A 24 yo G2P1001 with a h/o homozygous factor V leiden on prophylactic lovenox presents in labor. Her last dose of lovenox was 4 hours ago.
When can she get an epidural?
When can lovenox be restarted after epidural removal?
Prophylactic lovenox should be held 12h before epidural
Restart 4 hrs after catheter removal
Additional information
Therapeutic LMWH should be held 24h before delivery. Restart 4 hrs after catheter removal
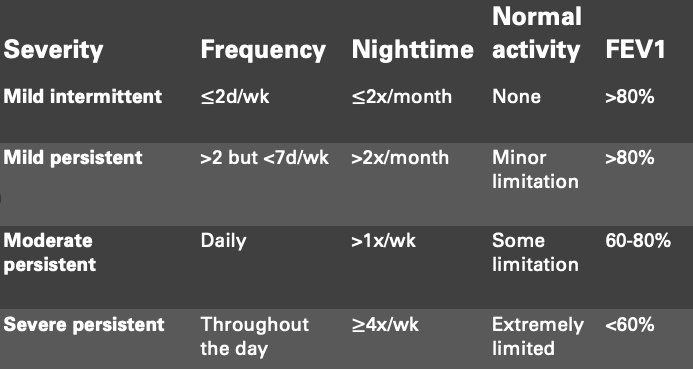
A 24yo G2P1 at 14wks gestational presents for routine visit. Her medical history is significant for asthma. During her appointment, the patient states that she has been using her albuterol 5 days a week for shortness of breath and wheezing. What is the most appropriate next medication to RX?
Inhaled corticosteroids (ex: budesonide)
Additional information:
In which scenario would you NOT recommend or offer a CD to prevent perinatal HSV?
A) Active genital lesions
B) HSV lesion on buttock, back or thigh
C) Prodromal symptoms of pain/burning
D) Primary or non-primary first episode of genital HSV during the third trimester
B) HSV lesion on buttock, back or thigh
Additional information:
Neonatal HSV infections can be classified as disseminated disease (25%); CNS disease (30%); and disease limited to the skin, eyes, or mouth (45%).
Neonatal mortality: 30% for disseminated disease and 4% for CNS disease.
Approximately 20% of survivors of neonatal herpes have long-term neurologic sequelae
Tx primary outbreak: 1000 mg BID x 10d, suppression 500 mg BID starting at 36w
36 yo G3P2 undergoes cfDNA screening at 11 weeks of gestation. The results are consistent with trisomy 21. What is the most appropriate next test?
Chorionic villus sampling
Additional information:
Performed at 10-13 weeks, performed abdominally/vaginally, loss rate 1 in 455
Amniocentesis at >15/16 weeks
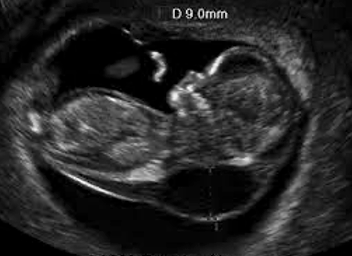
What is this condition?
Cystic hygroma
Also accepted: Thickened nuchal translucency
Fibrinogen
Increased
Additional information:
Hypercoagulable state --> increased levels of coagulation factors caused by elevated estrogen levels mediating an increase in protein synthesis.
