Melanoma accounts for only about 1% of skin cancers but causes approximately what % of of skin cancer deaths?
What is 60%
What is the #1 risk factor for melanoma?
What is UV radiation?
Name the ABCDE criteria for melanoma.
What is asymmetry, border irregular, color variation, diameter > 6 mm, evolution?
The single most important histopathologic prognostic factor in melanoma is this measurement.
What is Breslow depth?
This is the biopsy method of choice for suspected melanoma.
What is an excisional biopsy?
Which melanoma is diagnosed most frequently in the elderly with chronic sun exposure?
What is lentigo maligna melanoma?
These lesions are now considered markers—but not direct precursors—of melanoma.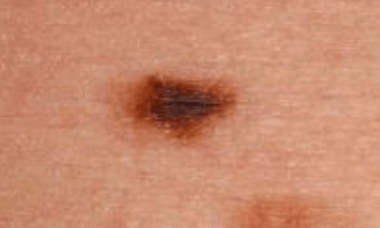
What are Clark/dysplastic/atypical nevi?
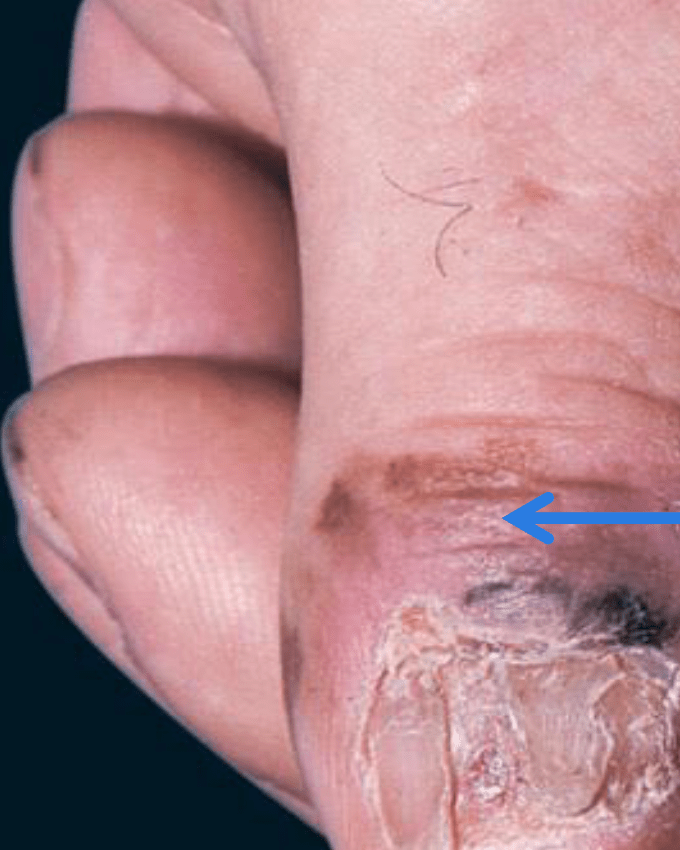
A widening, dark longitudinal nail streak with pigment extending onto the proximal nail fold is known as this sign.
What is Hutchinson sign?
