What role does Bromothymol Blue play in demonstrating the concept of pH in biological systems?
A) It acts as a nutrient source.
B) It changes color based on acidity levels.
C) It produces energy during photosynthesis.
D) It serves as a carbon source.
B) It changes color based on acidity levels.
In what ways does water facilitate biochemical reactions in living organisms?
A) It acts as a solvent and medium for transport.
B) It serves exclusively as a waste product.
C) It only supports photosynthesis.
D) It is unnecessary for cellular functions.
A) It acts as a solvent and medium for transport.
What processes contribute to the formation of sedimentary rocks?
A) Erosion and crystallization.
B) Weathering, compaction, and cementation.
C) Deformation and heat.
D) Rock cycling through metamorphism.
B) Weathering, compaction, and cementation.
How does sedimentation affect aquatic ecosystems?
A) It purifies water.
B) It can lead to the accumulation of nutrients, supporting diverse life forms.
C) It removes all forms of life.
D) It has no impact on ecosystems.
B) It can lead to the accumulation of nutrients, supporting diverse life forms.
How are metamorphic rocks formed?
A) Through the cooling of lava.
B) By the compression and alteration of existing rocks under heat and pressure.
C) By the accumulation of sediments.
D) By crystallization in water.
B) By the compression and alteration of existing rocks under heat and pressure.
Letter A represents:
A) Igneous rock
B) Metamorphic rock
C) Sedimentary rock
D) Sediment
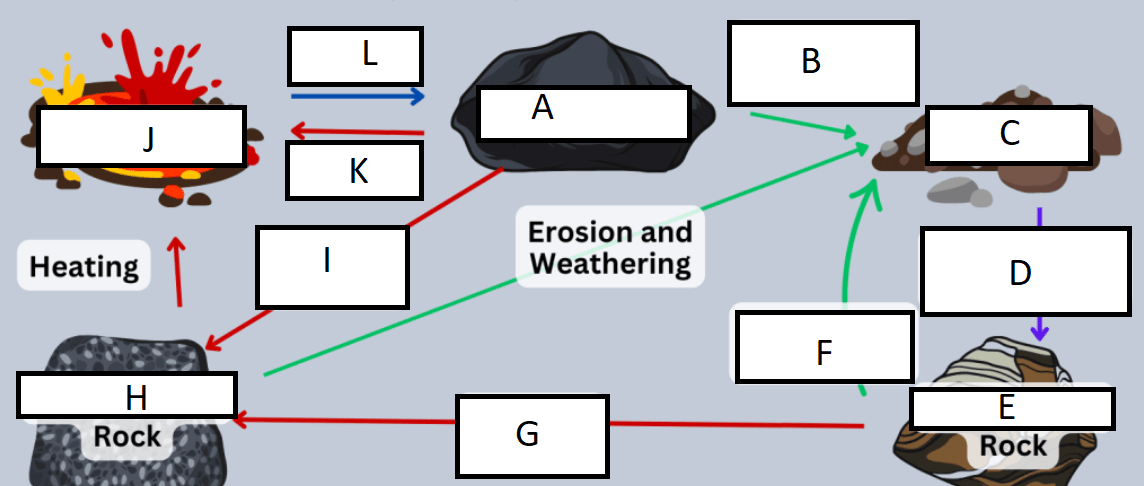
A) Igneous rock
G represents:
A) heat/pressure
B) weathering/erosion
C) cooling/heating
D) compaction/cementation
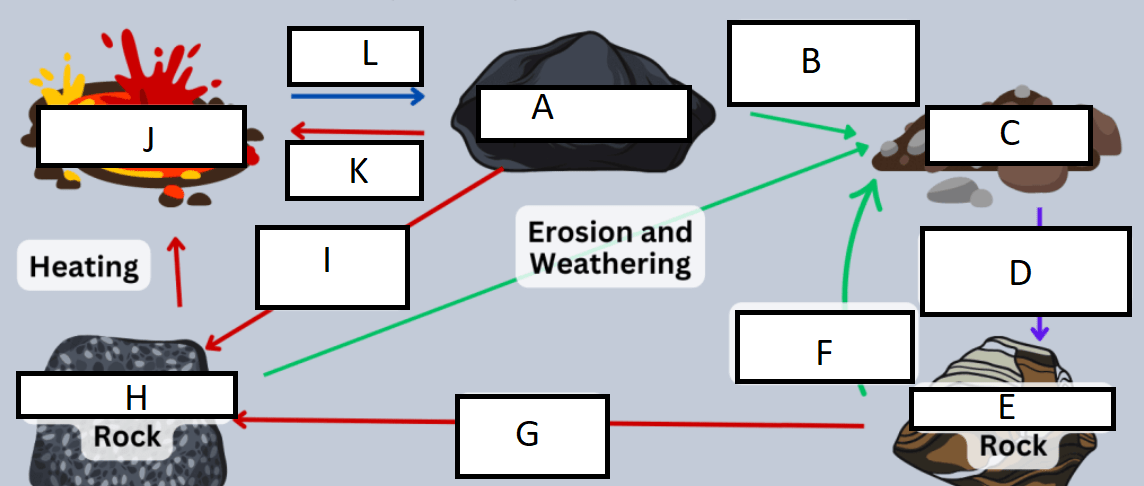
A) heat/pressure
How does the process of photosynthesis contribute to the carbon cycle?