Clotting factors 7, 8, 10, 12, vWF, and fibrinogen levels markedly increase
Valproic acid
Neural tube defect
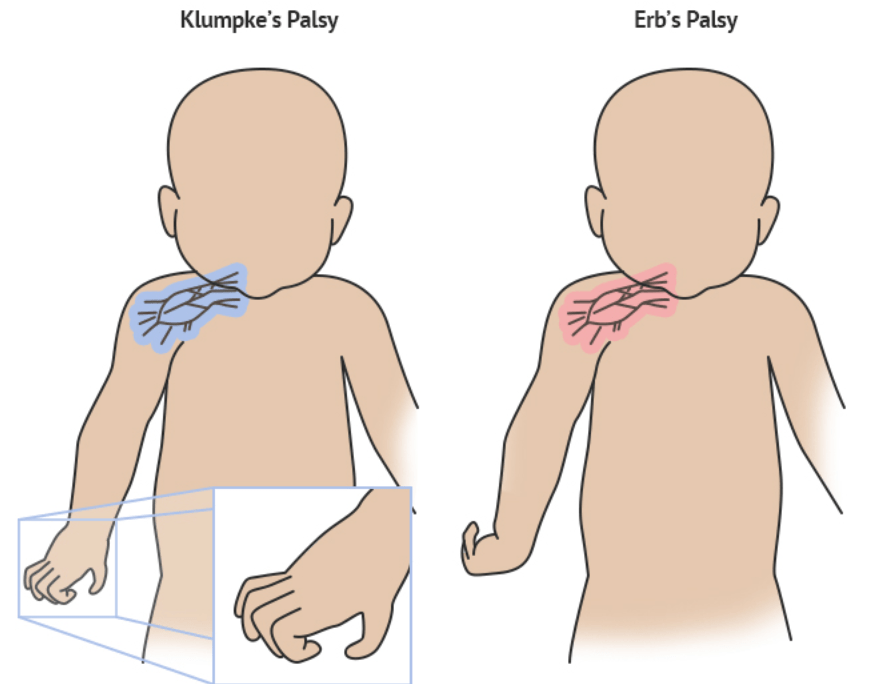
After a 5 minutes shoulder dystocia on DOL#1, the neonate exhibits isolated left hand paralysis with loss of grasp reflex and Horner's syndrome. Name this palsy.
Klumpke Palsy: C8-T1
Additional info:
Erb's Palsy (C5-C6): medial rotation, forearm pronated and extended
A 38yo G2P1 returns to the office for a routine prenatal visit at 30 weeks gestation. She reports eating 10 cups of ice daily and is found to have a hemoglobin level of 8.5g/dL, MCV of 77, and a platelet count of 247,000. The lab test that has the highest sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing her anemia is
A) Hemoglobin electrophoresis
B) Iron level
C) Serum ferritin
D) Total iron biding capacity
◦Transferrin saturation
C) Serum ferritin
Additional information:
• Most common cause of anemia in pregnancy: iron deficiency
• RBC volume increases about 20-30 percent, which increases the supply of iron and vitamins that the body needs to make hemoglobin.
• 30 mg elemental iron needed daily.
• Treat if Hgb <10.5 (1st and 3rd tri) or <11 (2nd tri) or ferritin <10-15mg/dL with oral Fe
• Screen in first trimester and at 24-28wks
Differential for microcytic anemia --> Iron deficiency anemia, Thalassemias, Anemia of chronic disease
Differential for macrocytic anemia --> Folic acid and vitamin B12 deficiency
35 year old at 16w0d presents with a reticular rash on her trunk and joint pain. She works at a daycare. At her anatomy scan 4 weeks later at 20w0d, US shows size equal to dates with fetal hydrops (ascites and pleural effusion). What additional screening test would you want?
A) Umbilical artery dopplers
B) Ductus venosus dopplers
C) Middle cerebral artery dopplers
D) Uterine artery dopplers
C) Middle cerebral artery dopplers
Additional information:
Parvovirus (B19): replicates in bone marrow causing anemia > heart failure > hydrops
Mother: rash, arthritis, flu-like illness, or asymptomatic
Diagnosis: ELISA for IgG/IgM of mom; PCR on amniotic fluid is more sensitive
Treatment: PUBS for anemia and possible transfusion if hydrops present
Classic US question: ascites
A 35 yo G1P0 undergoes a nuchal translucency US at 13w4d and NT measures 3.1 mm. The patient elects to diagnostic testing which reveals a normal karyotype and microarray analysis. What is the most likely fetal structural abnormality if one were to be detected.
