What are the functions of the skeletal system.
support, protection, mineral storage, blood cell formation, movement of muscles
the straightening of a limb after it has been bent
extension
movement of the sole of the foot upward
dorsiflexion
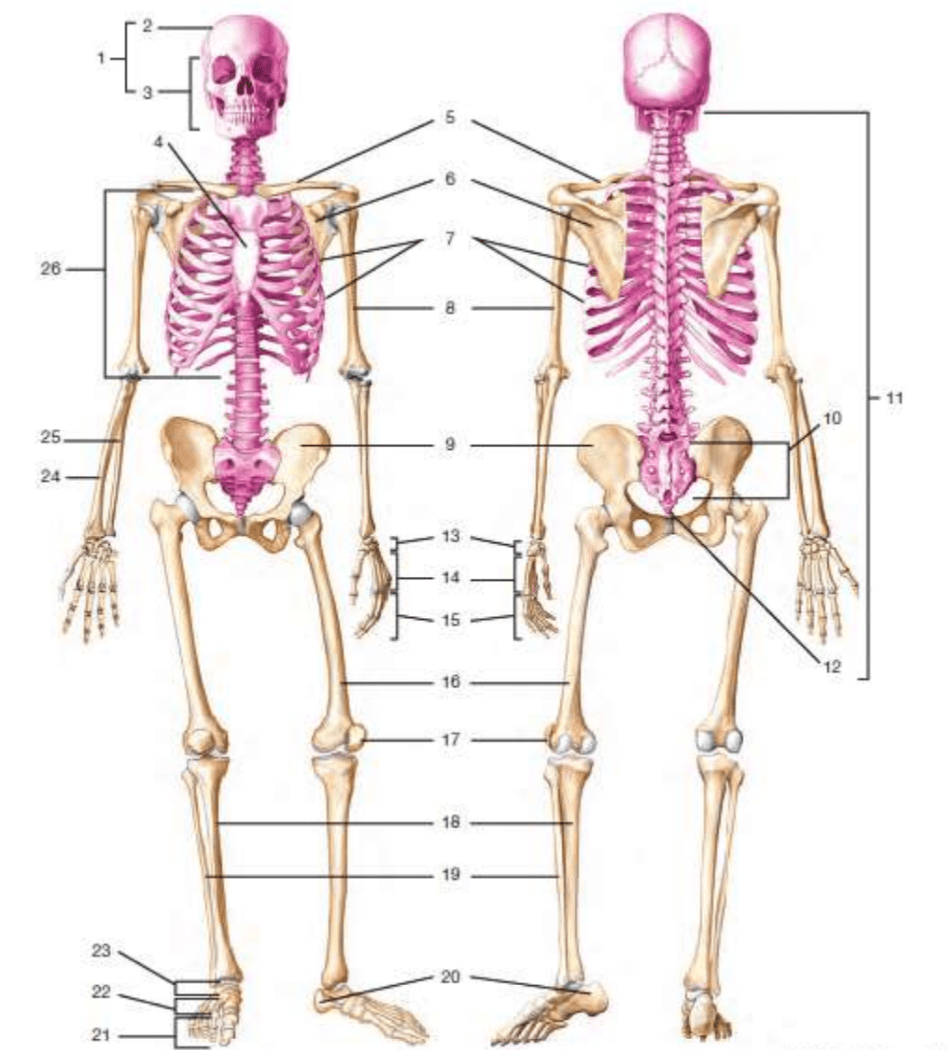