A) It releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
B) It converts solar energy into chemical energy, storing carbon in organic molecules.
C) It breaks down glucose into energy.
D) It relies solely on soil nutrients.
B) It converts solar energy into chemical energy, storing carbon in organic molecules.
How do producers and consumers differ in their acquisition of energy?
A) Producers create energy, while consumers only use it.
B) Both create energy in the same manner.
C) Consumers produce energy through photosynthesis.
D) Producers obtain energy by consuming other organisms.
A) Producers create energy, while consumers only use it.
How does weathering contribute to soil formation?
A) It removes nutrients from the soil.
B) It breaks down rocks into smaller particles that develop into soil.
C) It exclusively transports soil.
D) It has no significant impact on soil.
B) It breaks down rocks into smaller particles that develop into soil.
What is the result of rock deformation under stress?
A) Rocks remain unchanged.
B) Rocks may bend, break, or change their position.
C) Rocks become more stable and resistant.
D) Deformation only occurs in sedimentary rocks.
B) Rocks may bend, break, or change their position.
How does the rock cycle illustrate the dynamic nature of Earth’s geology?
A) It shows that rocks are static and unchanging.
B) It illustrates the continuous transformation of rocks from one type to another through various geological processes.
C) It only applies to igneous rocks.
D) It does not involve metamorphic rocks.
B) It illustrates the continuous transformation of rocks from one type to another through various geological processes.
Letter B represents:
A) compaction
B) sedimentation
C) Heat and pressure
D) weathering and erosion
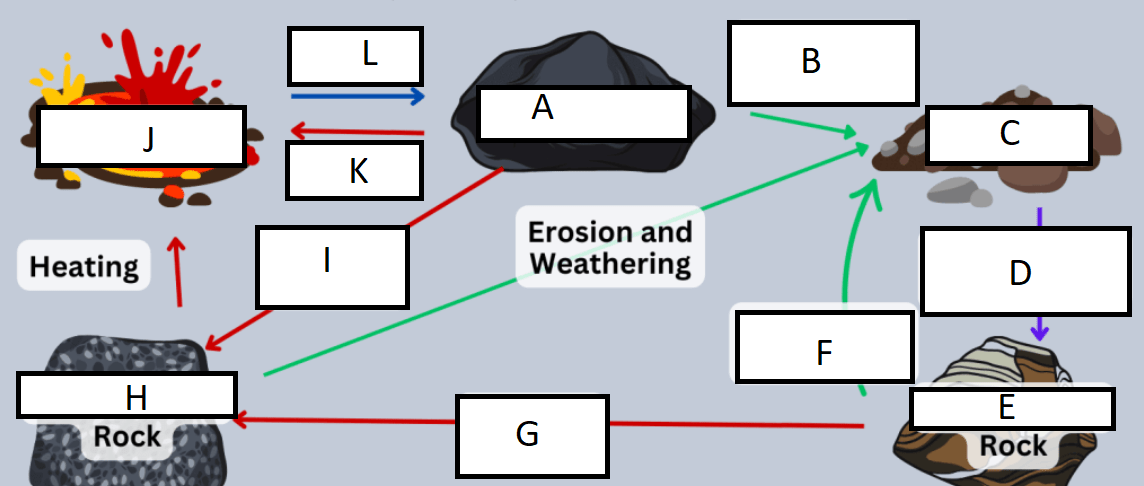
