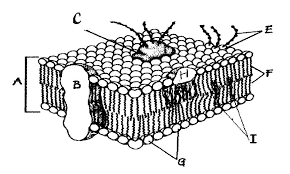
 what is A pointing to? (the whole thing)
what is A pointing to? (the whole thing)
phospholipid bilayer
what is the function of the heart?
pumps blood and nutrients around the body
is osmosis an example of passive or active transport?
passive transport
name 1 disease that will result if the cardiovascular system membrane stops functioning?
answers may vary
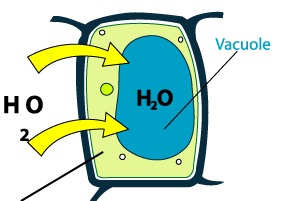 what type of solution is this?
what type of solution is this?
hypotonic solution
 What is g pointing to? is it hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
What is g pointing to? is it hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
phosphate head, hydrophilic
which of the organs of this system are known as blood vessels?
arteries, heart, capillaries, veins
veins, arteries, and capillaries
large particle of food engulfed by an amoeba
*hint*: bulk transport
endocytosis
name 2 diseases that will result if this system's membrane stops functioning?
answers may vary
when a cell is placed in salt water, there is a higher concentration of salt outside of the cell than inside, so water moves ___ and the cell _______?
out, shrivels or shrinks
 What is I pointing to?
What is I pointing to?
cholesterol
what do the capillaries do?
hint: arteries + veins
they help connect arteries and veins for the flow and exchange of blood, nutrients, and wastes
large particles of proteins exiting the cell after they are made
*hint*: bulk transport
exocytosis
name 3 diseases that will result if this system's membrane stops functioning?
answers may vary
Imagine an egg in a cup of salt water. The egg contains 60% water and 40% salt. The solution it is sitting in is 75% salt. Which way should the water move, in or out?
The water should move out
 Which structure would be involved with active transport?
Which structure would be involved with active transport?
(cholesterol, channel protein, gylcolipid, phosphate head)?
channel protein
what is the innermost layer of the veins and arteries called?
tunica intima
During active transport, molecules move _______ the concentration gradient from and area of ___ to ____ concentration
against, low to high
What is the simplified name for myocardial infarction?
*hint*: most people feel pain or tightness in their chest when this happens
heart attack
If a cell contains 35% salt (the rest: water) and it's sitting in a 35% salt water solution, which way should the water move? why?
the water will move both in and out to remain in a state of equilibrium
what is the name of the heart's membrane or outermost layer?
hint: SSL WORDS! (peri...)(cardi...)
pericardium
what are the two types of passive transport?
simple and facilitated
why do doctors use salt water instead of pure water as an IV solution?
Giving large amounts of pure water directly into a vein would cause your blood cells to become hypotonic, possibly leading to death.