Period after the Fall of the Roman Empire in the west marked by domination of numerous Barbarian tribes.

What was the Dark Ages?
Frankish king that converted to Christianity during the Dark Ages.

Who was Clovis?
Baptism, marriage, funerals and the communion were part of this Medieval church practice.

What were the Holy Sacraments?
Name for the tract of land given to the vassal under the feudal contract.
What was the fief?
Germanic word for the amount paid for wrong doing based upon one's rank in society.
What was the Wergild?
Name for the rebirth of civilization in Medieval Europe under Charlemagne's Holy Roman Empire.
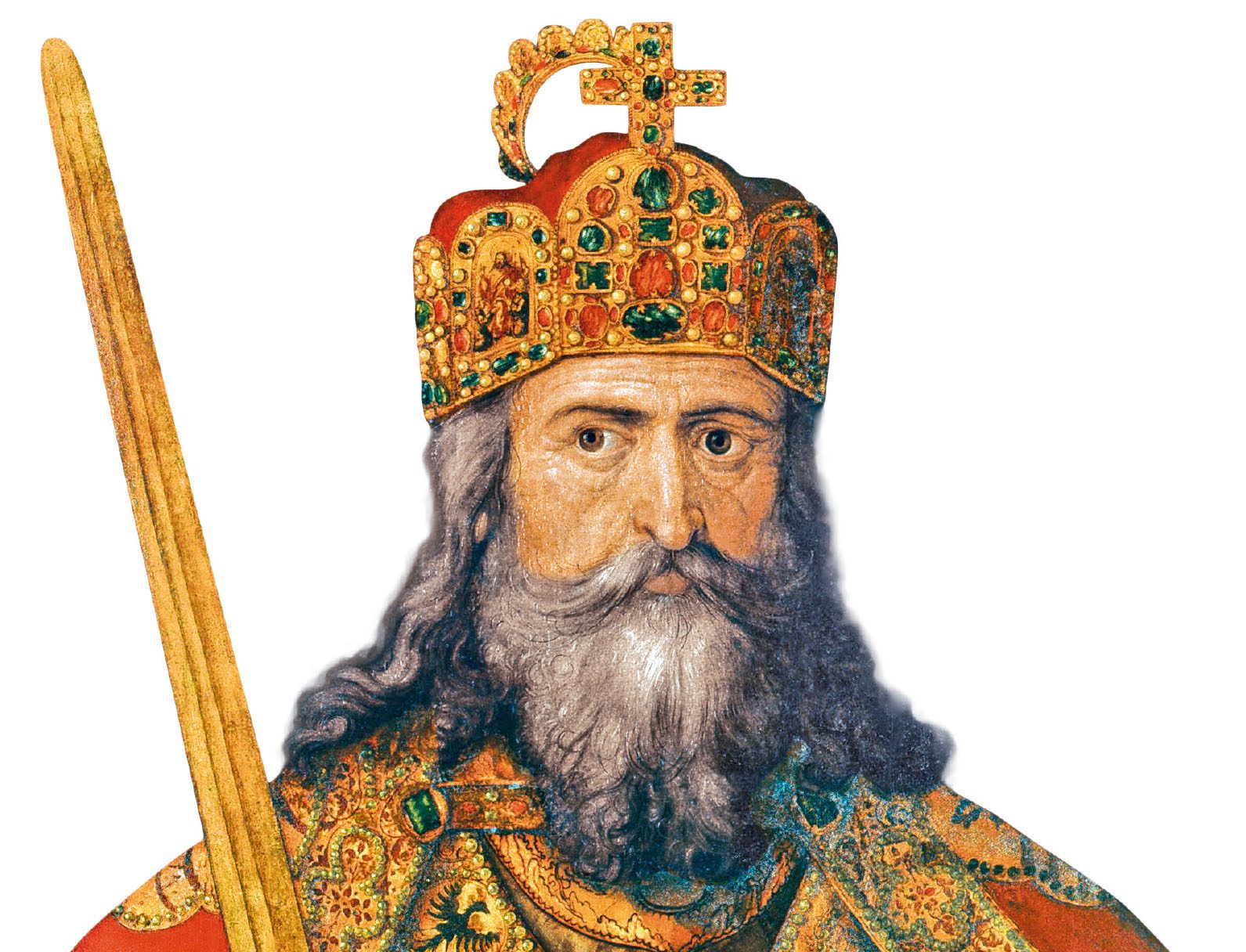