# 5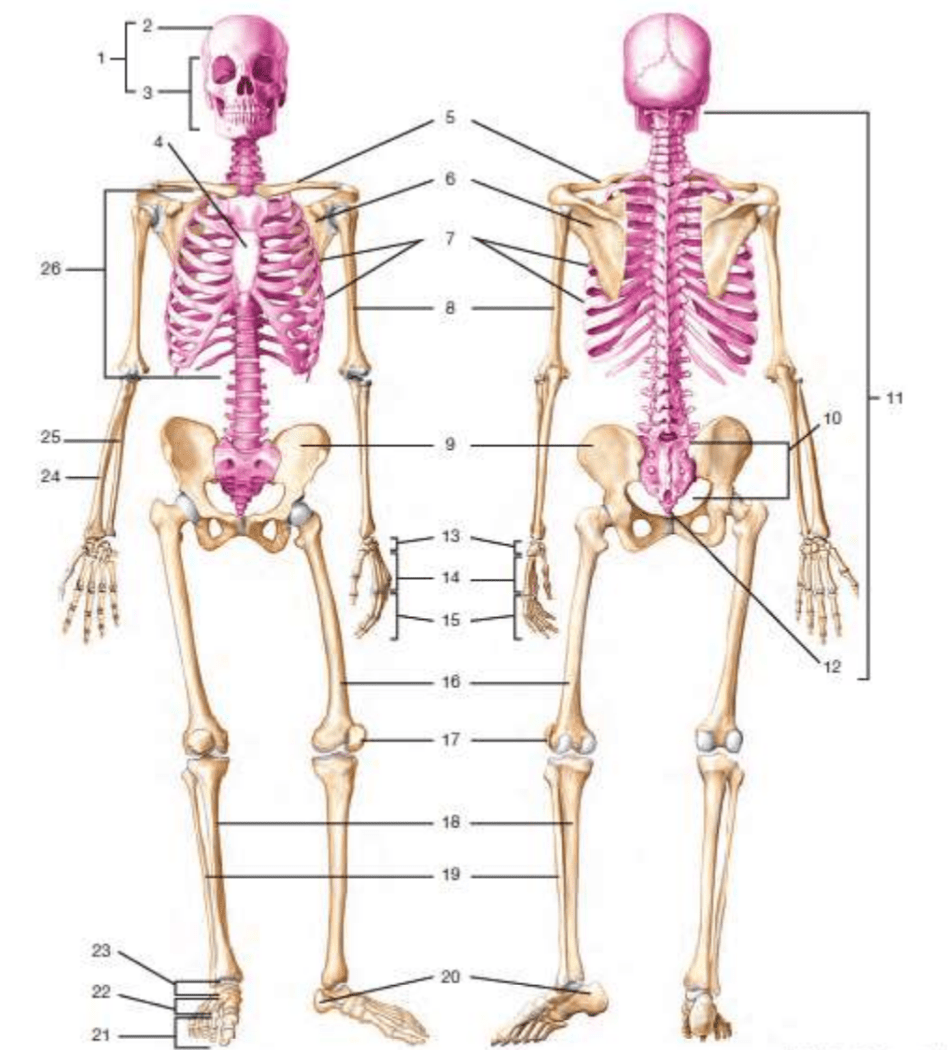
clavicle
#1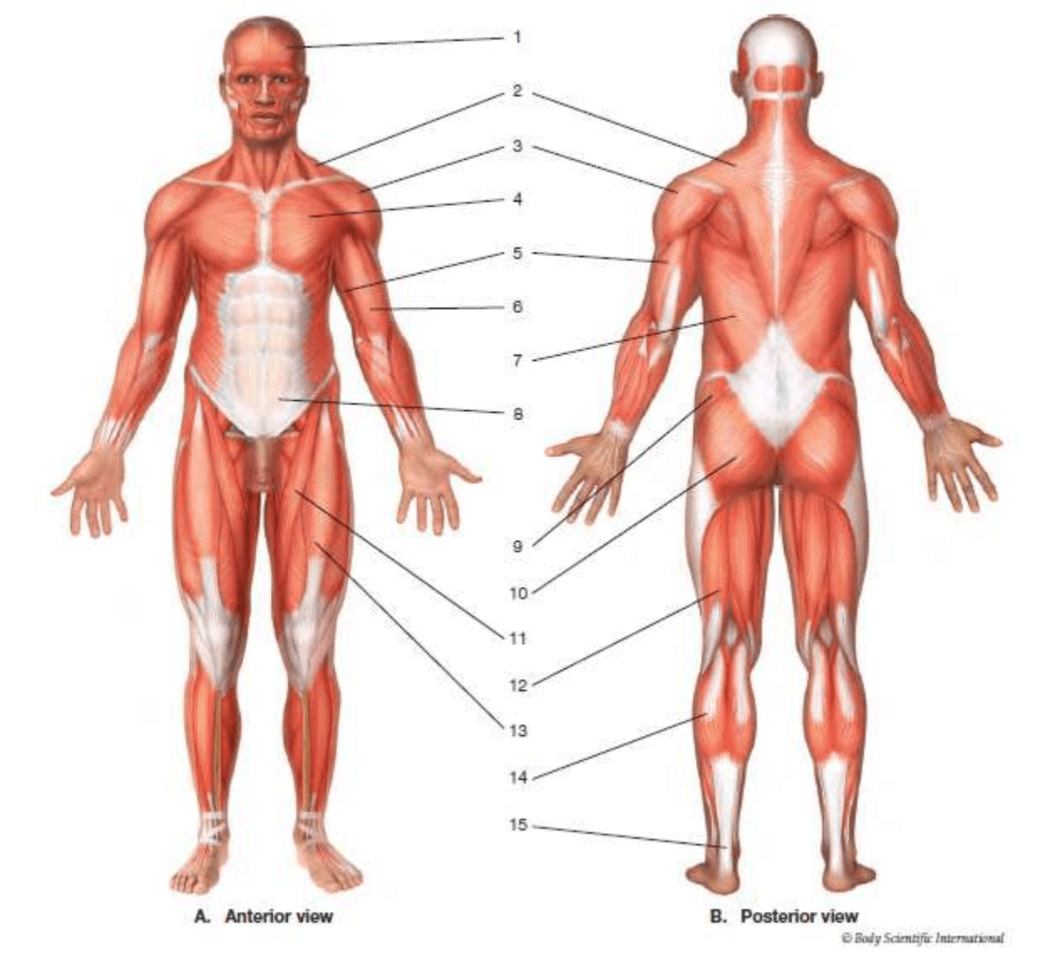
frontalis
partial dislocation of a bone from its joint
subluxation
inability to coordinate voluntary muscle activity
ataxia
#10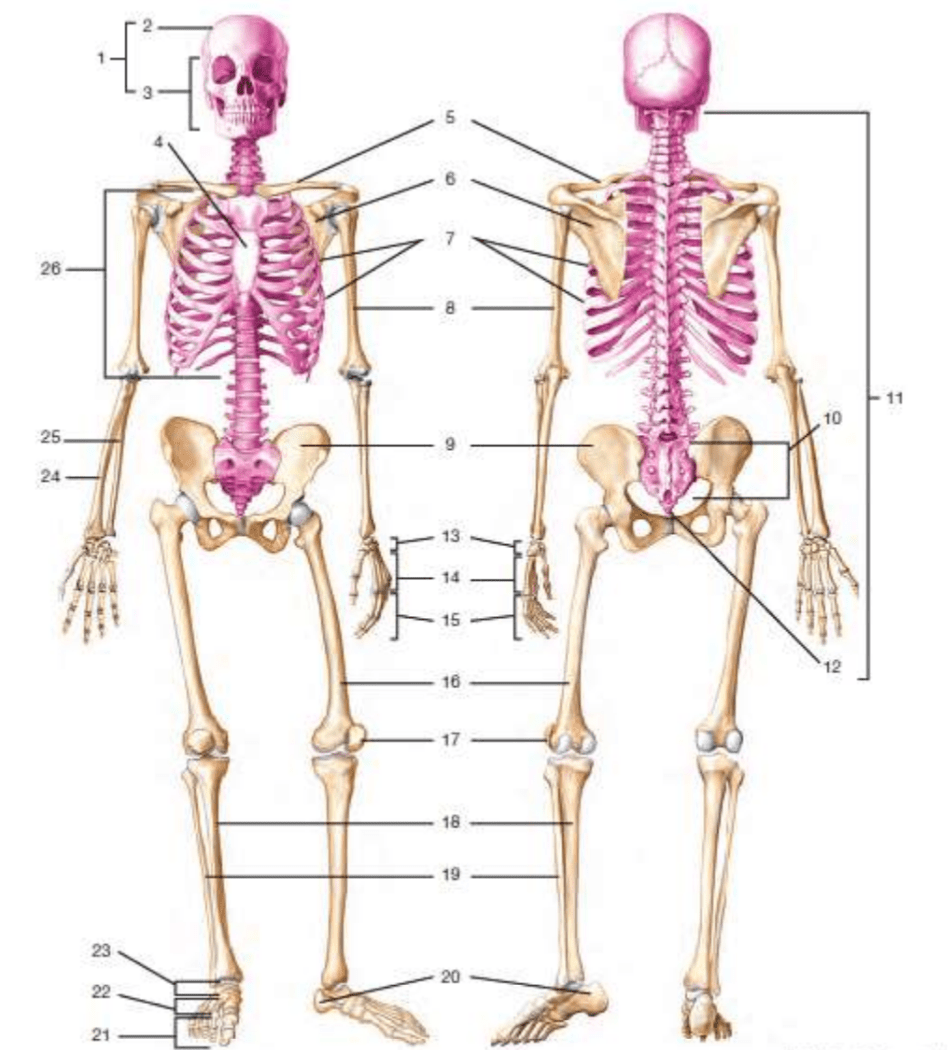
sacrum