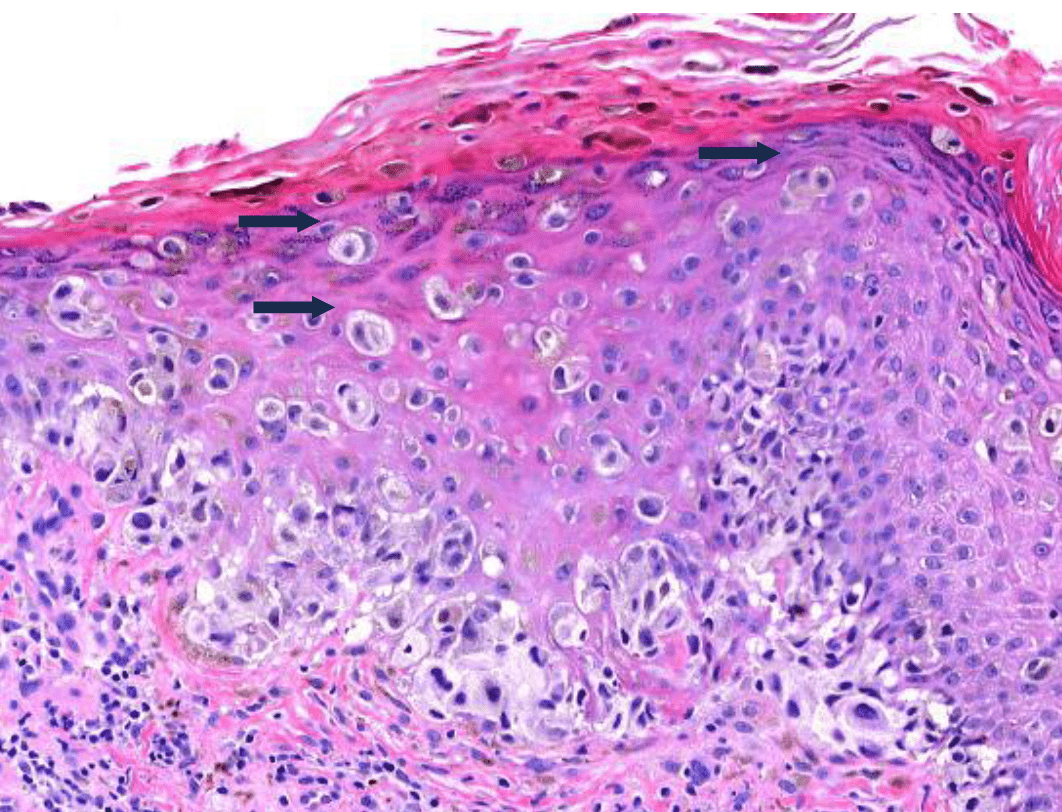
This histologic feature describes melanocytes scattered at all levels of the epidermis and is characteristic of superficial spreading melanoma.
What is pagetoid spread?
This histologic finding upstages melanoma at every thickness and worsens prognosis.
What is ulceration?
Despite rising incidence, mortality from melanoma has declined in the past decade largely due to the availability of these therapies.
What are immunotherapy and targeted therapy?
A congenital nevus larger than 20 cm confers a 3–6% lifetime risk of melanoma and is commonly known by this name.
What is a bathing trunk nevus?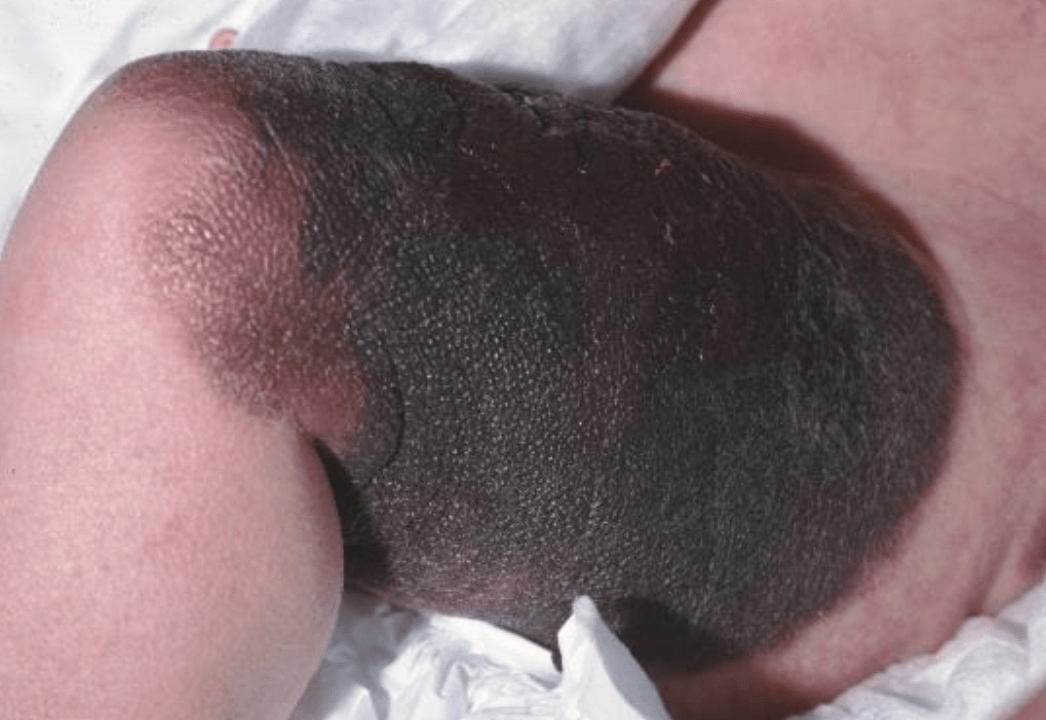
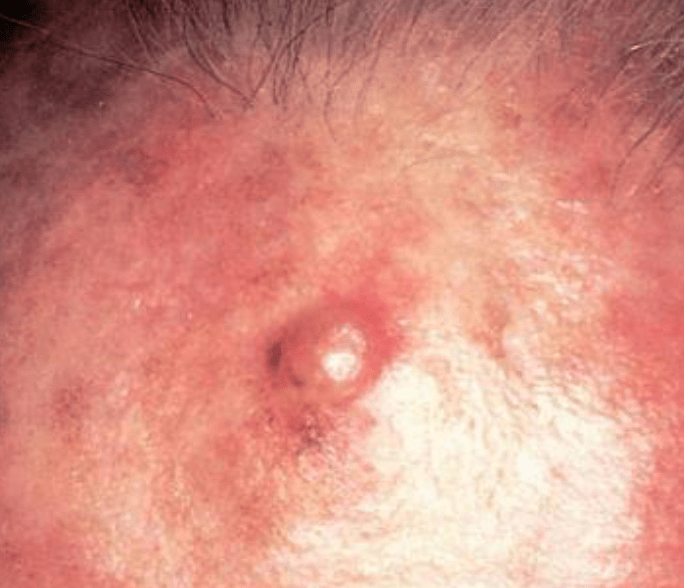
