Give one example of enzyme inhibition
Competitive, non-competitive, feedback, or end product
Where does glycolysis occur?
In the cytosol
What is the proton motive force?
Accumulation of H+ ions within the intermembrane space that creates a gradient
What is chlorophyll and what is its role in photosynthesis
It is a green pigment that is used to capture light for photosynthesis
How do you differentiate photosystems?
Max absorption wavelengths
Differentiate between the lock & key model and the induced fit model

What are the two types of anaerobic respiration?
Lactic acid and alcoholic
Differentiate between reduction and oxidation
Reduction - gain of electrons/ hydrogen or loss of oxygen
Oxidation is the loss of electrons/ hydrogen and gain of oxygen
What is the light independent reaction more commonly referred to as?
The calvin cycle
Explain light dependent reactions
Light is absorbed by chlorophyll which releases electrons to produce ATP
The electrons are donated to carrier molecules NADP+
The electrons lost from the chlorophyll are replaced by water, which is split to produce oxygen and hydrogen
This occurs in the intermembrane space of the thylakoids
Differentiate between exergonic and endergonic
Exergonic - reactants contain more energy than the product. Usually catabolic (breaking down)
Endergonic - reactants contain less energy than the products. Usually anabolic (building up)
What acts as the final electron acceptor?
What is the net output of glycolysis?
2 ATP, 2 NADH + H+, and 2 pyruvate
What is rubisco and it's role in photosynthesis?
Rubisco is an enzyme and catalyzes the attachment of a CO2 molecule to RuBP
What is the GAP Project?
Global Artificial Photosynthesis Project - International idea to copy the natural process of photosynthesis to develop more efficient solar energy harvesting technologies
Define allosterism and discuss how it can be positive or negative
Modulation of an enzyme's activity via the binding of an effector molecule to a site OTHER than the active site
Positive leads to activation
Negative leads to inhibition
Where does the krebs cycle occur?
In the matrix of the mitochondria
Per glucose molecule what does the krebs cycle produce?
4 × CO2, 2 × ATP, 6 × NADH + H+, and 2 × FADH2
Differentiate between a thylakoid and a granum
Thylakoid is a single disc shaped structure used for photophosphorylation and granum is a stack of thylakoids
Explain the lollipop experiment
Radioactive carbon-14 is added to a lollipop apparatus with green algae and light is shone to induce photosynthesis
After different time periods, the algae is killed and analyzed using 2D chromatography to separate the different carbon compounds
Comparing different periods of light exposure, the order that carbon compounds were generated was determined
Explain how enzymes work - specifically discussing lowering the activation energy
When an enzyme binds to a substrate, it stresses and destabilizes the bond in the substrate
This reduces the overall energy level, so less energy is needed to convert it into a product and proceeds at a faster rate
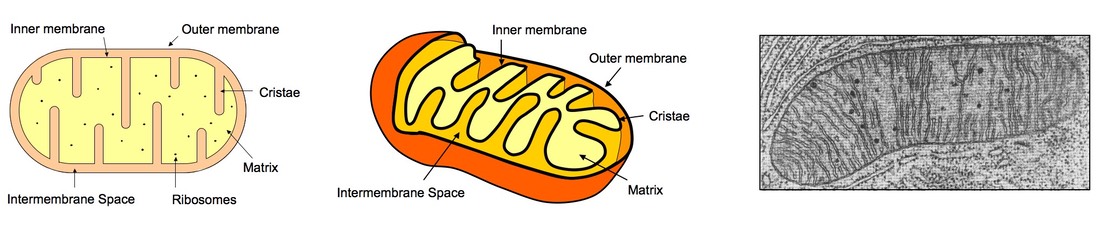
Draw & annotate a mitochondria
Differentiate between the phosphagen system, anaerobic system, and aerobic system in terms of energy
Phosphocreatine synthesizes ATP more rapidly, but reserves are quickly depleted
Anaerobic Respiration provides a more sustained pool of ATP, but produces lactic acid
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, but produces large amounts of ATP
Draw and annotate a chloroplast

Explain how carbon dioxide is used in C4 and CAM plants
C4 Pathway - CO2 is physically separated from oxygen
CAM Pathway - CO2 reserves are created