What are the functions of muscles?
movement, producing body heat, aiding in blood flow, movement of food/fluids
the movement of two body surfaces toward each other
flexion
movement of body part toward the body
adduction
#8
humerus
#6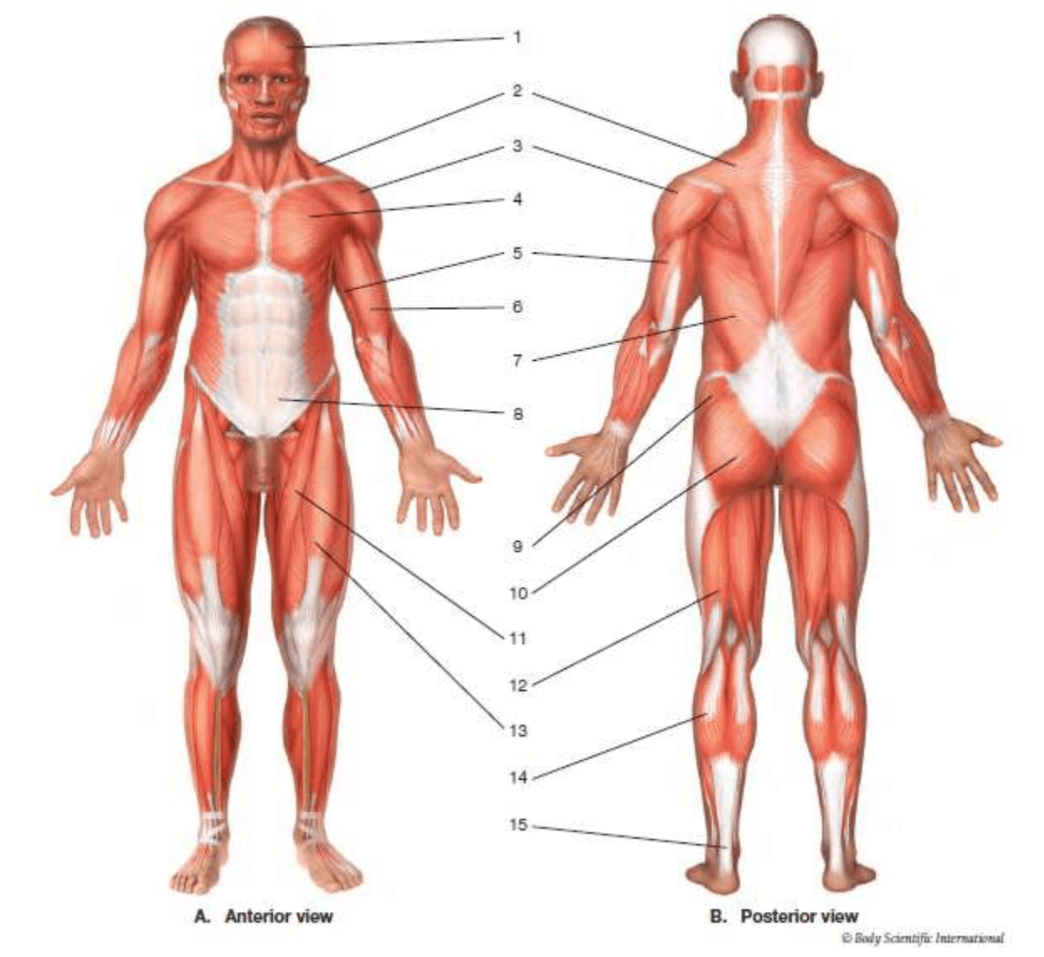
biceps brachii