D) weathering and erosion
H represents:
A) Igneous rock
B) Sedimentary rock
C) Metamorphic rock
D) Sediment
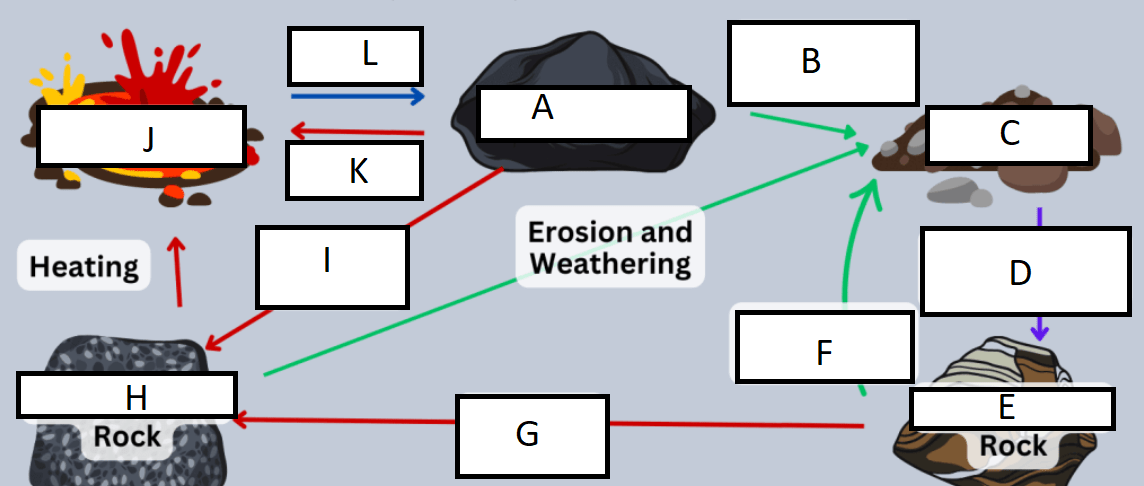
C) Metamorphic rock
In what way does cellular respiration support cellular functions in living organisms?
A) By converting sunlight into glucose.
B) By providing ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
C) By storing carbon in fossils.
D) By releasing oxygen into the atmosphere.
B) By providing ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
How does the law of conservation of matter apply to chemical reactions in ecosystems?
A) Matter is created during reactions.
B) Matter is destroyed in closed systems.
C) Matter is neither created nor destroyed but transformed.
D) Matter is irrelevant in ecological contexts.
C) Matter is neither created nor destroyed but transformed.
In what way does erosion shape the landscape?
A) By depositing nutrients.
B) By transporting soil and rock material from one location to another.
C) By creating new rocks.
D) By solidifying existing structures.
B) By transporting soil and rock material from one location to another.
How does crystallization contribute to the formation of igneous rocks?
A) It occurs only on the surface of the Earth.
B) It results from the cooling and solidification of molten rock.
C) It only applies to sedimentary rocks.
D) It has no relevance to rock formation.
B) It results from the cooling and solidification of molten rock.
In what way does gravity influence geological processes on Earth?
A) It has no effect on sediment transport.
B) It drives the movement of water and tectonic plates, impacting erosion and sedimentation.
C) It only affects atmospheric phenomena.
D) It is irrelevant to rock formation.
B) It drives the movement of water and tectonic plates, impacting erosion and sedimentation.