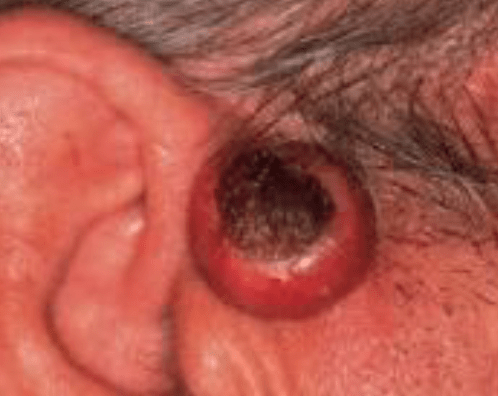
What kind of melanoma is this?
What is amelanotic/desmoplastic?
This melanoma subtype most commonly shows a papillary and reticular dermal component with a prominent vertical growth phase.
What is a nodular melanoma?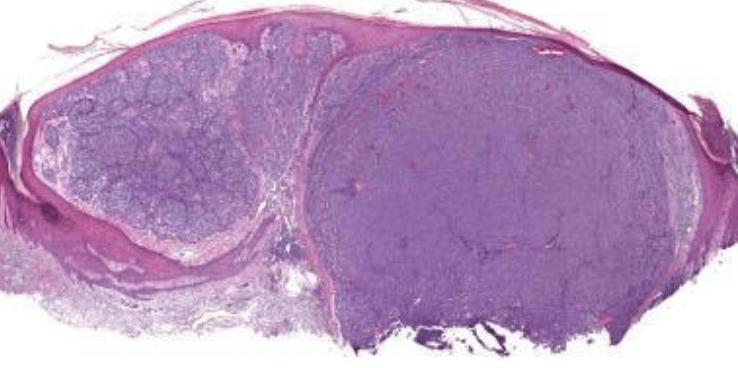
Sentinel lymph node biopsy is recommended beginning at this melanoma stage.
What is Stage IB?
Most melanomas are diagnosed at this stage, which is associated with greater than 99% five-year survival.
What is localized disease (Stage I–II)?
This autosomal dominant mutation confers a 76% lifetime risk of melanoma and a 15% risk of pancreatic cancer.
What is CDKN2A?
Which melanoma is the most rapidly growing?
