Define Homeostasis?
The body's ability to maintain a steady internal state (equilibrium).

Stratified squamous
What are the ABCD's for identifying a potentially cancerous mole?
Asymmetry, Border (irregular), Color, Diameter
Which side of the heart has deoxygenated blood?
Right
Explain what in happening to the pressure and volume in the lungs when exhaling.
Volume=Decrees
Pressure= Increase
Which body system contains the organs: Kidney, Ureter, Bladder, and Urethra?
Excretory system
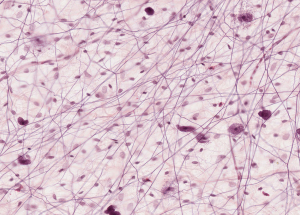
Loose connective
What layer of the integumentary system is responsible for fat storage?
Hypodermis/subcutaneous
What structures aid in opening up the AV valves in the heart?
Chordea Tendenea
What structure aids in adding resonance to the voice?
Sinus cavities
What is the role of a receptor in a homeostatic control system?
a. It carries out the body's response to a stimulus.
b. It detects changes in the internal environment and sends signals to the control center.
c. It amplifies the stimulus.
d. It removes excess waste products.
B
What 2 ways are epithelial tissues classified?
2. Layers
What are the 5 main functions associated with the skin?
1. Protection
2. Vitamin D regulation
3. Regulate water loss
4. Regulate body temperature
5. Sensory information
What is #5 pointing to?
Aorta
What structure is responsible for closing off the air pathway to the trachea when swallowing?
Epiglottis
Put the following in order from simple to most complex.
Brain, Mitochondria, Pseudostratified epithelium, Carbon
Carbon, Mitochondria, Pseudostratified epithelium, Brain

Cardiac muscle
What is the name of the smooth muscle that contracts to produce goosebumps?
Arrector pili
What is the valve found between #5 and #9?
Aortic semilunar valve
What is the correct order for air as it moves from the nose to the larynx?
Nasopharynx. oropharynx, laryngopharynx, larynx
Define negative and positive feedback.
In negative feedback, the response will reverse or cause the opposite effect of the original stimulus.
Positive feedback amplifies changes.

Pseudostratified columnar
Give a brief description on how to identify 1st, 2nd and 3rd degree burns.
1st=redness (epidermis)
2nd= blistering (epi and dermis)
3rd= bleeding and blackening of the the skin (epi, dermis and hypodermis)
Name the 3 layers of heart tissue from outer to inner
Epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
Describe the process of gas exchange in the alveoli.
Gasses (CO2 and O2) diffuse down their concentration gradient from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. O2 diffuses into the blood stream via alveoli and co2 diffuses into the lungs.