C represents:
A) sedimentary rock
B) sediment
C) weathering
D) compaction
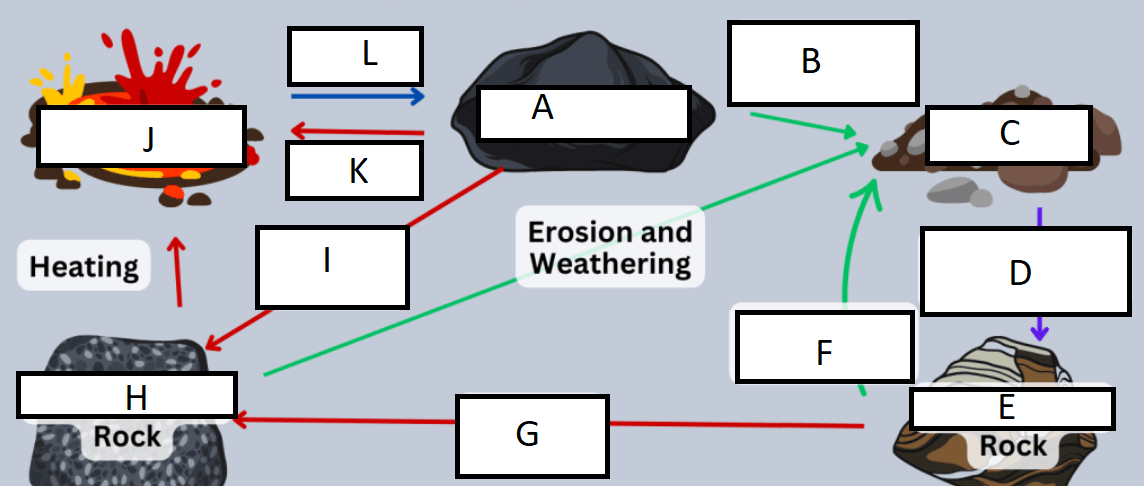
B) sediment
I represents:
A) compaction
B) sedimentation
C) Heat and pressure
D) weathering and erosion
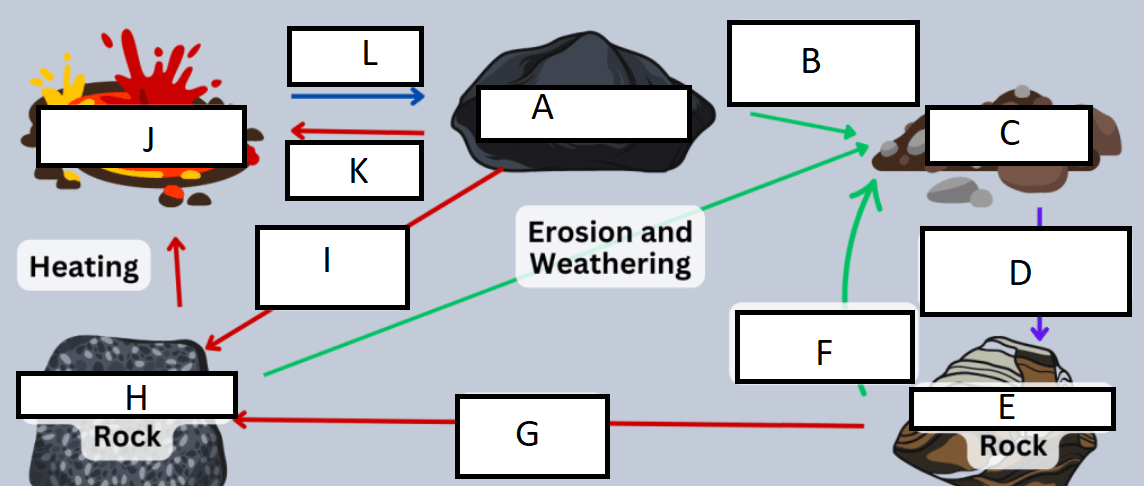
C) Heat and pressure
How does increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere affect global temperatures?
A) It cools the Earth.
B) It has no effect.
C) It contributes to the greenhouse effect, trapping heat.
D) It enhances photosynthesis without consequences.
C) It contributes to the greenhouse effect, trapping heat.
What role does glucose play in cellular metabolism?
A) It is a waste product of respiration.
B) It is a primary energy source for cells.
C) It is a form of carbon dioxide.
D) It serves only in structural functions.
B) It is a primary energy source for cells.
How does pressure play a role in the formation of metamorphic rocks?
A) It decreases the temperature of existing rocks.
B) It can cause rocks to melt into magma.
C) It alters the mineral composition and structure of rocks.
D) It has no effect on rock formation.
C) It alters the mineral composition and structure of rocks.
What distinguishes igneous rocks from other rock types?
A) They are formed through weathering processes.
B) They are formed from the solidification of molten material.
C) They contain fossils.
D) They are formed exclusively underwater.
B) They are formed from the solidification of molten material.
How do photosynthesis and cellular respiration illustrate the concept of energy transformation and matter cycling in an ecosystem?
A) Photosynthesis converts carbon dioxide into oxygen, while cellular respiration uses oxygen to produce glucose.
