This is the one variable that you change in an experiment.
What is an independent variable?
365 for the earth to orbit the sun
What is a revolution?
The highest point of a transverse wave
What is a crest?
Atoms to molecules to cells to tissues to organs to organ systems to this.
What are organisms?
Which variable do you watch and measure throughout an experiment?
What is the dependent variable?
This is smaller than a galaxy but larger than a star.
What is a solar system?
This is the bending of waves as they pass through a different medium (ex. light passing thru water)
What is refraction?
cell walls and chloroplasts
What are organelles only in a plant cell?
This is where in a lab report a scientist addresses if the data matches the hypothesis.
What is a conclusion?
This is the alignment of the Earth, Sun, and moon during a solar eclipse.
What is Earth - moon - Sun?
When a roller coaster reaches the top of a hill, it has its maximum of this type of energy.
What is potential?
A tick living on a dog.
What is an example of parasitism?

The plant height in the experiment
What is the dependent variable?
This is caused by the moon's gravitational pull.
What are tides?
The two forces that affect gravity
What is weight and mass?
The passage of genetic instructions from one generation to another.
What is heredity?

The soil pH
What is the independent variable?
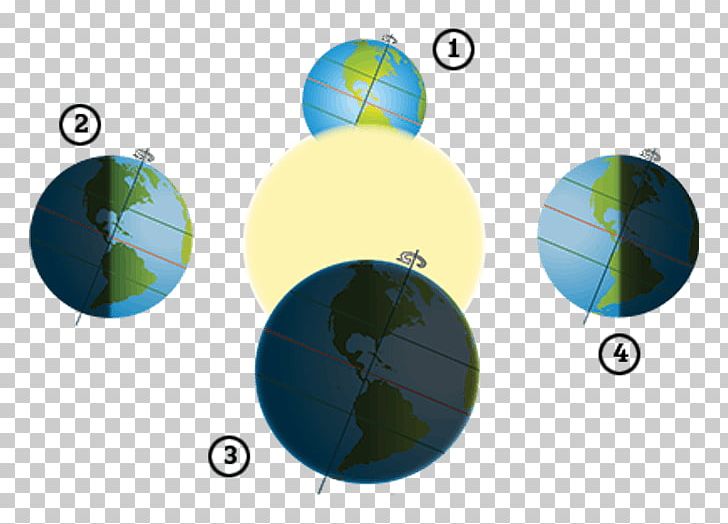
Season in southern hemisphere in southern hemisphere.
What is autumn?
Water boiling is an example of this kind of change.
What is a physical change?
the process whereby organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring
What is natural selection?