What was the Carolingnian Renaissance?
This Saxon king provided his people written law in England.
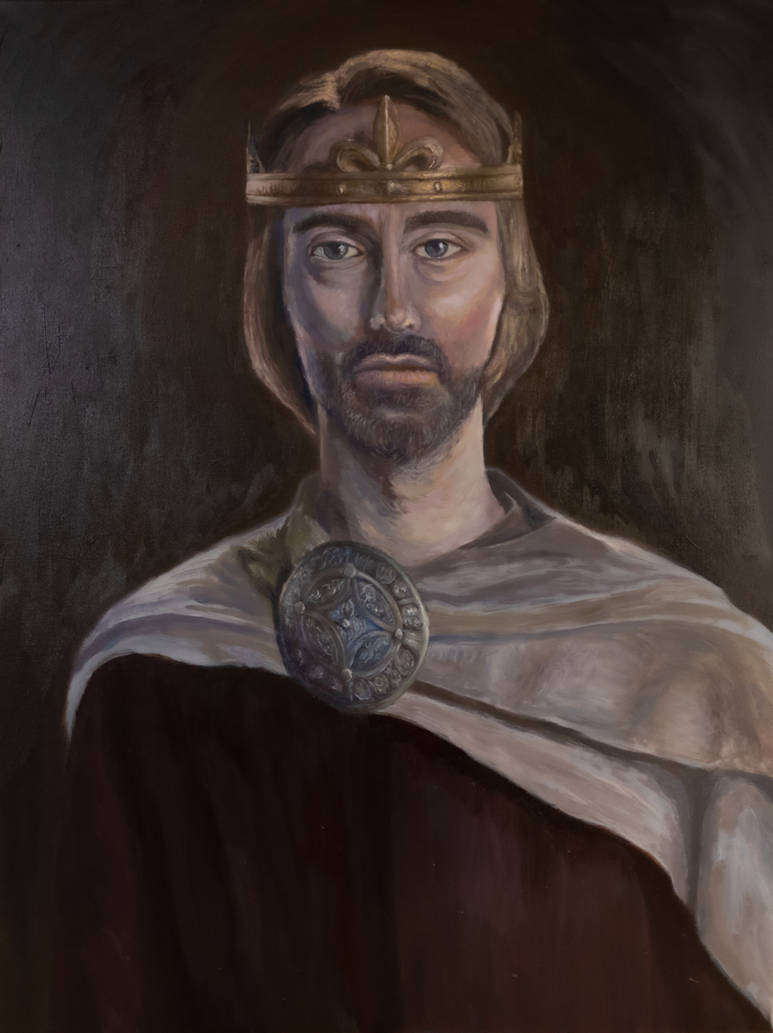

Who was Alfred the Great?
Under the hierarchy of the Catholic Church this leader exercised supremacy over religious and political affairs.
What was the Pope?
Another name for peasants bound to the land that served the lord.

Who were the serfs?
Physical combat used among the Germanic tribes in determining innocence or guilt.

What was the Ordeal?
Described the division between the Roman Catholic Pope and the Patriarch of Constantinople over the use of icons during the 12th century.

What was the Great Schism?
He was crowned emperor marking the rebirth of the Holy Roman Empire in 962.
Who was Otto I?
Geographic area under the control of a church bishop.
What was the Diocese?
The code for all knights under feudalism.
What was Chivalry?
Alphabet that formed the basis for the Russian language.
What was the Cyrillic?
Famous battle between William the Conqueror and the last Saxon king of England in 1066.
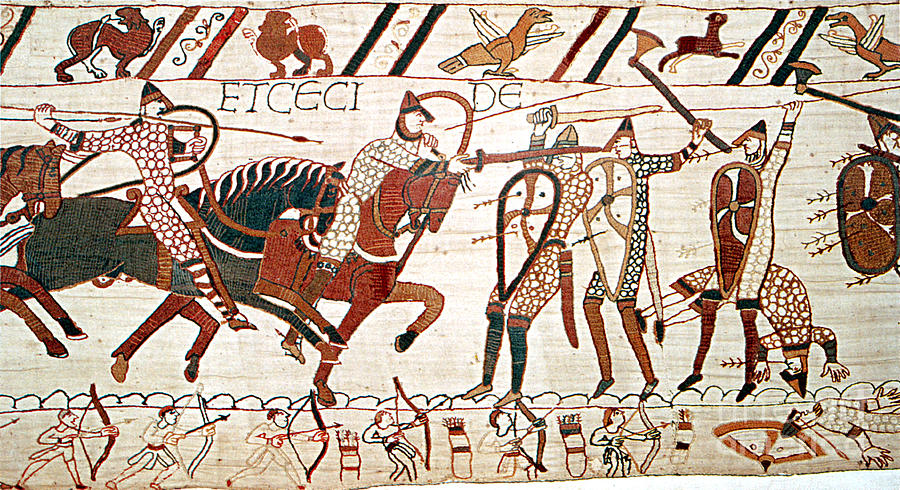

