
Name Structure 1
Helix
What nerve can be injured during microtia reconstruction?
Facial
How many hillocks contribute to the formation of the auricle?
6 Hillocks
What is the most common anatomical cause for protruding ears?
Lack of / poorly defined antihelical fold
Is microtia more common in males or females?
Males

Name structure 9
Intertragic notch
What imaging should be acquired in the preoperative workup prior to microtia reconstruction?
High res CT to evaluate the middle ear (looking for air)
Ultrasound to determine presence/absence of STA
Name the dominant blood supply of the posterior and anterior surfaces of the ear. (+50 each for up to two additional blood supplies).
Posterior auricular artery is dominant
Superficial temporal
Occipital artery
Superior/Inferior/ Medial auricular arteries
In post-traumatic ear reconstruction, you should sterilize the ear canal with what medication?
Cephalosporin drops
Name any two syndromes associated with microtia/ atresia
Treacher Collins
Nager syndrome
OAVS/Goldenhar
DiGeorge
Crouzon
Mobius
Kleippel-fel
Fanconi
Vater
CHARGE
Pierre-Robin
etc
Name structure 10

Lobule
When elevating the skin flap during a microtia reconstruction, the dissection should be between what two layers?
Fibrous tissue layer and fat layer
If there's too much fibrous tissue, the flap will lose definition. If there's too little fat, the flap will be left ischemic.
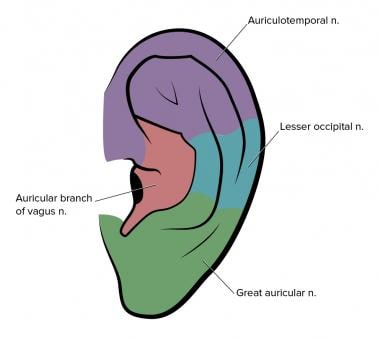
Name any nerve that provide sensation to the external ear
Great auricular nerve (lower half of A/P)
Auriculotemporal nerve of V3 (upper half of A, anterior external auditory canal)
Lesser occipital nerve (upper half P)
Auricular branch of vagus nerve (concha and posterior external auditory canal)
What is the mainstay of treatment for protruding ears secondary to poorly defined antihelical fold?
Mustarde sutures combined with anterior scoring
In an implant-based microtia reconstruction, the goal is to include the _______ fascia underneath and the _______ fascia overlying it
In an implant-based microtia reconstruction, the goal is to include the subgaleal fascia underneath and the temporoparietal fascia overlying it
Name structure 5

Antitragus
How many stages are in the Nagata and Brent methods?
(+100 for Park and Firmin methods)
Nagata = 2 stages
Firmin = 2 stages
Park = 3 stages
Brent = 4 stages
What two embryological structures contribute to the formation of the hillocks?
First and second branchial arch
Nonsurgical ear-molding for infants should ideally performed in what time period of life and why?
Within the first 3 years of life, because circulating maternal estrogens lend malleability to the auricular cartilage
Positioning of the ear should be how many degrees degrees posterior to the nasal dorsal line line?
10-15 degrees
Name the two parts of the concha (+100 for identifying them on the diagram) 
Cymba and Cavum

If you have an area of necrosis after microtia surgery, it is most likely to heal if the area of necrosis is in ________ and less likely to heal if it's _________.
If you have an area of necrosis after microtia surgery, it is most likely to heal if the area of necrosis is in the conchal bowl or scapha and less likely to heal if it's over a prominence.
Name one adult ear structure that comes from the anterior hillocks and one adult ear structure that comes from the posterior hillocks (+100 for each additional structure)
Anterior: tragus, helix
Posterior: antitragus, antihelix, and lobule
What percentage of newborns have an external ear deformity that does not self-correct?
Describe the following classes of microtia per the Nagata classification (200 pts per category):
Lobular:
Conchal:
Small conchal:
Anotia:
Atypical microtia:
Lobular type: remnant or malpositioned lobule with no concha, meatus, or tragus
Conchal: all elements present by smaller in size
Small conchal: all elements present but there Is a small indentation in the place of the concha
Anotia: no remnant
Atypical microtia: not otherwise encompassed in another category