midline Cathether
Midline catheters are used for therapies lasting from 1 to 4 weeks. Short peripheral catheters can be inserted by the nurse to use for antibiotic therapy, but can only stay in for up to 96 hours. If the length of intravenous therapy is longer than 6 days, a midline catheter should be chosen. Nontunneled central catheters and Hickman catheters are inserted by a physician.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension REF: p. 217
OBJ: Learning Outcome 7
TOP: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity (Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies)
Which of the following statements indicate that the client needs further information regarding advance directives?
a. “Having a living will can prevent my children from putting me in a nursing home.”
b. “I can decide who will make health care decisions for me if I write a Durable Power of Attorney.”
c. “A living will means that my family will know what life-sustaining measures I want taken.”
d. “Advance directives should be completed long before a medical crisis develops.”
ANS: A
A living will is a legal document that instructs physicians and family members about what life-sustaining treatment a person does or does not want at some future time if he or she becomes unable to make decisions. The living will does not address care issues such as nursing homes.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension
TOP: Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment (Management of Care)
MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Assessment)
Also known as "wet lungs", the symptoms often include:
- Difficulty in breathing
- Fast breathing
- Muscle fatigue and weakness
- Decreased blood pressure
- Discoloration in skin or nails
- Cough
- Fever
- Headaches
- A fast heart rate
- Mental confusion
What is ARDS (acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
The nurse suspects a colleague of diverting narcotics for personal use. Which intervention will the nurse implement first?
a.Discusses suspicions with the colleague in question
b.Reports suspicions to the nursing supervisor
c.Begins documenting colleague’s actions
d.Reports suspicions to the board of nursing
ANS: B (p. 17 - F. 1 Impaired coworker)
The nurse should report suspicious behavior to the board of nursing. The nurse [can then] report what has occurred to the nursing supervisor. It is not the nurse’s responsibility to document a colleague’s actions, nor should the nurse confront the colleague. Legally, there is no place for the nurse to document the colleague’s actions. The nurse may not be equipped to handle a confrontation of this nature. This is better left to a supervisor or someone in an authority position who has the resources to assist the nurse.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Application TOP: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity (Basic Care and Comfort)
MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Assessment)
During electroencephalography, the client is instructed to breathe deeply (hyperventilate). What is the nurse’s interpretation of this action?
a. Seizure activity may be increased because of cerebral vasodilation associated with hyperventilation.
b. Seizure activity may be increased because of cerebral vasoconstriction secondary to hyperventilation.
c. Seizure threshold is lowered by acidosis associated with hyperventilation.
d. Seizure threshold is lowered by hypoxemia associated with hyperventilation.
ANS: B
Hyperventilation produces cerebral vasoconstriction and alkalosis, which increases the likelihood of seizure activity. The client is asked to breathe deeply 20 to 30 times for 3 minutes.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Application
TOP: Client Needs Category: Health Promotion and Maintenance (Health Screening)
MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Analysis)
Which IV order would the nurse question?
a.Flush Groshong catheter with 10 mL normal saline every 8 hours
b.Infuse 20 mEq potassium chloride in 1000 mL D5W at 50 mL/hr
c.Infuse 500 mL normal saline over 1 hour
d.Infuse 0.9% normal saline at keep vein open (KVO) rate
ANS: D
To be complete, IV orders for infusion fluids should specify the rate of infusion. This order does not specify the rate of infusion and is not considered complete.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Application
OBJ: Learning Outcome 1
TOP: Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment (Safety and Infection Control) MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Analysis)
A client has been transferred to the postanesthesia care unit (PACU). Which action does the receiving nurse perform first?
A. Complete a nursing assessment sheet.
B. Change the client’s arm band.
C. Enter client data into the computer.
D. Participate in a hand-off report.
Correct Answer: D
Explanation/Rationale:
ANS:D
After the surgery is completed, the circulating nurse and the anesthesia provider accompany the client to the PACU. A hand-off report that meets National Patient Safety Goal 2 requires effective communication between health care professionals.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher
TOP: Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment (Management of Care-Continuity of Care)
When working with a patient who has diabetes mellitus, the nurse reviews the results of testing for glycosylated hemoglobin (Hb A1C) to evaluate for
a. glucose levels 2 hours after a meal.
b. glucose control over the past 3 months.
c. circulating, nonfasting glucose levels.
d.hypoglycemic episodes in the past 90 days.