What was the Battle of Hastings?
Famous queen from Aquitaine married Henry II of England after her annulment with the French king.
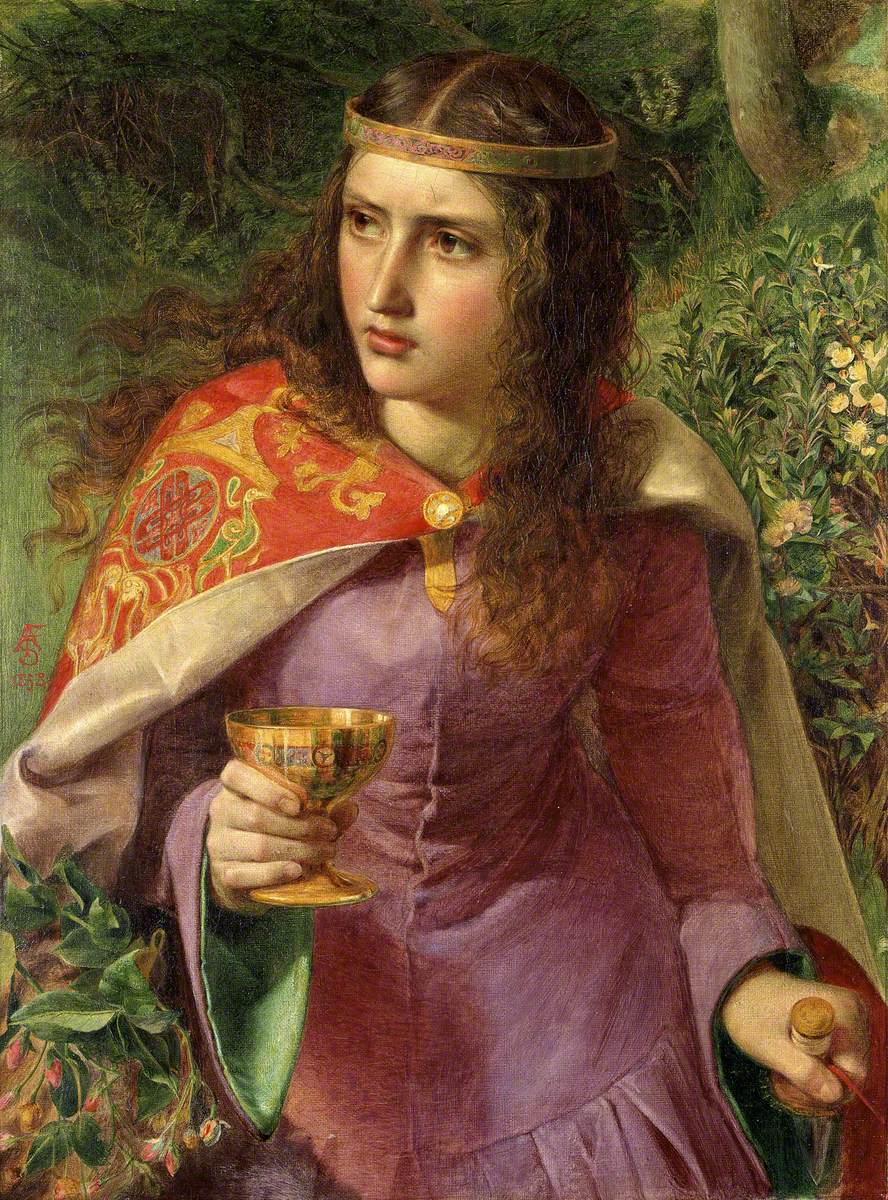

Who was Eleanor?
St. Benedict founded this movement that practiced celibacy, practice medicine and taught theology for young men entering the priesthood.