B) Photosynthesis stores energy in glucose, which is then released during cellular respiration, demonstrating a cyclical flow of energy and matter.
C) Cellular respiration generates energy that is then used to perform photosynthesis, creating a closed system.
D) Both processes are independent of each other, with photosynthesis occurring only in plants and cellular respiration occurring only in animals.
B) Photosynthesis stores energy in glucose, which is then released during cellular respiration, demonstrating a cyclical flow of energy and matter.
D represents:
A) heat/pressure
B) weathering/erosion
C) cooling/heating
D) compaction/cementation
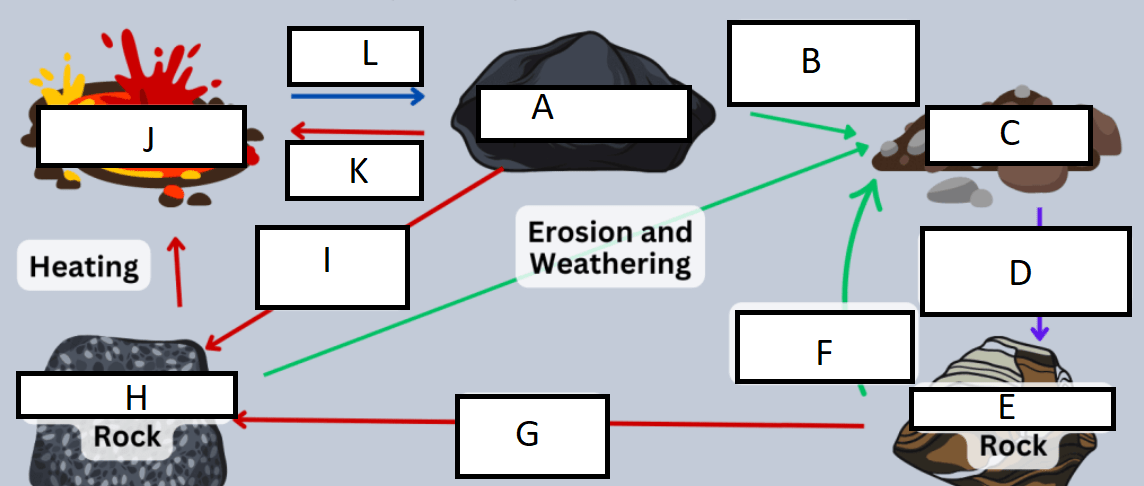
D) compaction/cementation
J represents:
A) Igneous rock
B) Sedimentary rock
C) Metamorphic rock
D) Magma/Lava
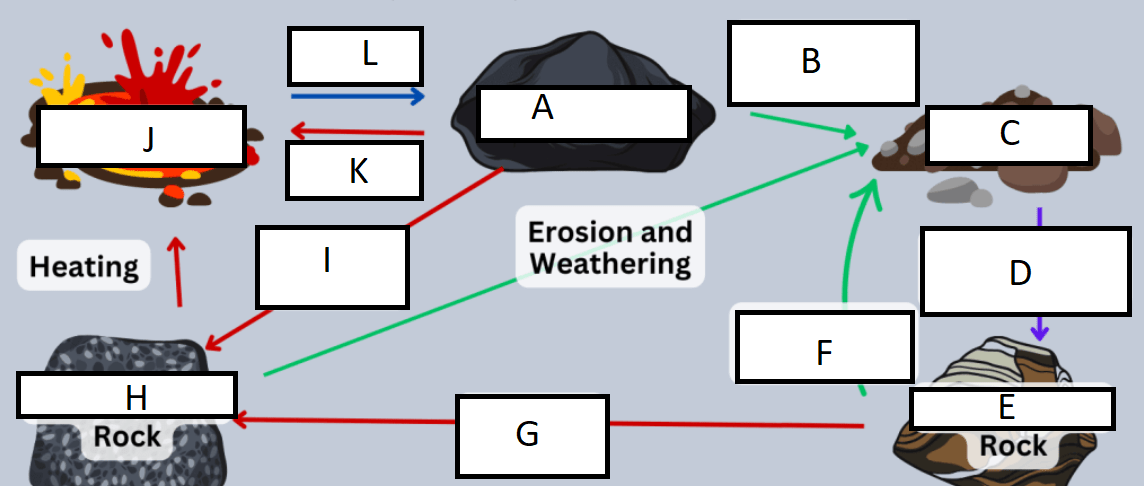
D) Magma/Lava
Why is oxygen vital for aerobic organisms?