cancer of the plasma cells that originates in the bone marrow
myeloma
weakness or slight paralysis on one side of the body
hemiparesis
# 17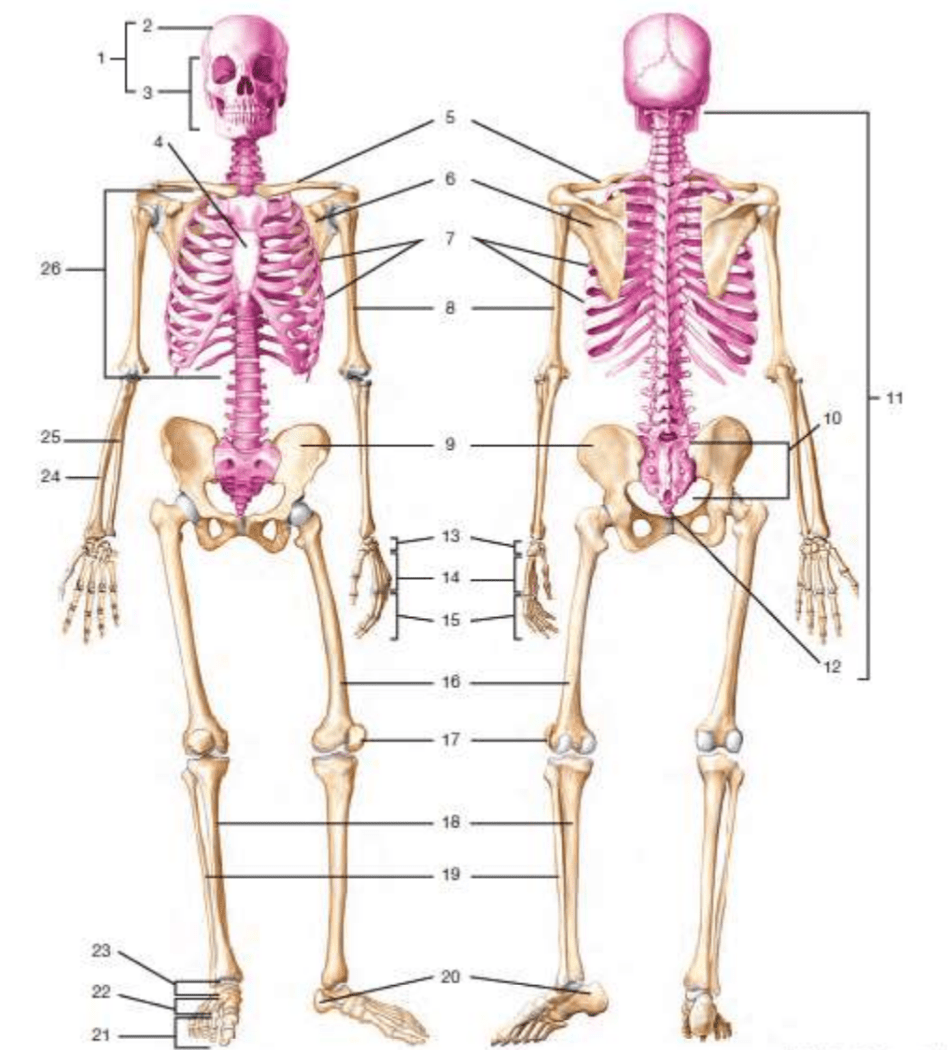
patella
Give an example of each of the following types of bone: long, short, flat, irregular, sesamoid.