What was monasticism?
Masonry Medieval fortifications built to protect the lord, his family and the people.
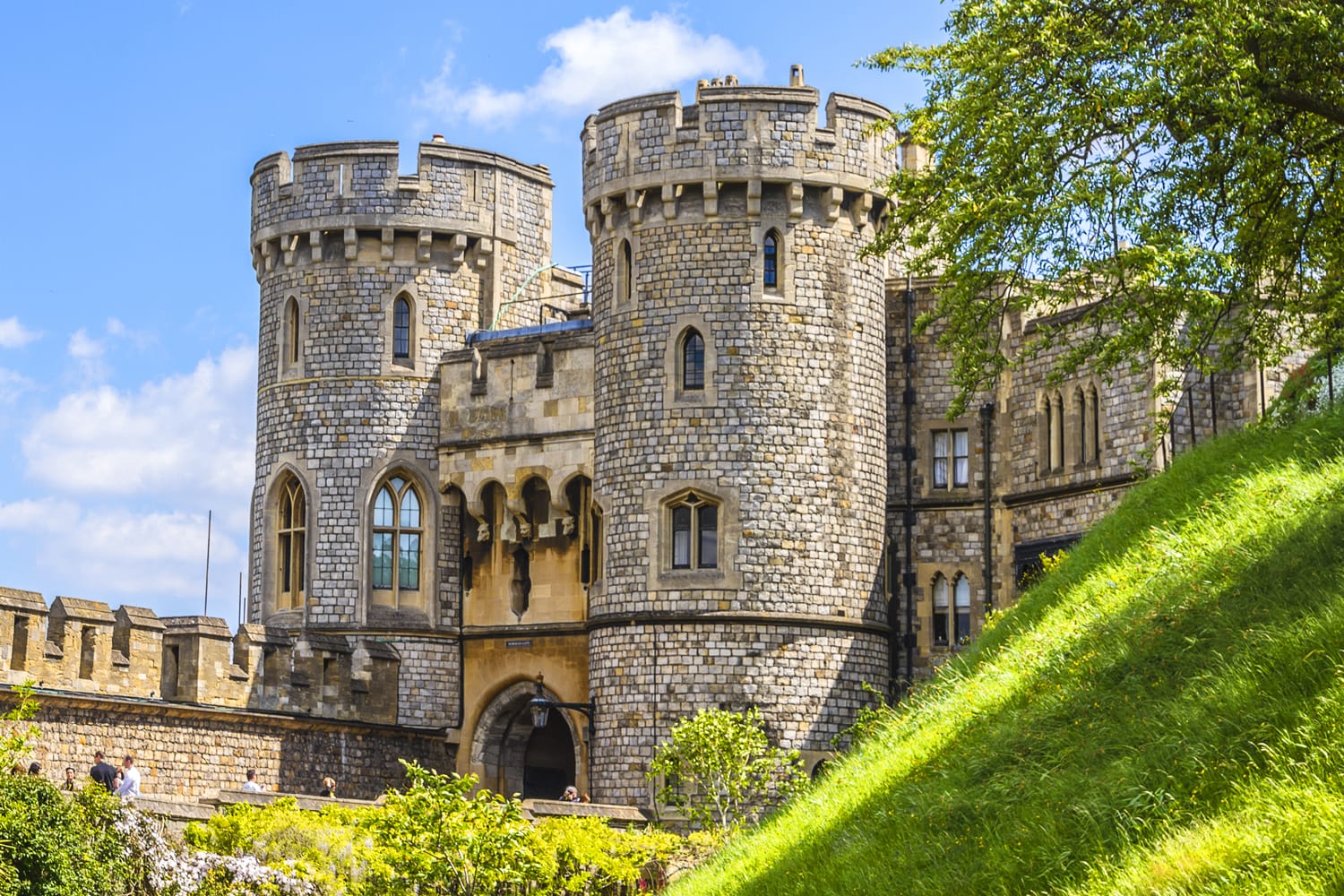

What were castles?
Became the legislative body in England consisting of the House of Lords and Commons.
What is Parliament?
This legal document signed by England's King John limited the power of the monarchy.