A) It is a byproduct of cellular respiration.
B) It is necessary for photosynthesis.
C) It is required for the breakdown of glucose to release energy.
D) It serves as a carbon source.
C) It is required for the breakdown of glucose to release energy.
Why is ATP often referred to as the "energy currency" of the cell?
A) It stores energy temporarily for immediate use.
B) It is the only form of energy available.
C) It is produced only during photosynthesis.
D) It does not participate in metabolic reactions.
A) It stores energy temporarily for immediate use.
What is the significance of heat in the rock cycle?
A) It cools down rocks during formation.
B) It is essential for the melting of rocks into magma and metamorphic transformation.
C) It has no role in the processes of rocks.
D) It only affects sedimentary rocks.
B) It is essential for the melting of rocks into magma and metamorphic transformation.
What is the primary characteristic of sedimentary rocks?
A) They are formed from molten magma.
B) They are composed of particles transported and deposited by water, wind, or ice.
C) They contain no minerals.
D) They are formed under extreme heat and pressure.
B) They are composed of particles transported and deposited by water, wind, or ice.
In what way do photosynthesis and cellular respiration collectively ensure the stability and functionality of ecosystems, particularly in terms of energy flow and nutrient cycling?
A) Photosynthesis produces glucose, which is then directly consumed by primary consumers without any further transformation.
B) Cellular respiration releases nutrients back into the soil, allowing for continuous plant growth without the need for photosynthesis.
C) The interdependence of photosynthesis and cellular respiration creates a continuous cycle of energy transfer and matter recycling, supporting diverse life forms and ecosystem resilience.
D) Both processes are linear, with photosynthesis occurring only during the day and cellular respiration occurring only at night, limiting the cycling of nutrients.
C) The interdependence of photosynthesis and cellular respiration creates a continuous cycle of energy transfer and matter recycling, supporting diverse life forms and ecosystem resilience.
E represents:
A) Igneous rock
B) Sedimentary rock
C) Metamorphic rock
D) Sediment
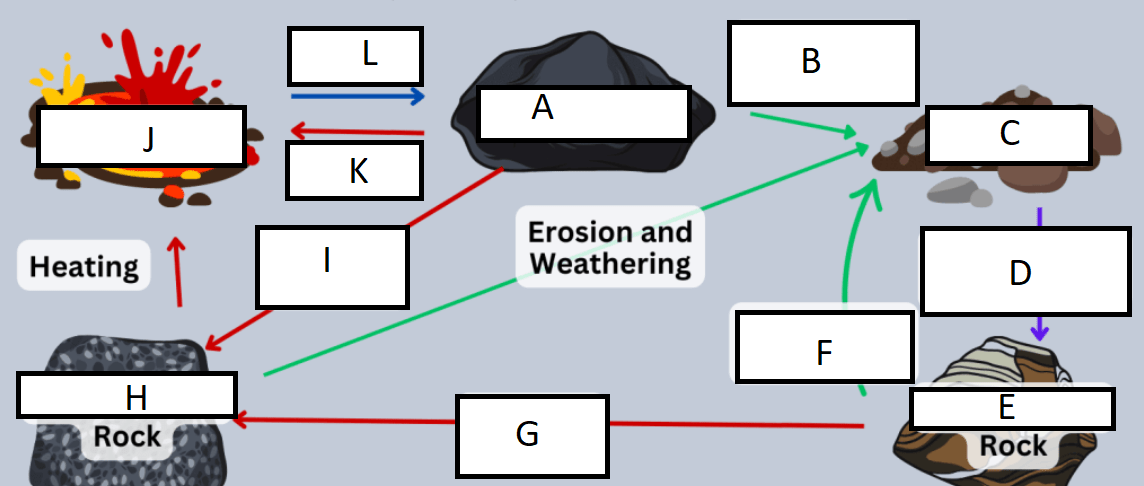
B) Sedimentary rock
K represents:
A) heating
B) weathering/erosion
C) cooling
D) compaction/cementation
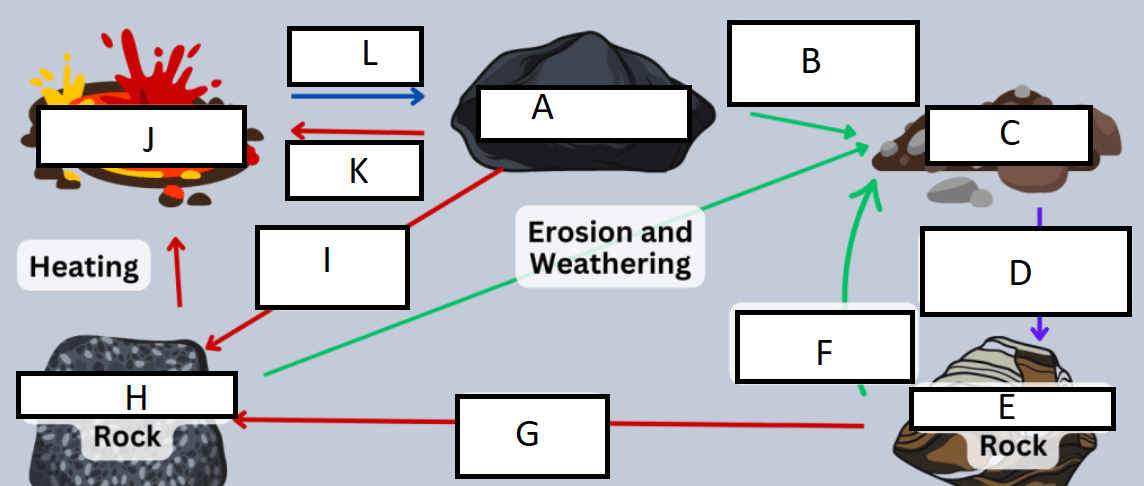
A) heating
How do disruptions in the processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration affect the balance of energy flow and nutrient cycling in an ecosystem?
A) Disruptions in photosynthesis lead to increased oxygen levels, benefiting aerobic organisms.
B) A decline in either process can result in decreased energy availability for consumers, causing imbalances in food webs and nutrient cycles.