answers will vary but must list one for each category
motion of the plantar surface away from the midline of the body
plantar flexion
Rotational motion of the forearm in which the palm moves to face downward
pronation
#11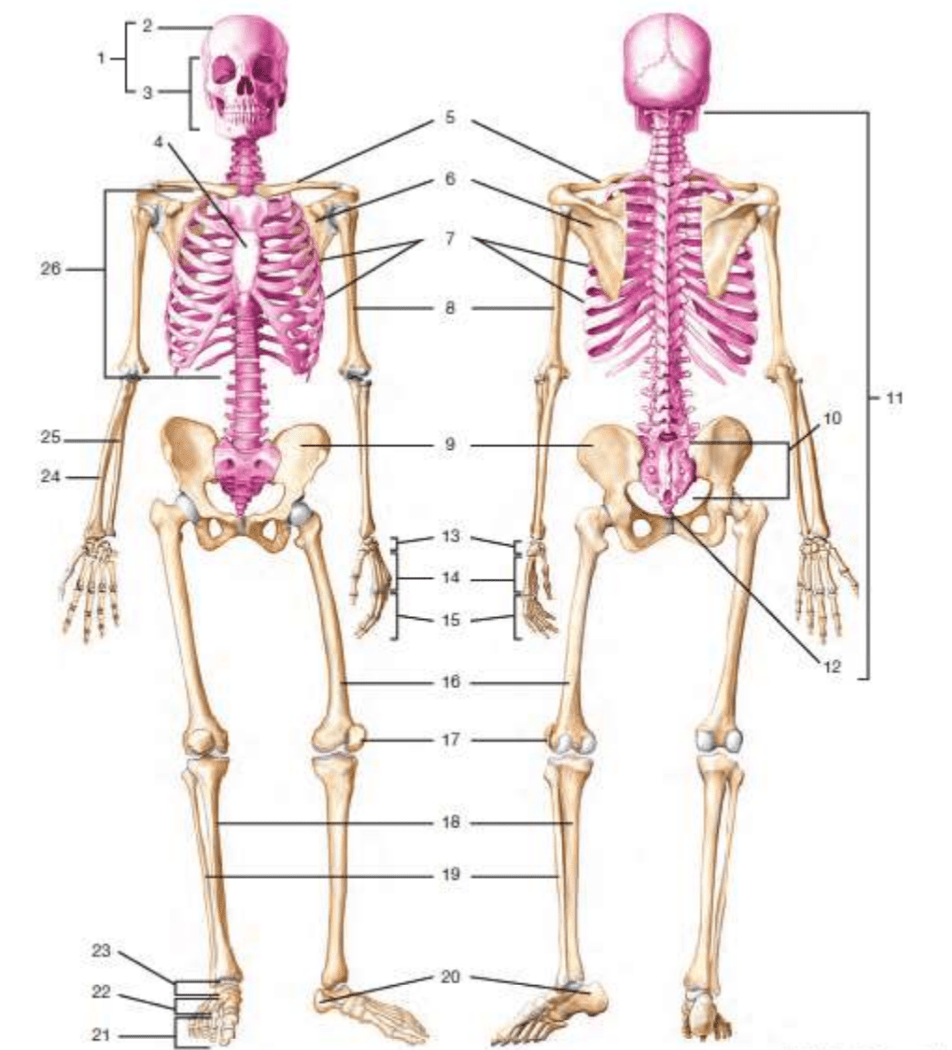
vertebral column/vertebrae
#11
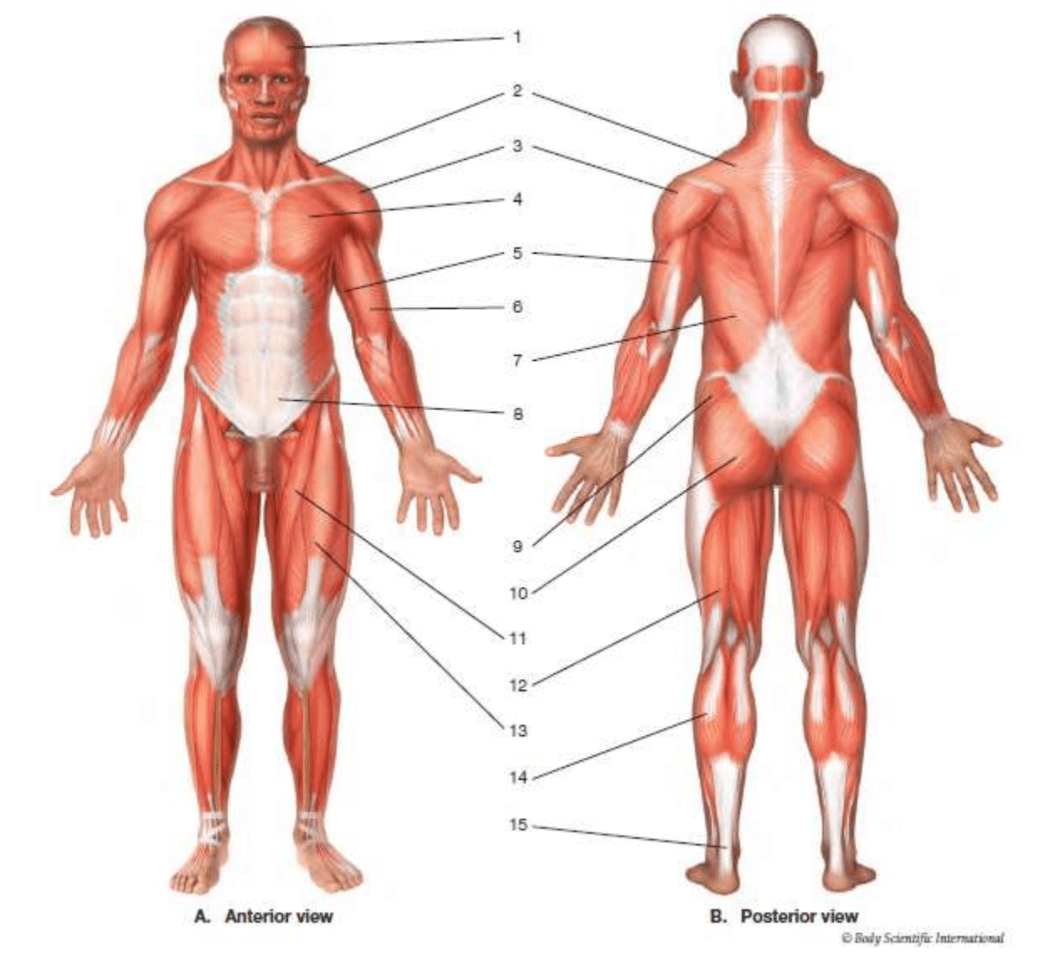
sartorius
form of arthritis in which uric acid builds up in the blood causing joint swelling
gout
total paralysis on one side of the body
hemiplegia
Explain the difference between the axial and appendicular skeleton.