What was the Magna Carta?
This prince of Kiev converted to Orthodox Christianity.
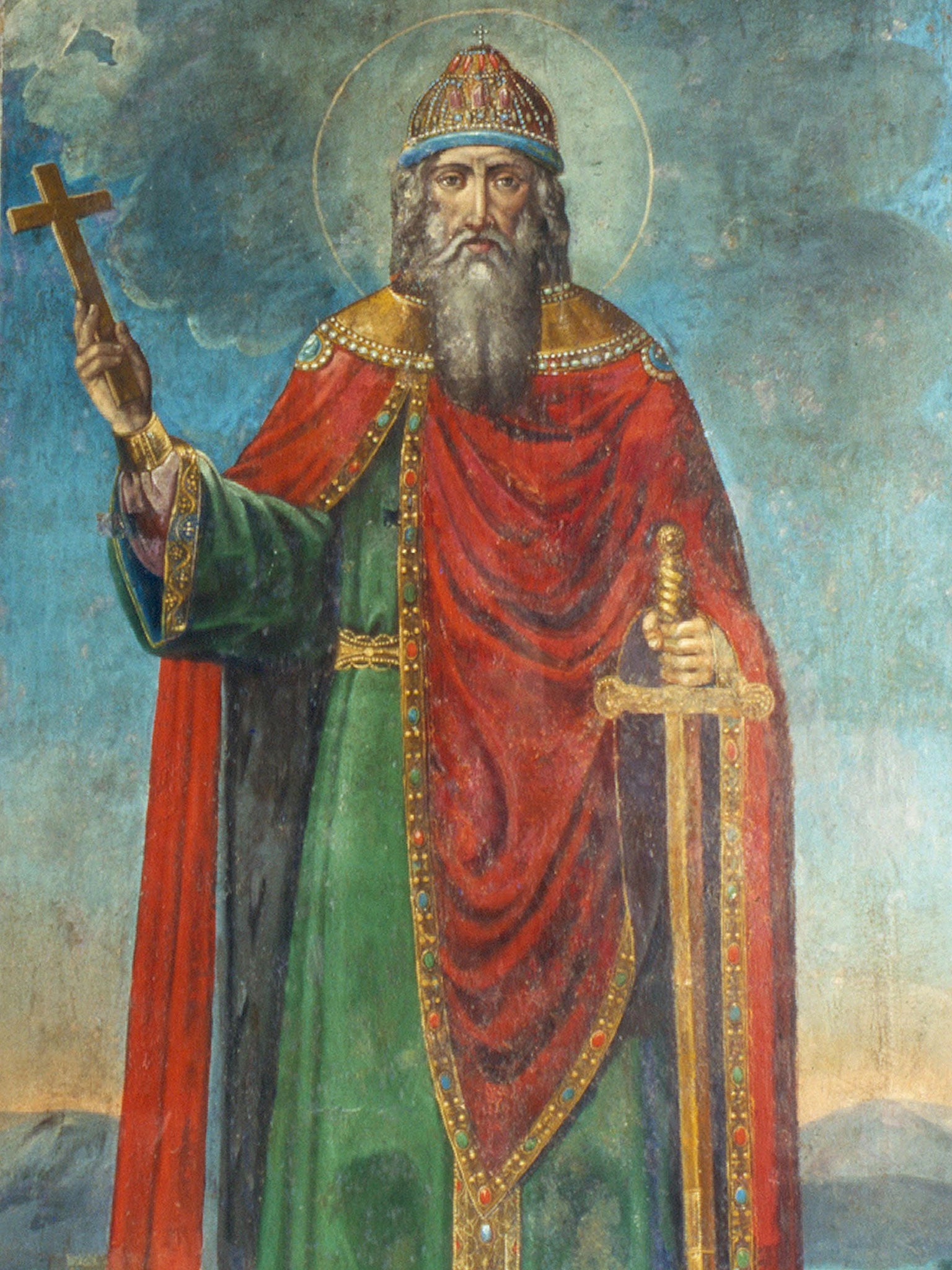

Who was Vladimir?
Practice among the priesthood of becoming totally committed to the church without marriage.
What was celibacy?
Tied to feudalism this agricultural system engaged in self-sufficiency regarding farming and craft making.
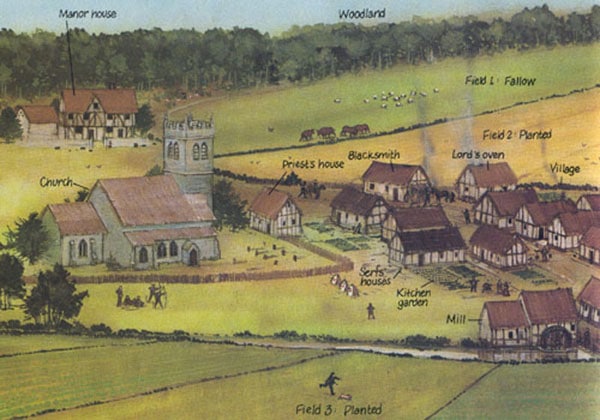
What was the Manorial System?
Religious wars fought between the Christians and the Muslims for the control over Jerusalem and the Holy Land.

What were the Crusades?