C) Cellular respiration can function independently of photosynthesis, ensuring that ecosystems remain stable.
D) Only photosynthesis impacts nutrient cycling; cellular respiration does not play a significant role.
B) A decline in either process can result in decreased energy availability for consumers, causing imbalances in food webs and nutrient cycles.
In what manner do changes in environmental conditions, such as increased carbon dioxide levels, influence the balance between photosynthesis and cellular respiration in ecosystems?
A) Increased carbon dioxide enhances photosynthesis, potentially leading to higher primary productivity and oxygen levels, which benefits cellular respiration.
B) Higher carbon dioxide levels solely benefit cellular respiration, causing a decline in photosynthesis.
C) Environmental changes have no significant impact on the balance between photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
D) Increased carbon dioxide only affects animal respiration, not plant processes.
A) Increased carbon dioxide enhances photosynthesis, potentially leading to higher primary productivity and oxygen levels, which benefits cellular respiration.
What role do photosynthesis and cellular respiration play in maintaining biodiversity within ecosystems?
A) They do not affect biodiversity; other factors are more critical for species diversity.
B) By facilitating energy flow and nutrient cycling, they support a variety of organisms and their interactions, promoting ecosystem resilience and biodiversity.
C) Photosynthesis is more important for biodiversity, while cellular respiration is limited to energy transfer.
D) Both processes are detrimental to biodiversity as they limit the variety of available nutrients.
B) By facilitating energy flow and nutrient cycling, they support a variety of organisms and their interactions, promoting ecosystem resilience and biodiversity.
How do photosynthesis and cellular respiration contribute to the stability of the carbon cycle within ecosystems?
A) Photosynthesis removes carbon from the atmosphere, while cellular respiration releases it, creating a balanced carbon cycle that supports life.
B) Both processes solely rely on soil nutrients and do not influence atmospheric carbon levels.
C) Cellular respiration is the only process that affects the carbon cycle, as it consumes carbon for energy.
D) Photosynthesis and cellular respiration have no significant impact on the carbon cycle in ecosystems.
A) Photosynthesis removes carbon from the atmosphere, while cellular respiration releases it, creating a balanced carbon cycle that supports life.
What impact does deforestation have on the interconnected processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration within an ecosystem?
A) Deforestation enhances photosynthesis by allowing more sunlight to reach the ground.