The axial skeleton includes bones along the axis, while the appendicular skeleton
includes bones in the appendages, or extremities.
Explain the difference between origin and insertion.
Origin: attachment site for muscles that doesn't move
insertion: attachment site for muscles that does move
movement of body part away from the midline
abduction
rotation of an arm or leg
circumduction
#24
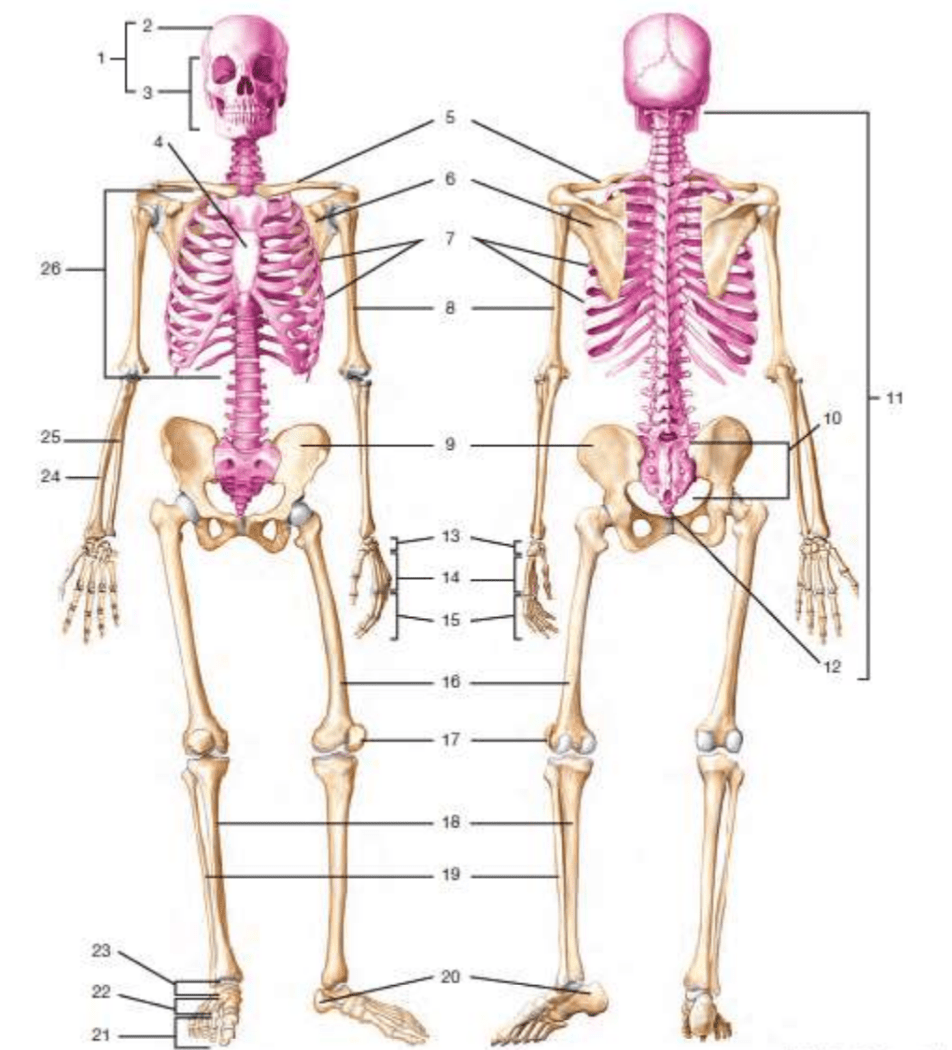
radius
#14
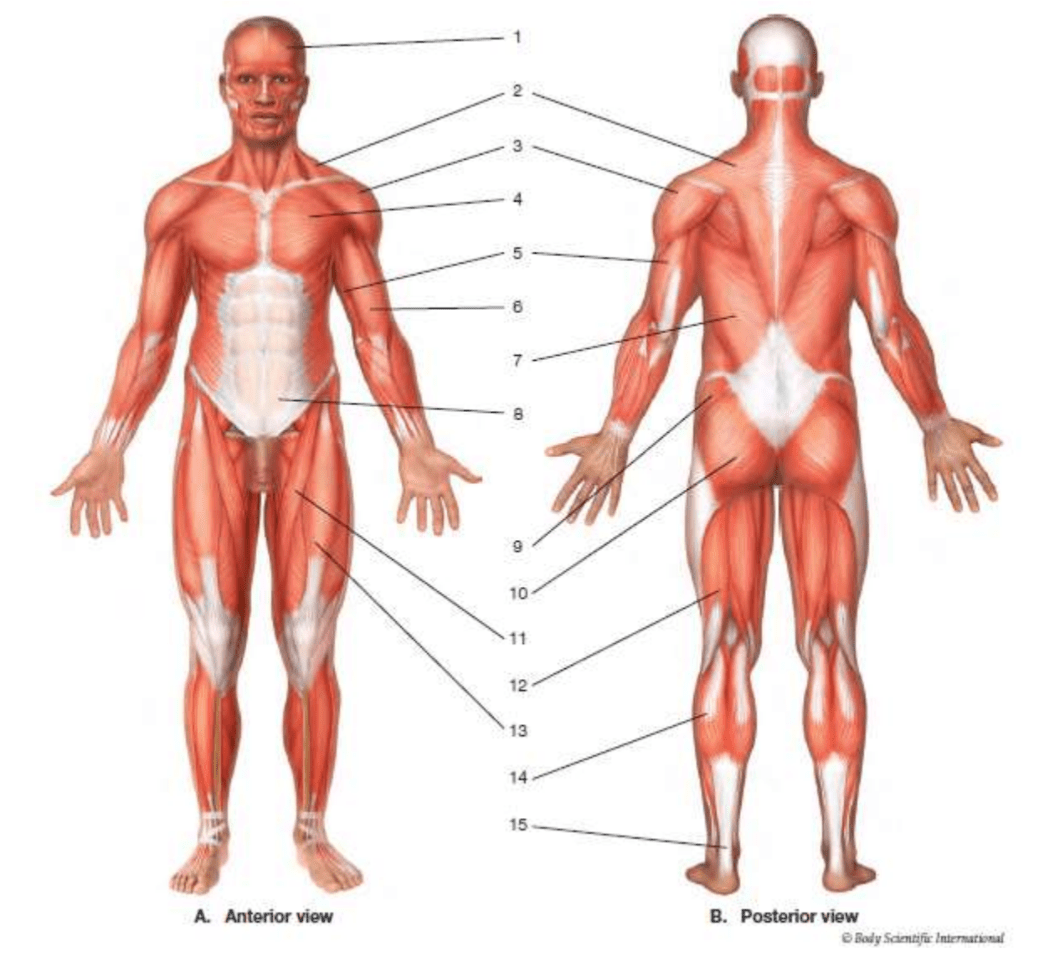
gastrocnemius
chronic disease that is characterized by inflammation in the joints and leads to crippling deformities
rheumatoid arthritis
