Describe factors that result in natural variations in climate….e.g. past glacial and interglacial periods
include ocean currents (distribution of cold and warm water around Earth), ocean-atmospheric oscillations, intensity of the sun, time of year, and volcanic eruptions. Long term variability can be explained by the 3 Milankovitch cycles. The first involves the elliptical orbit stretching and shortening (100,000 years). The next cycle entails the angle of tilt of earth’s axis shifting (40,000 years). And lastly, the earth “wobbles” on the axis (26,000 years) (p. 210-213).
These non-native species can cause environmental harm when introduced to a new area, often outcompeting local species.
What are invasive species?
What is a closed system?
A closed system is a natural physical system that does not allow transfer of matter in or out of the system
What is the Shannon-Wiener Index?
A mathematical measure used in science to quantify the diversity in an area
What are the temperatures that the UN/countries are aiming not to go over/limit to in terms of warming? What is one of the big reasons for global warming? Think of your mock UN meeting.
2 degrees Celsius; it is even better to be under 1.5 degrees Celsius
Emmissions: CO2 from fossil fuels
which month had the highest precipitation?

March
This type of symbiotic relationship benefits both species involved, such as bees pollinating flowers while collecting nectar.
What is Mutualism?
What is a Marine Protected Area?
Designated areas of the ocean, including estuaries and Great Lakes, set aside for conservation and management to protect marine life and habitats, while potentially allowing for sustainable use of resources
Would the abundance of creatures be different at night? Why or why not?
Yes, because species can be nocturnal, diurnal, and crepescular, the amount of animals, and the number of different species changes depending on the time of day
Describe your forceps/spoon lab. What was being simulated in A? What was being simulated in B?
Forceps: Native predator. Spoon: Non-native or invasive predator. Beads: Food/Prey
Sim A: Native predator being out-competed by invasive predator
Sim B: Native predator and non-native predator feeding on the same prey/food, not competition
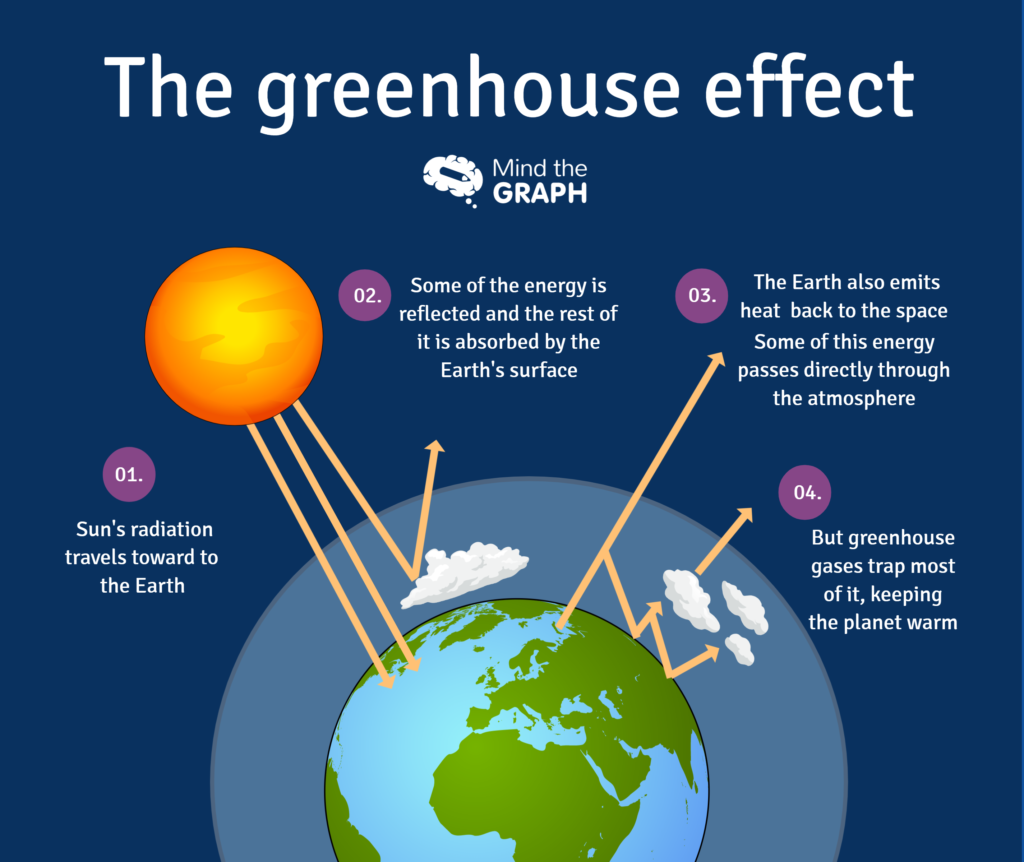
Draw a diagram illustrating the greenhouse effect
This occurs when individuals of different species compete for the same resource in an ecosystem, such as food or space.
What is interspecific competition?
What is a primary producer?
Plants, algae, and certain bacteria that capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and convert it into forms that living cells can use.
Describe how you measured biodiversity in your coral snapshot lab. How did you differentiate diversity between the sites?
Counted species, calculated percentage of transect, found richness, evenness, and Shannon-Wiener Index
Describe your bioassay lab. Points to consider: How did you measure toxicity? What was the point/term where 50% of your test samples (RIP Daphnia, let's pour one out for the homeboys) died? How do toxic substances affect different demographics?
Dose/response study – Where response includes the biological changes caused by exposure to a chemical. Bioassay is a standardized method to determine chemical toxicity. LD50 is where half of the test subjects die. The same dose of a chemical (eg: 5mg of cyanide) will affect children differently than it will affect an adult. Pregnant women and the elderly may also be affected differently.
list 5 effects of climate change
5 effects of climate change are (p. 219):
In 50 years there has been an 8 inch rise in global sea level from thermal expansion, melting glaciers, and melting ice sheets.
An increase in the frequency of wildfires as well as pests.
Earlier springs lead to early flowering, migration, and hotter summers from the onset of warm weather.
Heavier storms from the increased energetic atmospheric circulation.
- Cumulative costs for damaged infrastructure, lost property values, and health costs due to climate change.
These long-term changes in the Earth’s orbit and tilt are believed to be a significant factor in triggering ice ages.
What are Milankovitch Cycles?
What is biotic potential?
the maximum rate at which a species can reproduce under ideal conditions
What is richness?
Number of different species in a given area
What is the Earth overshoot day, and what does it represent? If your overshoot day is April 24th, what does that mean?
August first; The day when humanity's demand for natural resources exceeds the Earth's capacity to regenerate them
That means you/if everyone used resources the same as you/your resources would be used up by April 24th.
What are some conclusions you can draw from this graph?

Keeling curve, increase since industrial revolution from anthropogenic activity
This type of factor, such as food or disease, limits population growth more significantly as population density increases.
What is a density dependent factor?
What is the tropic level pyramid; draw and label it!
:)
What are the pros and cons of protected marine areas?
They can help protect biodiversity, allowing fish populations and coral reefs to recover while supporting surrounding fisheries through the spillover effect. They also boost ecotourism and research opportunities, but they can be costly to enforce, may create economic hardships for fishing communities, and still face threats from climate change and pollution.