Cardiac defect
Additional information:
Performed 10w-13w6d, enlarged 3mm or > OR >99% for CRL, poor sensitivity/specificity in isolation
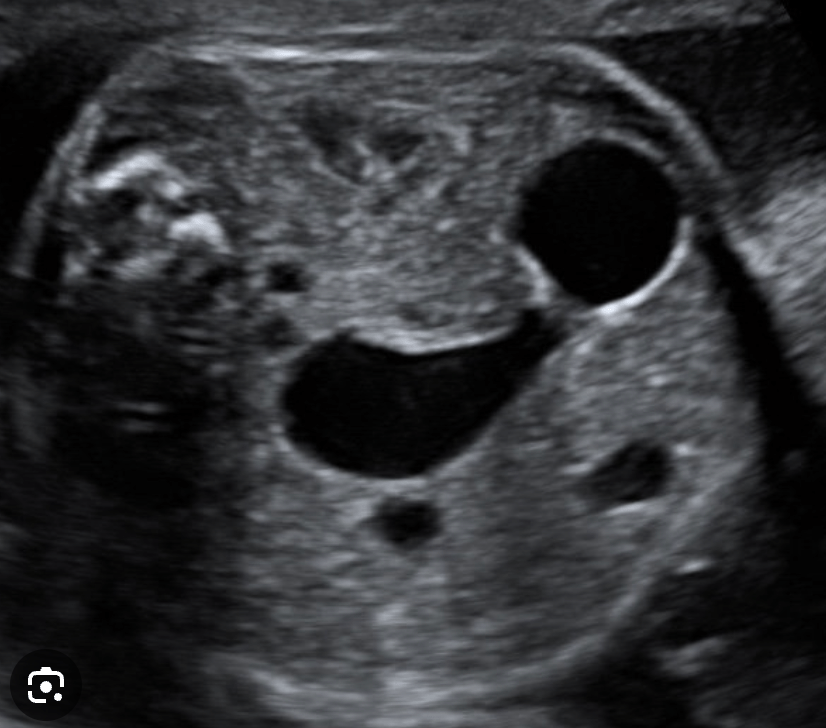
What is the condition?
Duodenal atresia
Aka: Double bubble sign
Systemic vascular resistance
Decreased
Additional information:
Peripheral vasodilation also leads to a decrease in blood pressure early in pregnancy, with blood pressure reaching its lowest point at about 20 weeks gestation leading to physiologic hypotension.
Tetracyclines
Discolored teeth (yellow brown coloring)
17 yo G1P0 presents at 29w4d for persistent nausea, vomiting and diarrhea for the past 2 days. On initial evaluation she is ill appearing and reports generalized abdominal pain. Her temp is 38.5 C, BP 146/98 mmHg, HR 121 BPM. Neurological exam normal. Laboratory results show WBC 17, hct 28%, PLT 17K, Cr 3.1 and normal LFTs. Schistocytes are identified on peripheral smear. What is the most likely dx.
Hemolytic uremic syndrome
Additional info:
TMA with thrombocytopenia and significant renal involvement. Complement or e.coli shiga toxin mediated. Dx of exclusion and need to differentiate between other TMA (TTP, PreE/HELLP, AFLP)
A 32-year-old G3P1011 presents for her first prenatal visit at 11w3d. She has a prior DVT after a femur fracture. You order a thrombophilia panel to assess for underlying predisposition to VTE. The test result that is most influenced by pregnancy is
(A) factor V Leiden mutation
(B) methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) mutation
(C) protein C activity level
(D) protein S activity level
D) protein S activity level
Additional information:
Protein S decreases in pregnancy and is not a reliable test in pregnancy
A 23-year-old G1P0, presents at 11w0d. Her prenatal labs shows a positive RPR with a titer of 1:16. TP:PA is positive. She has no known history of syphilis and denies any symptoms. Her current partner has no history of syphilis. She has no drug allergies. What is her best treatment option.
IM Penicillin G benzathine x 3 weekly doses
Additional information:
•Screen all pregnant women in T1, 28wks, at delivery
•Nontreponemal test: VDRL or RPR
•Treponemal test: FTA-ABS, or TP-PA
Primary syphilis (occurs about 3wks after infection): painless ulcer or chancre --> Tx: Benzathine PCN G 2.4mU IM x 1
Secondary syphilis (weeks to months after primary infection): skin rash (classically involves palms/soles), fever, ocular symptoms --> Tx: Benzathine PCN G 2.4mU IM x 1
Latent syphilis: NO SYMPTOMS
• Early latent (1y): Benzathine PCN G 2.4mU IM x 1
• Late latent (>1y): Benzathine PCN G 2.4mU IM weekly x 3 doses
• Jarish-Herxheimer reaction: within 24h of therapy; febrile reaction; self-limited but can precipitate PTL
Which of the following is NOT a reason for a no call result with cfNDA
A) Early gestational age (<9-10 weeks)
B) Genetic conditions (T13 or 18)
C) Low maternal BMI (<18 kg/m2)
D) LMWH
C) Low maternal BMI
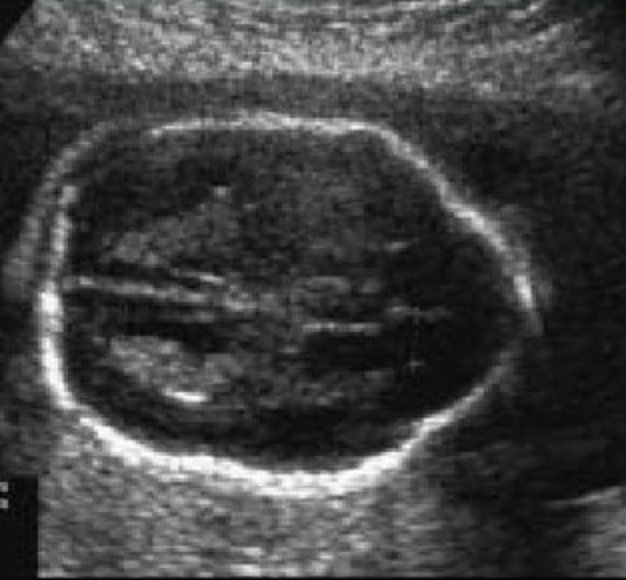
What is the condition?
Open neural tube defect
Aka Lemon sign
Tidal Volume
Increased
Additional information:
Increased progesterone concentrations, beginning in the first trimester, cause an increase in tidal volume by approximately 30-50%.
Lithium
Ebsteins anomaly
Additional information:
Apical displacement of the tricuspid valve leading to severe TR and atrial enlargement
A 28 yo G2P0101 has a cervical length of 20 mm noted at 16 weeks. The cervical length was ordered because of her history of a prior preterm delivery at 30 weeks. What is the most appropriate treatment and why?
Cerclage
Additional information:
Criteria for cerclage --> exam indicated, history indicated, ultrasound indicated
Vaginal progesterone --> recommended for asymptomatic individuals without a history of preterm birth with a singleton pregnancy and a short cervix (<25 mm)
A 33yo G3P2 at 36wks with immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) comes to your clinic for evaluation for a repeat c-section. She has had two prior c-sections. She reports no bruising or bleeding. Her most recent CBC showed a platelet count of 51K. You obtain another today that has decreased to 37K. The most appropriate next step is:
◦Immunoglobin transfusion
◦Corticosteroids
◦Plasma exchange
◦Platelet transfusion
◦Splenectomy
Corticosteroids
Additional information:
• ITP: can be primary (idiopathic) or secondary (SLE, HIV, leukemia, lymphoma)
• Treat for plt <30k or if <50k and needs surgery; most use 70k as cutoff for placing epidural
• Treatments: prednisone > IVIG > splenectomy. PLT transfusion if bleeding or need immediate increase in PLT #
• PLTs 70-150K think gestational thrombocytopenia
24 yo G3P1011 at 36 weeks GA, who is living with the diagnosis of HIV positivity. Her labs are: VL 2000, CD4 400. In order to decrease risk of vertical transmission, what would be your:
1. delivery mode/timing
2. Peri-delivery medications
Prelabor cesarean section at 38 weeks gestation and IV Zidovudine 3 hours preoperatively
Additional information:
• Viral load <1000: IV zidovudine until delivery; can have SVD
• Viral load >1000: CD prior to labor/ROM (schedule at 38wks); give IV zidovudine for 3h prior
• Viral load unknown: CD if no labor or SROM
What carrier testing is recommended by ACOG for all pregnant patients?
Spinal muscular atrophy
Cystic fibrosis
Hemoglobinopathies
Additional testing if:
Fragile X syndrome --> if family history of fragile X related disorders or family history of intellectual disability, unexplained ovarian insufficiency <40yo)
Tay-Sachs disease --> if Eastern or Central European Jewish descent (Ashkenazi)
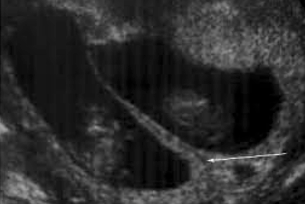
What is the diagnosis?
Dichorionic diamniotic twin gestation
Aka: Lambda or twin peak sign
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)
Increased
Additional information:
Estrogen produced by the placenta increases the synthesis of angiotensinogen by the liver, which leads to an increase in angiotensin II.
Renin is released from the ovaries and decidua of the uterus.
At approximately eight weeks of gestation, aldosterone levels rise and continue to increase 3-6x the upper limit of normal in the third trimester.
The result is a net gain of approximately 1.5 liters of water
Aminoglycosides
Ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity
Name 3 conditions in which pregnancy is contraindicated (mWHO Risk Class IV)
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Systemic ventricular dysfunction (EF <30%)- Previous peripartum cardiomyopathy with any residual impairment of LV function
- Severe symptomatic MS
- Severe symptomatic AS
- Aortic dilation >45 mm w/ marfans
- Aortic dilation > 50 mm in bicupsid aortic valve
- Vascular Ehlers-Danlos
- Fontan circulation with any complication
Additional information:
Associated with a >27% risk of maternal cardiac event
A 24yo G1 presents at 26wk to your office reporting swelling in her neck, palpitations, and heat intolerance. She has no personal or family history of thyroid disease. Her blood pressure is 140/90mmHg and her HR is 104 bpm. Examination does not demonstrate opthalmopathy, but you notice some fullness of her thyroid gland on the right. Her TSH is <0.02 and her free thyroxine (T4) is high at 5.0ng/dL. Her only medication is PNV and she has no other medical history. What is her diagnosis and the next best step for treatment:
Hyperthyroid. Treat with methimazole
Additional information:
• Normal physiologic changes: estrogen increased TBG, which increases total T3/4 (but free levels of T3/4 and TSH are unchanged)
Hypothyroidism: high TSH, low free T4
• Treat with levothyroxine
Hyperthyroidsm (Graves): low TSH, high free T4
• 1st trimester: PTU (but can be used throughout pregnancy. Associated with hepatotoxicity)
• 2nd trimester: methimazole (teratogenic)
Thyroid storm: elevated HR, CNS, GI and thermoregulatory dysfunction
• Give PTU first, then iodide
• Also give steroids, beta blockers, etc.
A 28 yo woman delivered a stillborn infant at 35wks gestation. The pregnancy was complicated by a flu-like illness and low-grade fever on the day before delivery. The infant had a papular rash on the back and thighs, and placental histology showed subchorionic abscesses and gram-positive bacteria. What is the most likely causative organism is?
Listeria monocytogenes
Additional information:
• Acquired from food products (unpasteurized milks/cheeses, raw vegetables/fruits, undercooked meats, deli meats, raw fish)
• Dx by blood culture and placental culture after delivery
• If symptomatic but afebrile then can either test blood cultures (treat if positive) or observe without testing
• If febrile with or without other symptoms: test and treat
• Treatment: Ampicillin 6g/day for 14+ days (if PCN allergy, then trimethoprim w sulfamethoxazole preferred)
37 year-old G1P0 at 20w0d presents for a routine second trimester anatomy US which shows fetal holoprosencephaly and a midline facial cleft. What is the most likely abnormal fetal karyotype.
Trisomy 13
Additional information:
T21: mild UTD, absent/short nasal bone, thickened nuchal fold, mild ventriculomegaly, echogenic bowel
T18: strawberry shaped skull, rockerbottom feet, CPC, cardiac defect, overlapping fingers/clenched hand
45 XO: cystic hygroma, hydrops
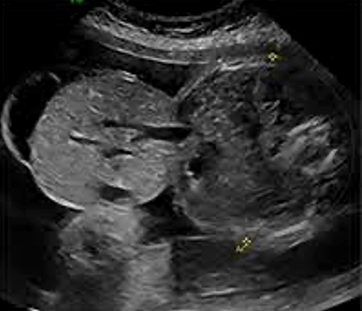
What is the condition
Omphalocele
Glomerular filtration rate
Increased
Additional information:
Increased cardiac output leads to increased blood flow to the kidneys and increased glomerular filtration rate (GFR) by about 50%.
This increased GFR leads to a subsequent decrease in the serum concentration of creatinine, urea, and uric acid.
Warfarin
Bone deformities - stippled vertebrae and femoral epiphyses
Nasal hypoplasia w/ depressed nasal bone
Choanal atresia
Fetal hemorrhage
Miscarriage
A patient has 2 prior CS and is planning her third repeat CS. She is noted to have a placenta previa on US. What is her a priori risk of accreta?
40%
Additional information:
Most important US association with accreta in the 2nd/3rd trimester is the presence of placenta previa, which is present in more than 80% of cases
Previa with:
0 CS (3%)
1 prior CS (11%)
2 prior CS (40%)
3 prior CS (61%)
4 prior (67%)
What are the clinical criteria for antiphospholipid syndrome?
Vascular thrombosis or pregnancy morbidity
One or more clinical episodes of arterial, venous, or small vessel thrombosis, in any tissue or organ
OR
1. One or more unexplained deaths of a morphologically normal fetus at or beyond 10 weeks
2. One or more premature births of a morphologically normal neonate <34w because of eclampsia/severe pre-eclampsia or placental insufficiency
3. Three or more unexplained consecutive spontaneous pregnancy losses <10 weeks with maternal anatomic or hormonal abnormalities and paternal and maternal chromosomal causes excluded.
Additional information:
Laboratory criteria --> Lupus anticoagulant, Anticardiolipin, Anti-β2-glycoprotein present on 2 occasions >12 weeks apart
What ultrasound findings and neonatal findings are associated with fetal toxoplasmosis infections?
Ultrasound: intracranial calcifications, ventriculomegaly, microcephaly, hepatosplenomegaly
Neonatal: chorioretinitis, hydrocephalus, severe developmental disability, hearing loss
Additional information:
Maternal symptoms: asymptomatic lymphadenopathy, fever, malaise, night sweats, myalgias, and hepatosplenomegaly
More severe disease when infected in early pregnancy
What are the components of a first trimester genetic screening test?
First trimester screen: NT + PaPP-A, bHCG, AFP
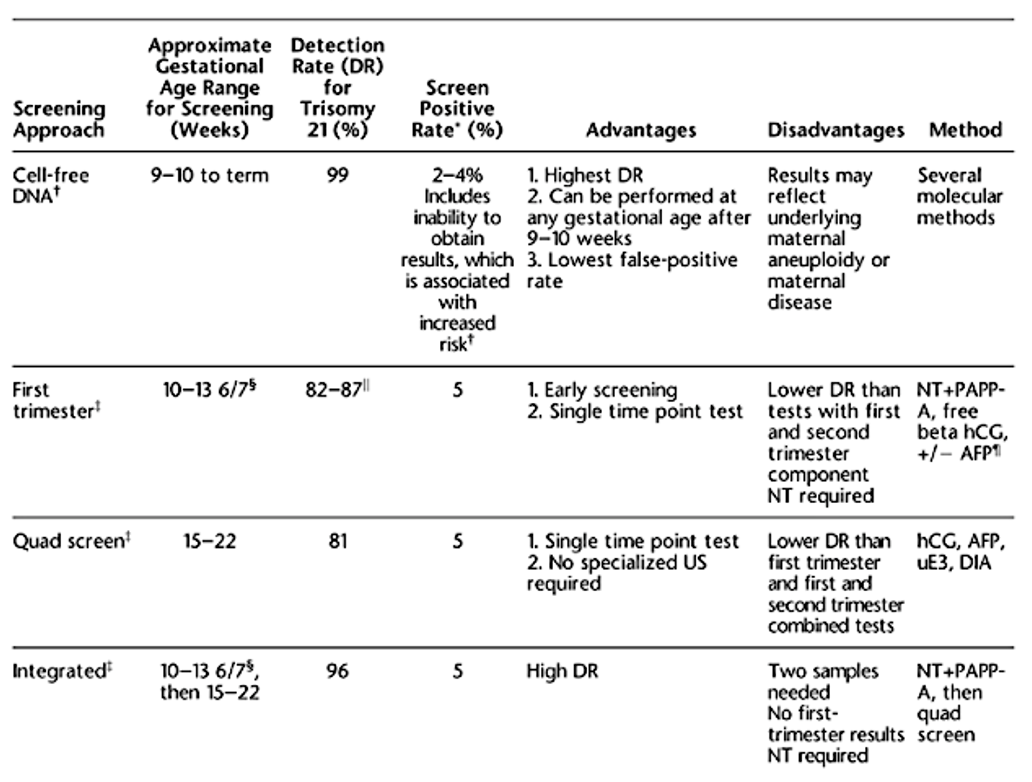
A 23 yo G1P0 presents for her first ultrasound. She is 16w6d by a reliable LMP. Her ultrasound CRL measures consistent with 18w0d. What is the patients gestational age and why?
GA is 16w6d --> LMP and US must be more than 10 days apart to support redating
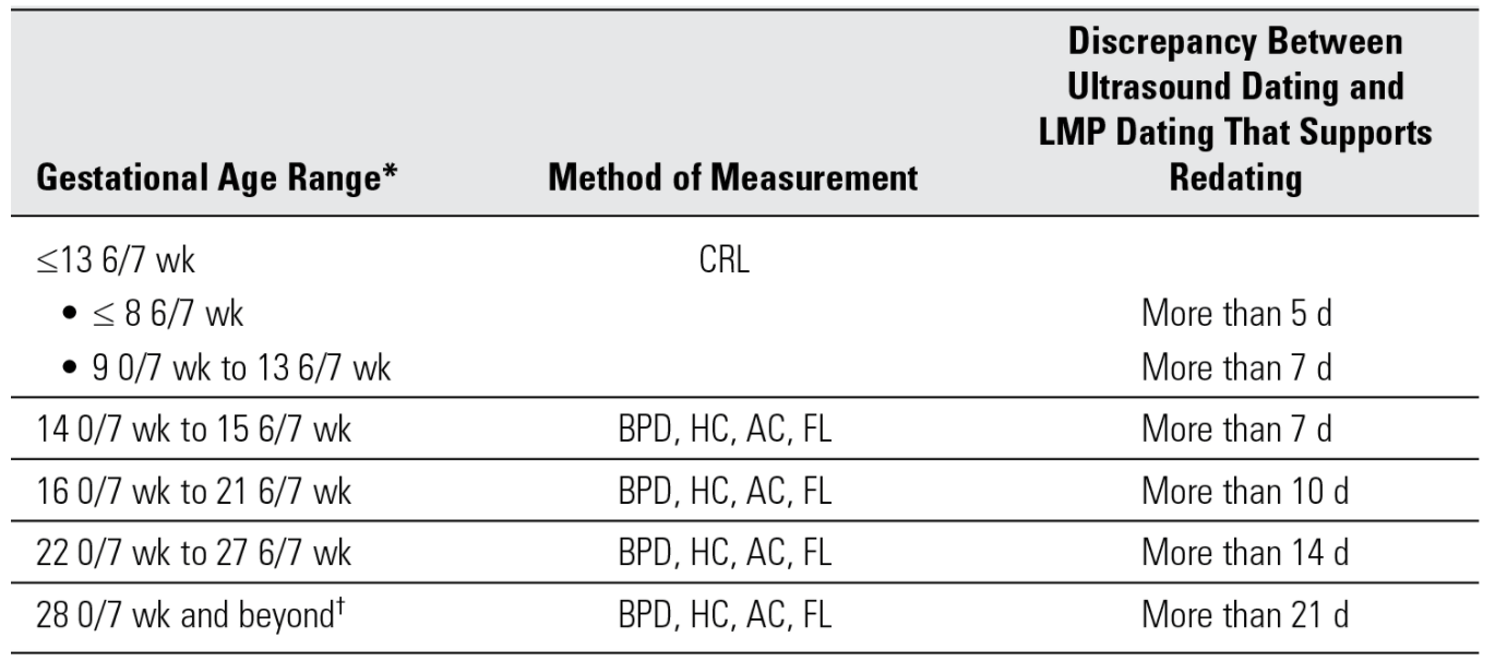
Maternal PCO2
Decreased
Additional information:
Increased tidal volume lowers the blood p CO2 resulting in a respiratory alkalosis
Methimazole
Aplasia cutis