abnormal sensation, tingling, numbness, itching (body parts falling asleep)
paresthesia
Explain the difference between lordosis, kyphosis, and scoliosis.
Lordosis: Swayback
Kyphosis: Humpback
Scoliosis: "S" or "C" curve to the back
List the three types of joints and put them in order from least moveable to most moveable.
synarthroses: immoveable
amphiarthroses: slightly moveable
diarthroses: freely moveable
Rotational motion of the forearm in which the palm moves face up
supination
movement of a body part its longitudinal axis
rotation
#12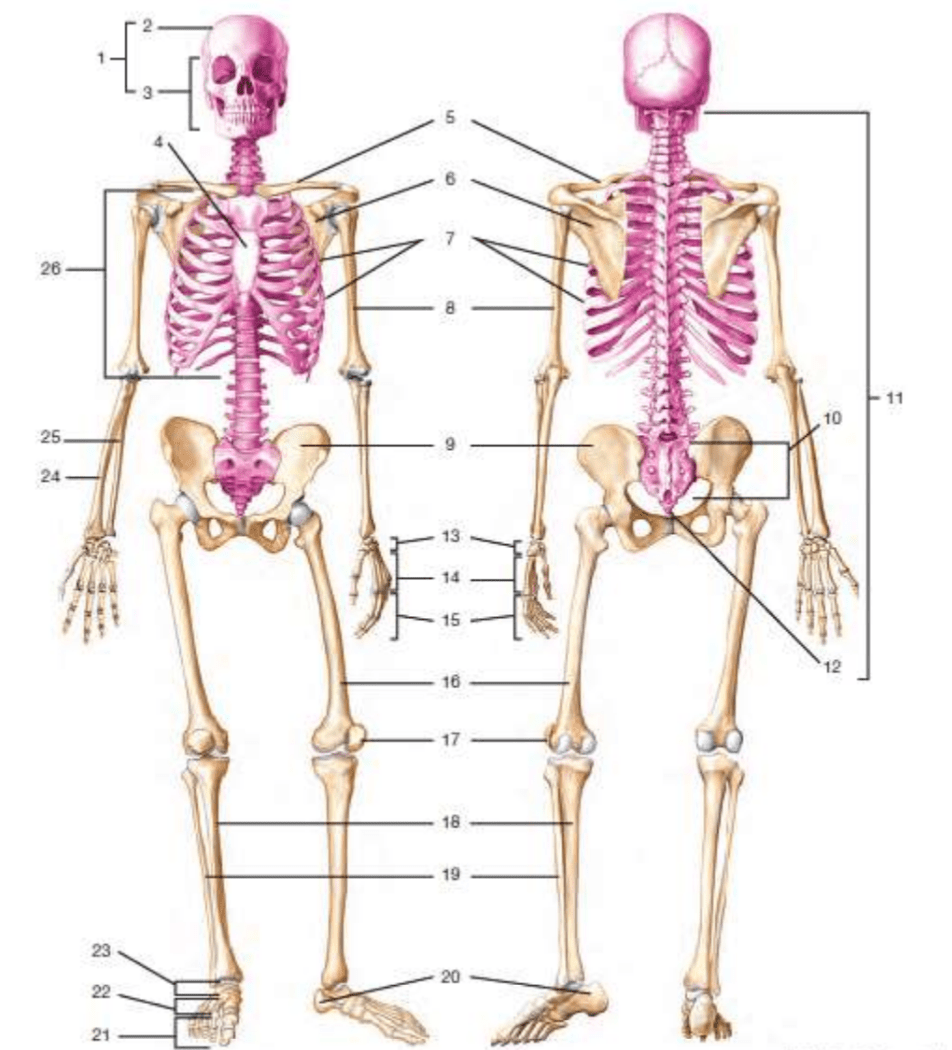
coccyx
#9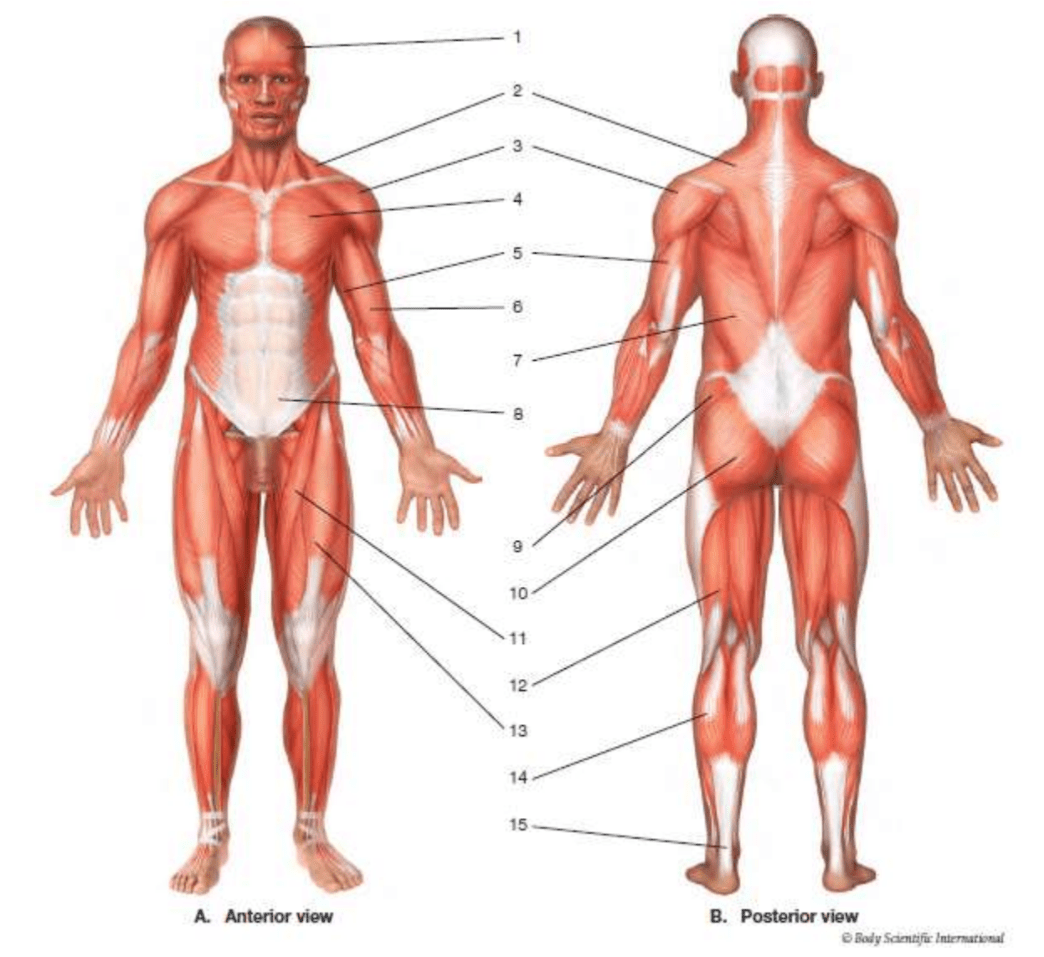
gluteus medius
joint disease that mostly affects cartilage between the bone and joint
osteoarthritis
paralysis on the lower half of the body
paraplegia
Explain the 3 different types of muscle tissue and where you can find each one. Explain what each one does.
Cardiac: Is an involuntary muscle that is only found inside the heart. It is what causes the heart to beat.
Smooth: Is an involuntary muscle that is found along the internal organs. It helps the digestive system move food through your body.
Skeletal: Is a voluntary muscle that is connect to your bones. It is in charge of moving your body.