Correct Answer: B
Rationale: Glycosylated hemoglobin testing measures glucose control over the last 3 months. Glucose testing after a meal or random testing may reveal impaired glucose tolerance and indicate prediabetes, but it is not done on patients who already have a diagnosis of diabetes. There is no test to evaluate for hypoglycemic episodes in the past.
Cognitive Level: Application
Nursing Process: Assessment
NCLEX: Physiological Integrity
What interventions will help an older adult client adjust to being admitted to a skilled nursing facility following surgery? (Select all that apply.)
a. Make sure that she has her hearing aid and glasses.
b. Offer her the anxiolytic that her physician has prescribed.
c. Encourage her family to bring in her favorite pictures.
d. Ask her where she wants the room furnishings placed.
e. Encourage her to eat meals in her room.
f. Invite her to group activities.
ANS: A, C, D
An anxiolytic may increase the difficulty that the client has in interpreting her surroundings. Making sure that she can see and hear will help the environmental interpretation, familiar possessions will provide a sense of identity, and having some input into the organization of her immediate surroundings helps develop a sense of control.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension
TOP: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity (Basic Care and Comfort)
MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Planning)
Which statement indicates that the client has an accurate understanding of a scheduled brain scan?
a.“After the injection, it will take 2 hours for my brain to absorb the isotope.”
b.“I will have an oral airway placed whenever I have a seizure.”
c.“I will be asked to change positions during the course of the test.”
d.“I will be asked to hyperventilate for 15 seconds.”
ANS: A
The client receives an injection of a radioactive isotope for this test. There is a 2-hour delay in the test while the brain absorbs the isotope.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Application
TOP: Client Needs Category: Health Promotion and Maintenance (Health Screening)
MSC: Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning
If the client is to receive the entire 250-mL bag of saline over the next 4 hours and the drop rate of the IV tubing chamber is 15 drops/mL, at what drop rate per minute will the nurse set this IV? ____________ drops/min
what is 16
volume / total minutes x drip factor
250/240 x 15 = 15.625 = 16 (rounded to whole number)
DIF: Cognitive Level: Application REF: N/A for Application and above
OBJ: Learning Outcome 9
TOP: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity (Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies) MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Implementation)
When is the nurse correct in decreasing the dose of pain medication in a client with end-stage cancer?
a. The spouse is worried that the client may become addicted.
b. The client wants to remain alert during the visit of a long time friend.
c. The client has lost considerable weight and does not want to eat.
d. The client is becoming combative at night.
ANS: B
The client has the right to choose whether or not to take the pain medication. The analgesic regimen should not interfere with the client’s sleep, rest, appetite, level of physical mobility, or driving ability. Close relationships are important factors in providing ongoing support for effective pain management intervention.
TOP: Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment (Management of Care)
MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Implementation)
Which nursing diagnosis is appropriate for a woman who abuses anabolic steroids and has begun to experience side effects from the medication?
a.Risk for Injury related to decreased muscle coordination
b.Hypothermia related to decreased metabolic rate
c.Chronic Confusion related to sodium and water retention
d.Disturbed Body Image related to presence of facial hair
ANS: D
The use of anabolic steroids (testosterone) in women causes the physical changes of growth of facial hair, male pattern baldness, deepened voice, and changes in menstrual patterns. The other nursing diagnoses would not be as applicable.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension
TOP: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity (Physiological Adaptation)
MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Analysis)
A client is about to undergo noninvasive temporary pacing (NTP). Which action is most appropriate for preparing this client for the procedure?
a. Apply alcohol to the skin before electrode placement.
b. Prepare the skin by washing it with soap and water.
c. Shave the area where electrodes will be placed.
d. Place the electrodes at the V1 position.
ANS: B
For NTP, the correct procedure is to wash the skin with soap and water. The skin should not be shaved, nor alcohol or tinctures applied, because these cause irritation when electrical current flows through the patches. The leads are placed on the client’s back and anterior chest between V2 and V5.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Application
Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity (Basic Care and Comfort)
MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Implementation)
In taking the history of a client suspected of having bacterial meningitis, which question is most important for the nurse to ask?
a. “Do you live in a crowded residence?”
b. “When was your last tetanus vaccination?”
c. “Have you had any viral infections recently?”
d. “Have you traveled out of the country in the last month?”
ANS: A
Meningococcal meningitis tends to occur in outbreaks. It is most likely to occur in areas of high-density population, such as college dormitories, prisons, and military barracks.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Application
TOP: Client Needs Category: Health Promotion and Maintenance (Health Screening)
MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Analysis)
What is Home IV therapy?
