relative frequency of occurrence of an event or outcome.
What is Probability
a theoretical or ideal model that was obtained from a mathematical equation.
What is a Normal Curve
A set of individuals who share at least one characteristic.
What is a population
Researchers deal with the uncertainty in estimating the standard error of the mean with this distribution
t-distribution
Test hypothesis with a single group mean in a population variance with an unknown variance.
One sample
True or False: A probability varies from 0 to 10
False
True or False:
100% of scores fall under the area of a normal curve.
True
100% of members in this type of sample have an equal chance of being selected.
What is a Random Sample
Standard confidence interval in social science.
.05
Cohen's d effect sizes
Small = <.2
Medium = .2 < d < .8
Large = >.8
The probability of getting a 5 option question right.
What is .20
Characteristics of a normal curve
Symmetrical, unimodal, extend indefinitely in both directions
Every nth member of the population is taken from a list and included in the sample.
Claiming significance when there is none
What is Type I error
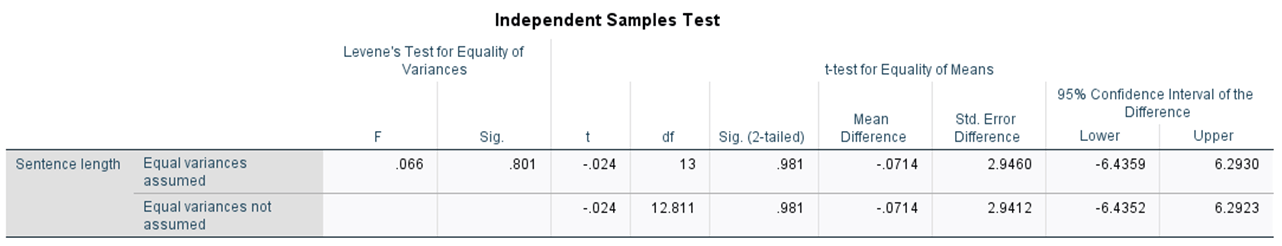
Identify the t-value and degrees of freedom
-.024, 13
A probability of 0.
____ is to theoretical events as ____ is to actual events.
Normal distribution; Frequency Distribution
These two types of sampling require breaking the population into smaller groups before drawing a sample.
Cluster and Stratified
Sampling error is not responsible for obtained differences
Reject the Null Hypothesis
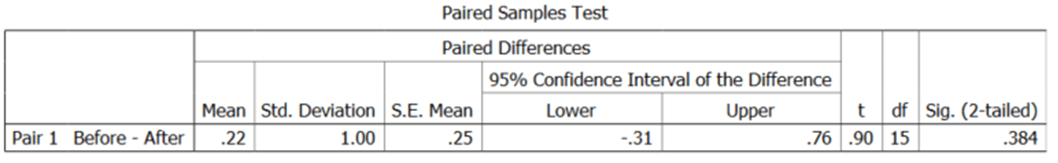 Identify the difference between means.
Identify the difference between means.
.22
The probability of obtaining any one of several different and distinct outcomes.
True or False:
A normal curve can be skewed.
False
The inevitable difference between a random sample and its population.
____ is to difference between means as _____ is to no difference between means
Alternative, null
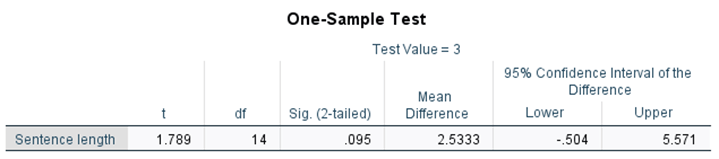
Determine the significance.
Not significant. Fail to reject null