(x3 + 3x2 + 5x − 4) − (3x3 − 8x3 − 5x + 6)
-2x3 + 11x2 + 10x - 10
45d5 - 15d3
15d3(3d2 - 1)
Determine the end behavior.
y = -3x2 -x + 6
degree: 2
LC: negative
End Behavior: down down
4sqrt(12) + 2sqrt(27)
14sqrt(3)
-4x2(-5x + 8x3)
20x3 - 32x5
y2 - 4y - 21
(y - 7)(y+ 3)
Determine the end behavior.
y = x2 (x+3)(x - 5)4
Degree: 7
LC: positive
End Behavior: down up
5sqrt(200) - 3sqrt(50)
35sqrt(2)
(2x - 5) (3x + 4)
6x2 - 7x - 20
9a2 - 49c2
(3a + 7c)(3a - 7c)
Determine the solutions algebraically.
(x2 + 7x + 12)(x - 8) = 0
{-3, -4, 8}
2sqrt(3)(3sqrt(6) - 3sqrt3)
18sqrt(2) - 18
(21x^3 - 35x^2)/(7x)
3x2-5x
Factor Completely
3x2 -75
3(x + 5)(x - 5)
State the degree, the zeros and the end behavior and make a sketch.
f(x) = x(x2 - 9)(x2 + 9x + 18)
0 mult 1 3 mult 2
3 mult 1 -6 mult 1
degree 5 LC positive
down up
(2sqrt5 + 6 sqrt15)/(2sqrt5)
1 + 3sqrt3
(x^3 -15x + 6)/(x + 4)
x2 - 4x + 1
2/(x+4)
x4 - 5x3 + 2x - 10
(x3 + 2)(x - 5)
Determine the solutions and then write a possible equation for the graph in factored form.
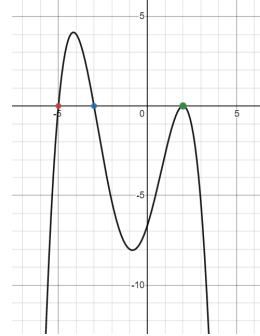
-5 mult 1 -3 mult 1 2 mult 2
degree 4 LC negative
f(x) = -(x + 5)(x + 3)(x - 2)2
7/(3 - sqrt2
3 + sqrt(2)
3x2 + 14x + 8
(3x + 2) (x + 4)