variable that is measured outcome of the experiment
BONUS
dependent variable
BONUS
give me a simple hypothesis.
digestion(metabolism) is an example of which characteristic of life
obtain/use energy
what is the two word naming system used to identify organisms
BONUS
binomial nomenclature
BONUS
who came up with this system?
what is the difference between biotic and abiotic factors? name 2 examples of each
abiotic: nonliving [wind, sun, temperature]
biotic: living [grass, fungi, animals]
how many electrons fit in each of the first 3 electron shells
2,8,8
identify this macromolecule
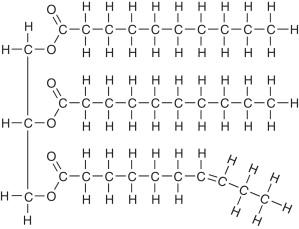
lipid
which organelle makes lipids
smooth ER
variable that is manipulated/tested to see what effect it has on the outcome
independent variable
Which characteristic of life is this an example of :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-641101778-b5ce934c6bcf428abf993f722af580d3.jpg)
responding to the environment
how are organisms classified
plants contribute to the water cycle by releasing water through what process
transpiration 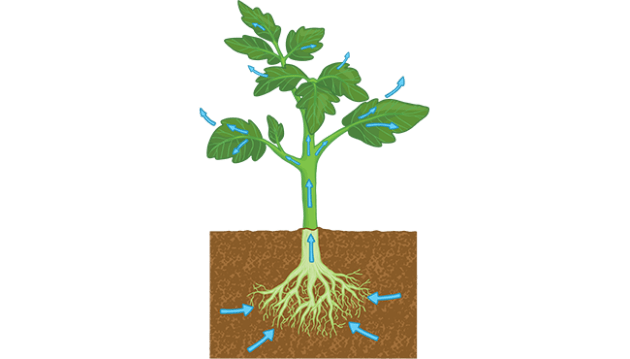
what type of bond is formed between individual water molecules and contributes to some of the many properties of water
BONUS
hydrogen bonds
BONUS
identify and explain one of the special properties of water
lipase is an example of... and what is its function
enzyme that breaks down lipids
name the three types of passive transport
diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
what are the two types of data we hope to collect from an experiment
qualitative and quantitative
 BONUS
BONUS
growth and development
BONUS: what is the difference between the two
what is the species of ursus martimus
martimus
name a process that releases carbon into the atmosphere and a process that takes in carbon from the atmosphere
in: photosynthesis
out: cellular respiration, combustion, decomposition
carbon forms ____ ______ bonds
(number and type)
four covalent
name two things that affect the function of enzymes
temperature, pH, amount of substrate
name 3 differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
prokaryotic: no nucleus, simple, unicellular
eukaryotic: nucleus, large, complex, membrane bound organelles
if you want to test which type of dog food makes your dog lose weight what would be the dependent and independent variables?
BONUS
dependent: how much weight the dog lost
independent: type of dog food
BONUS: 3 things that would need to be controlled in this experiment

responding to stimuli/environment
what is the genus of ursus americanus
ursus
which trophic level has the most amount of energy and where does this energy come from?
producers, the sun
draw the electron dot model for potassium (K)
Atomic #: 19

Stort term energy storage
BONUS
carbohydrates
specifically what form do humans store carbohydrates in [glycogen]
what 4 structures do ALL cells have
BONUS
-cytoplasm
-ribosomes
-DNA
-cell membrane
BONUS
name one structure that is unique to plant cells
what are the 3 parts of the cell theory
BONUS
1. all living things are made of one or more cells
2. all cells come from other cells
3. cells are the basic unit of structure and function of living things
BONUS
what makes this a scientific theory?
viruses are not living because they are unable to reproduce on their own. How do viruses reproduce ??
they hijack a hosts cells to reproduce for them
the size of blue jay population has increased 2% in one year, name one thing that may have occurred in that specific ecosystem that contributed to the population boost.
BONUS
decrease in predators, increase in prey, increase in food availability, decrease in diseases, increase in habitat space
BONUS
what is the term for an ecosystems ability to maintain a certain population based on the amount of resources available
identify the primary producer, primary consumer, a secondary consumer and a tertiary consumer
primary producer: phytoplankton
*other answers will vary
what is the function of enzymes
to speed up chemical reactions [by lowering activation energy]
which macromolecule makes up the cell membrane
BONUS
BONUS
how do lipids react with water and how does that help the cell membrane do its job?
 BONUS
BONUS
facilitated diffusion
BONUS
what is the type of transport that uses transport proteins that NEED energy [ATP] to operate