The emergency room nurse is caring for the following clients. Which client does the nurse prioritize to see first?
a. Blood pressure 100/60 mm Hg, right wrist painful and swollen
b. Complaining of chest pain and diaphoresis
c. Complaining of difficulty swallowing and nausea
d. Respiratory rate of 28/min and temperature of 101° F
ANS: B
A client experiencing chest pain and diaphoresis would be classified as emergent and triaged immediately to a treatment room in the emergency department.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Application
TOP: Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment (Management of Care)
MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Assessment)
A home care client who is currently on hydromorphone (Dilaudid) for pain management presents to the hospital complaining of abdominal cramping, nausea, and sweating. When taking the client’s history, the nurse should ask which question first?
a. “Are you in pain?”
b. “Did you take more Dilaudid than prescribed?”
c. “When did you take your last dose of Dilaudid?”
d. “When was your last bowel movement?”
ANS: C
Physical dependence occurs in everyone who takes opioids over a period of time. Withdrawal syndrome occurs when the client abruptly stops taking the medication. The symptoms include abdominal cramping, nausea, sweating, delirium, and convulsions. Although the other distractors may be asked as part of the admission assessment, they are not of priority.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Application REF: N/A for Application and above
TOP: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity (Physiological Adaptation)
MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Assessment)
After performing a physical assessment on an older adult client, the nurse notes that the client has a hypoactive response to a test of deep tendon reflexes. The nurse incorporates which intervention into the client’s plan of care?
a. Assisting the client with ambulation
b. Elevating the client’s lower extremities
c. Placing elastic support hose on the client
d. Massaging the client’s legs every 8 hours while he or she is awake
ANS: A
The older adult experiences certain neurologic changes associated with aging. Hypoactive deep tendon reflexes and loss of vibration sense can impair balance and coordination, predisposing the client to falls. The nurse or assistive personnel should assist this client with ambulation to prevent injury.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Application
TOP: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity (Basic Care and Comfort)
MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Implementation)
The nurse assesses for which predisposing factor for embolic stroke in the history of the client admitted to the hospital after having a brain attack?
a. Seizures
b. Psychotropic drug use
c. Atrial fibrillation
d. Cerebral aneurysm
ANS: C
Clients with a history of hypertension, heart disease, atrial fibrillation, diabetes, obesity, and hypercoagulopathy are at risk of embolic stroke.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Application
TOP: Client Needs Category: Health Promotion and Maintenance (Health Screening)
MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Assessment)
A nurse is preparing to administer mannitol (Osmitrol) to a client with a severe head injury. Which precaution will the nurse take before the administration of this medication?
a.Drawing up the medication using a filtered needle
b. Having injectable naloxone prepared and ready at the bedside
c.Preparing to hyperventilate the client before drug administration
d.Discontinuing a barbiturate-induced coma before drug administration
ANS: A
Mannitol (Osmitrol) must be drawn up using a filtered needle to eliminate microscopic crystals.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Application
TOP: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity (Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies) MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Implementation)
The nurse is alerted to a client’s telemetry monitor. After assessing the following ECG, what is the nurse’s priority intervention?
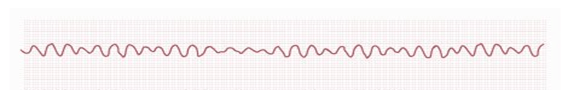
A. Start a large-bore IV.
B. Administer atropine.
C. Prepare for intubation.
D. Perform defibrillation.
- Correct Answer: D
Explanation/Rationale:
ANS:D
The client’s rhythm is ventricular fibrillation. This is a lethal rhythm that is best treated with immediate defibrillation. If the client does not already have an IV , other members of the team can insert one after defibrillation. Likewise, intubation can occur later if necessary. Atropine is not given for ventricular fibrillation.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher
How do the white blood cells know to respond at the site of injury?
a. Antibodies from damaged tissues attract the white blood cells to the site of injury.
b. Enzymes released from bacteria attract white blood cells to the site.
c. Histamine then filters white blood cells into the injured area.
d. Chemotaxins draw white blood cells to the area.
ANS: D
Cells near the injured area secrete certain chemicals called chemotaxins that attract other white blood cells to the area. Damaged cells would not release antibodies.
DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension
TOP: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity (Physiological Adaptation)
MSC: Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning