Gram(+) are primarily in _____ and Gram(-) are primarily _____ and ____
Upper gut
Anaerobic and Lower gut
What are the 2 most common probiotics?
1. Bifidobacterium
2. Lactobacillus
C.diff is a Gram(?), ___-forming, ___robic bacillus
Gram(+), Spore-forming, Anaerobic bacillus
C.diff is resistant to killing by _____, _____, ____, _____ but can be killed by _____.
Heath, acid, sanitizer, antibiotics
Bleach (that's the only way c.diff can be killed)
What is Dysbiosis?
Slide: 12
Disturbed homeostasis of the microbiota composition
Phyla are dominated by____ & _____
Firmicutes & Bacteroidetes
what are Prebiotics and Probiotics
Prebiotics: food that humans can't digest that get fermented by gut microbiota (food for microbiota)
Probiotics: live micro-organisms that when consumed lead benefit the host (add to microbiota)
Healthcare worker's hands are a major route of infection for C.diff, how can Healthcare worker's brake chain of infection?
Washing there hands if coming in contact with a patient that has C.diff. Alcohol-based sanitizers are ineffective and the physical act of washing the spores off is they only way to get rid of them.
What is the type of precaution used in C.diff? and what dose a nurse wear with that precaution.
Contact precautions: gloves, gown, mask, eyewear,
What is a Phylotype? and prokaryotic ribosomes is related to it?
slide: 9 (Tips sheet)
Phylotype is a microbial group defined by 16S rRNA sequence similarity. And it's a component of the 30S small subunit.
What are the 3 most common Functional gut disorders?
IBS
Constipation
Functional Dyspepsia (Tummy Ache)
Major MOA for probiotics are?
production of anti-microbial substances
modulate immune system
digestion and uptake of dietary nutrients
1. Recent antibiotic use
2. Age 65 and older
3. Previous C.diff infection
What is the cardinal symptom of C.diff?
Diarrhea. 3 watery unformed bowel movements per day.
Fiber-free diet __1__ growth of __2___ that __3__ gut mucus layer leading to the _4___ of tight junctions
slide: 62 (on tip sheet)
1. encourages
2. microbiota
3. erode
4. disruption
What are the major benefits of SCFA?
(tip sheet) slide: 65
energy source for colonic epithelium
maintains barrier function of colonic epithelium
Regulates cytokine production (Anti-inflammatory)
Tumor suppression (protects DNA damage)
Glucose control and insulin sensitivity
promotes robust immune response when needed
inhibits inappropriate lipogenesis
Generates hormones such as GLP-1
Probiotics ____ the adhesion of pathogenic bacteria to the ______
Prevent
Intestinal mucosa
What are the two types of Toxins in C.diff?
What do the two toxins cause?
Toxin A: causes inflammation leading to intestinal fluid secretion and mucosal injury
Toxin B: 10x more potent then toxin, causes much more damage to the colonic mucosa
colonic epithelial cell necrosis, apoptosis, and disruption of cellular tight junctions.
FTM is the administration of donor c.diff-free fecal matter into a pt with c.diff to hopefully reset there microbiome. It's used to treat Refractory C.diff
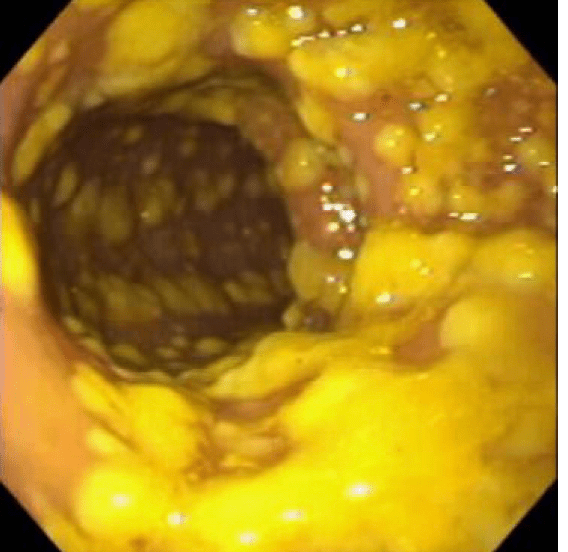 What is this an image of? how is it induced?
What is this an image of? how is it induced?
slide: 53
Pseudomembranous colitis happens following the c.diff induced ulcer formation. release of serum proteins, mucus, and inflammatory cells.
What is the hygiene hypothesis? and what are the response that alters a child's microbiome?
The idea is that being exposed to animal microbes trains the immune system to respond better.
Stress, smoking, diet, medications, mode of delivery
What can you not give to preterm infants? what can it result in?
1. Probiotics
2. Sepsis and Death
In the hypervirulent form of C.diff there is a 3rd toxin how is it different from Toxin A and Toxin B?
3rd toxin, CTD: is way more deadly than Toxin A and Toxin B. It works it's way into the host cell and modifies the cytoskeleton leading to cell collapse and death. (Kills cells from inside out)
Drug question: What drug is used to treat C.diff?
Oral form of Vancomycin
What is the brain-gut connection?
slide: 81
2-way communication between the ENS (enteric nervous system) and the CNS