The cell membrane allows certain substances to easily pass into or out of the cell, but not other substances. Which term applies to this aspect of the cell membrane?
Selective Permeability
The three types of Passive Transport are
Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, & osmosis
Water moves out of a cell when the cell is placed into a/an _____________ solution? (AKS 2a)
Hypertonic
Which of the following best describes the role of an enzyme in living organisms? (AKS 1a1)
Enzymes work as catalysts to speed up the rate of a reaction.
In what structure would one find the green pigment, chlorophyll?
Cholorplast
The "tails" of the bilayer are hydrophobic. What does this term mean?
Water fearing
The diagram above show which type of transport? 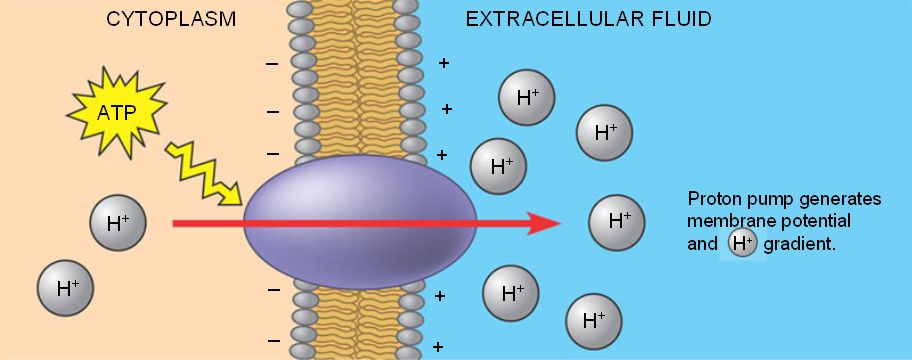
Active Transport
What is the term used to describe an animal cell bursting from too much water entering? (AKS 2a2)
Cytolysis
What is the term used to describe the energy needed to get a reaction started? (AKS 1a1)
Activation Energy
The model represents a process that occurs in organisms.
X -------------------> Y + Y
(substance) (2 smaller substances)
Which of the following could be represented by X and Y, if X is directly changed into Y?
X= protein and Y= amino acids
Describes the properties of the phospholipid bilayer?
The head region is called hydrophilic because they do interact with water molecules. The tail region is called hydrophobic because they do not interact with water.
The release of large amounts of wastes or other substances from inside the cell to outside the cell is called... (AKS 2a1)
Exocytosis
If a tulip plant is not watered, it wilts because it ________. (AKS 2a2)
Loses turgor pressure
The site where an enzyme bonds to its substrate is called the _______________. (AKS 1a1)
Active site
Which organic molecule is represented below? (AKS 1a)
Glucose
Observe the Fluid Mosaic Model of the cell membrane below. the large BLUE structures that pass across the entire membrane provide structure and help transport substances across the cell membrane. These structure are made from which organic macromolecule? (AKS 2a1)
Proteins
Which of the following IS NOT a form of passive transport?
1. Facilitated Diffusion 2.Endocytosis 3.Diffusion
Endocytosis
A sample of red blood cells are placed in an isotonic solution and viewed under the microscope. Then, sugar is added to the solution. The cells are viewed under a microscope again.
Which question might a student ask about what they see?
Did the red blood cells release water through osmosis because the sugar solution is hypertonic to the red blood cells?

According to the graph above, what is the ideal temperature for the enzyme?
40 degrees
Two products of respiration are _______.
Carbon Dioxide and Water
What are some roles that proteins play in the cell membrane?
To transport substances across the membrane and provide structure for the membrane.
Compared to small cells, large cells have more trouble.....
Transporting substances in and waste products out due to surface area to volume problems and stress on the membrane
Why do plant cells NOT burst when placed in hypotonic solutions? (AKS 1a)
The cell membrane pushes against the cell wall and the cell wall prevents bursting. This is called plant turgor.
In what way could you increase the rate of the reaction as it is taking place in Model C?
Add more enzymes to the reaction.
The total number of ATP molecules produced from the complete breakdown of a single molecule of glucose is ________.
36