What is nodular melanoma?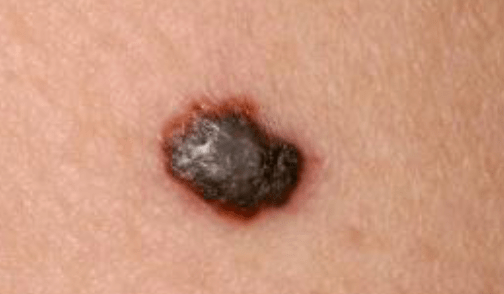
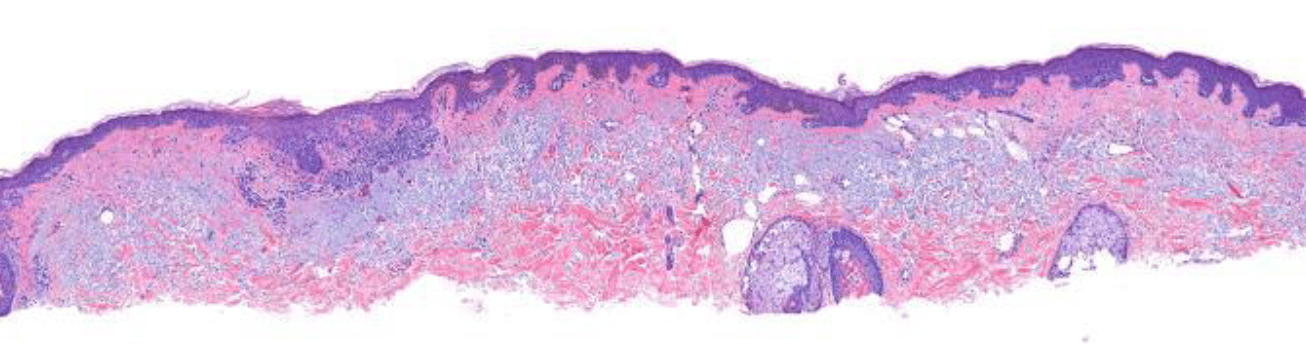
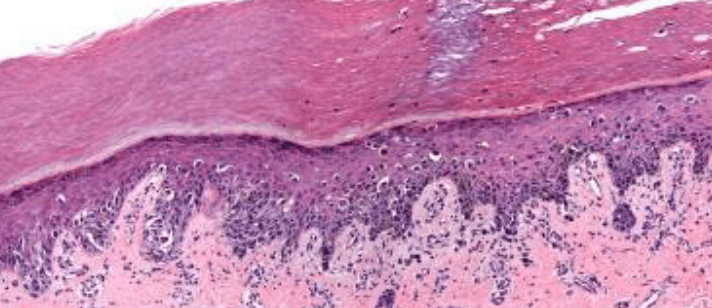
Name 2/3 characteristics from this biopsy that led to a diagnosis of lentigo maligna melanoma.
What is atrophic epidermis, effaced rete ridges, abundant solar elastosis?
This mutation, present in about 50–60% of melanomas, is targeted by BRAF and MEK inhibitors.
What is the BRAFV600E?
The increasing incidence of melanoma has primarily occurred in countries with a certain skin phenotype.
Name the skin phenotype plus 2/3 of the other high risk physical features for melanoma. +1 Bonus point if you can name someone with all of these physical features.
What is fair-skinned populations?
& blond/red hair, blue/green eyes, freckles
This melanoma subtype is most common in darker-pigmented individuals and is NOT associated with sun exposure.