B) It decreases the number of trees available for photosynthesis, reducing oxygen production and disrupting the balance of cellular respiration in the ecosystem.
C) Deforestation has no significant impact on these processes, as other organisms compensate for the loss.
D) It solely affects cellular respiration, leading to increased carbon dioxide levels.
B) It decreases the number of trees available for photosynthesis, reducing oxygen production and disrupting the balance of cellular respiration in the ecosystem.
F represents:
A) compaction
B) sedimentation
C) Heat and pressure
D) weathering and erosion
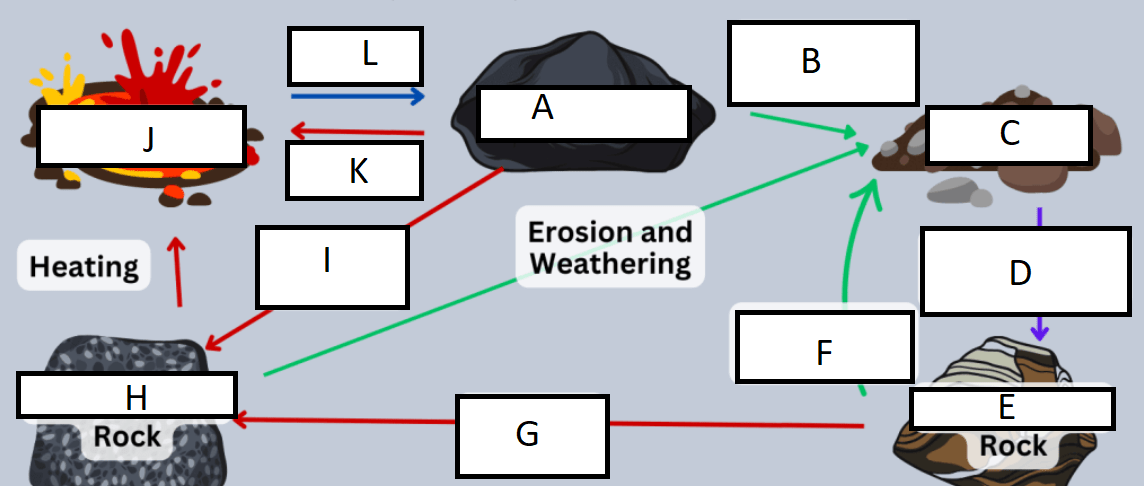
D) weathering and erosion
L represents:
A) heating
B) weathering/erosion
C) cooling
D) compaction/cementation
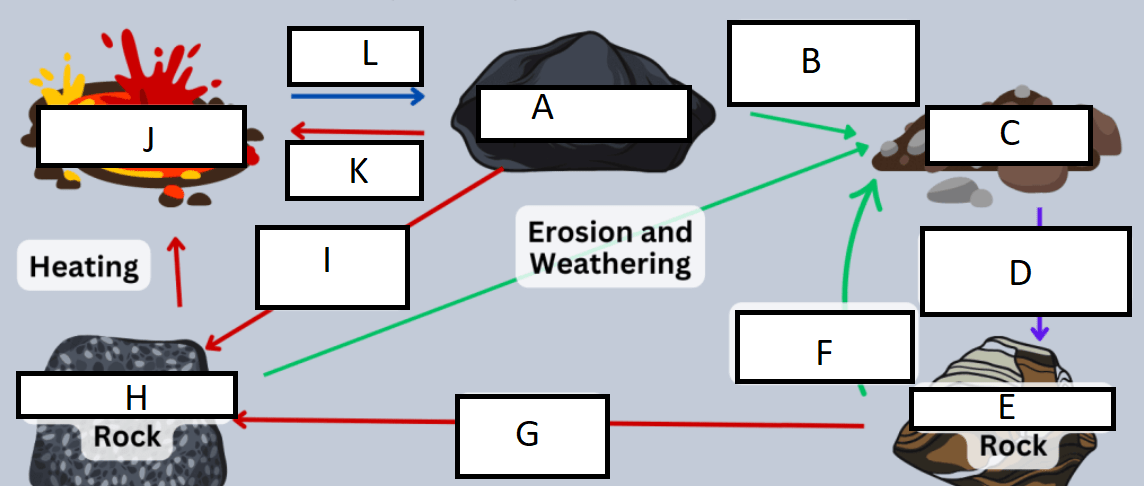
C) cooling