What is acral lentiginous melanoma?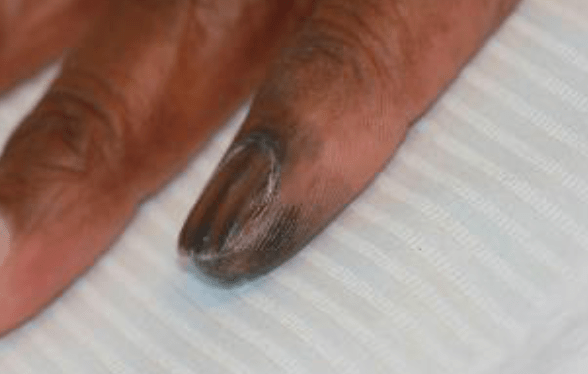
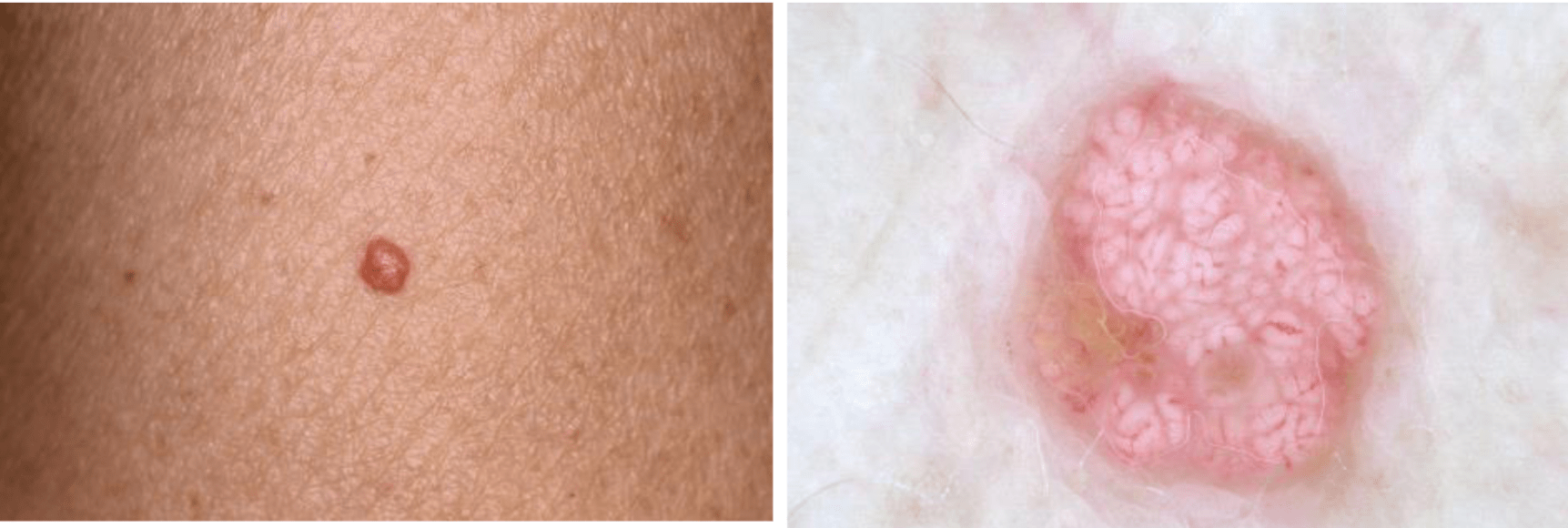
You see a patient with many of these lesions all over their body. They also tell you their father had colorectal cancer at age 56. What is the most common germline mutation causing the syndrome the patient most likely has?
What is MSH2 (Muir Torre syndrome)?
Where was the most likely biopsy site of this melanoma?
What is an acral site?
What is the diagnosis?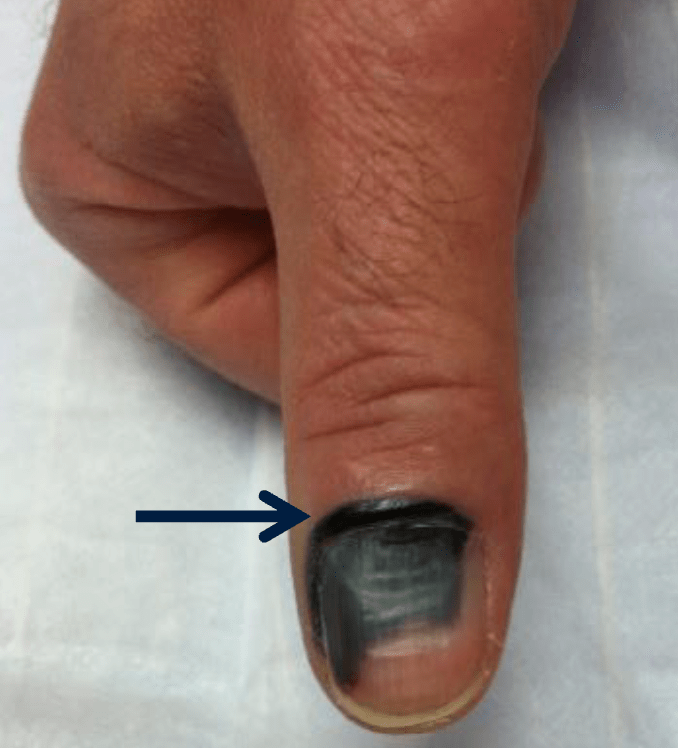
What is Subungual hematoma (pseudo-Hutchinson sign)?