A patient presents to you with high glucose. You Dx him with T2DM. When should you begin checking his urine for protein?
Immediately and then once a year after that
List the 3 things you must do in order to help prevent diabetic nephropathy from developing in a diabetic person
control blood sugar, reduce BP, reduce proteinuria
A patient being treated for bipolar disorder presents to the clinic with polyuria. Blood works shows high ADH, despite high urine output. Assume the medication being used to treat her bipolar disorder is causing her kidney condition and we don't want to stop this treatment. What other medication could be given that would improve the kidney's ability to respond to ADH?
Amiloride (pt has lithium nephropathy, which has caused a nephrogenic diabetes insipidus and amiloride is useful in reversing the diabetes)
a 23Yo African American patient presents with Foamy urine. UA reveals proteinuria, and Urine microscopy shows RBCs. A kidney biopsy is shown below:
A defect in a gene is implicated in the patients condition. What is the gene?
APOL1
First line medical treatment for hepatorenal syndrome
albumin and vasopressors
You see a patient and determine that they have a bacterial infection. You prescribe ciprofloxacin and send them on their way. A few days later, they present to the ED with a fever and a rash. BUN and Scr are elevated. A biopsy is done and you see this:
Additionally, urine microscopy reveal WBC casts. What is the best first step towards treatment?
Discontinue the cipro
Effacement of the podocyte foot processes
A patient with lesch nyhan syndrome develops kidney stones due to the build up of a certain compound caused by their disease. What pH level would the urine need to be at to ensure that the stones are soluble?
Pt has uric acid stones (lesch nyhan increased uric acid in the body). These stones are more soluble at pH's above 5.5
A patient with T2DM x 1 year has their urine checked, and their creatinine has risen from 1.1 to 5.7 in the last three months. Is it likely that they are suffering from diabetic nephropathy?
No, a rapid rise in serum creatinine and the short duration of type 2 DM means that there is likely something else going on. 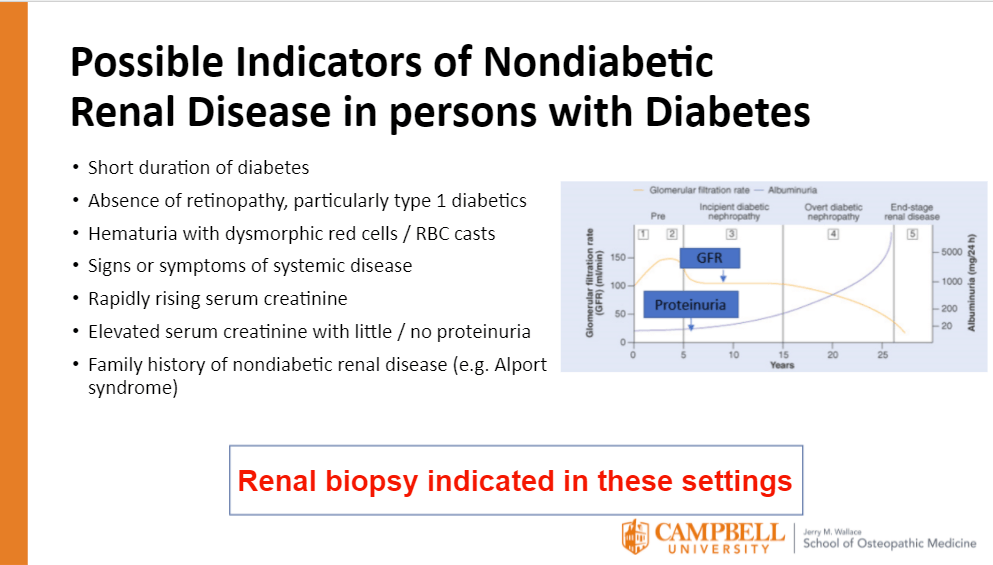
A patient has a urine dipstick completed during a yearly physical and comes back positive for blood in the urine. He presents to the nephrologist, who does a biopsy. Biopsy is seen below:
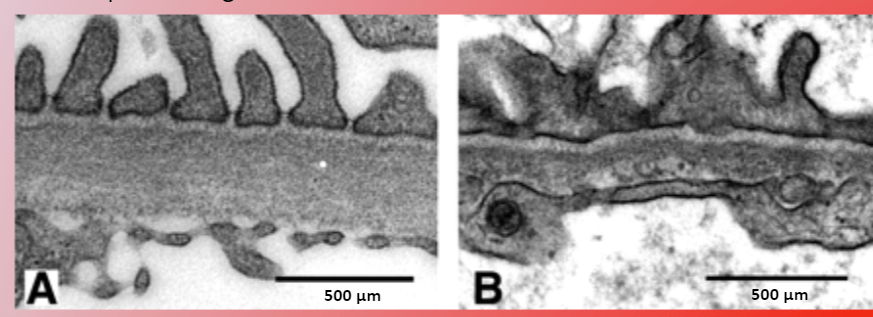
A normal GBM is on the left (A), and the patient's is on the right (B). What is the best treatment?
To do nothing. Thin basement membrane disease is benign
You have a patient with hypernatremia and hypokalemia due to diarrhea. Your attending wants to increased fluid in the blood by using an isotonic solution. He writes and order for D5 1/2NS. Why should he be fired?
Don't give dextrose containing fluid in someone with hypokalemia. The Dextrose will increase insulin, which further drives K+ into cells, lowering it even more.
A patient presents with hematuria. CT shows the below image:

Based on the arrow sign above, what is the most likely diagnosis if the patient is an adult male?
RCC
A patient presents with hematuria. It is found that the patient has also had a stomach bug for the past few days. Biopsy shows this:
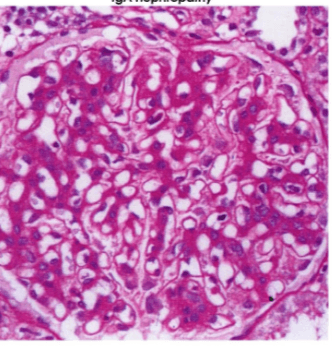
What is the likely diagnosis?
IgA nephropathy
A patient presents with HTN secondary to bilateral ureteral obstructions. Why would a patient with bilateral obstructions develop HTN
HTN from volume expansion, cant get rid of salt and water.
What would the treatment for a T3bc Renal cell carcinoma be?
radical nephrectomy + cavectomy to remove portion of the vena cava that the tumor has spread to
A 25 Yo male presents with signs of hematuria and hemoptysis. Lung biopsy shows IgG abs against the basement membrane in the lungs. If a 68 Yo female was diagnosed with the same disease, what organ system would most likely be affected?
Kidneys
A patient with renal stones requires immediate decompression. What are the two options available?
Percutaneous nephrostomy, Ureteral stent
A 15 year old male presents to the clinic with blood in his urine. Hx reveals that he went deaf around age 11. PE shows oddly shaped lenses bilaterally. If a genetic condition is the cause, what cellular component is not being properly created?
Type 4 collagen
In those with IgA nephropathy, what is wrong with the actual IgA antibodies that causes them to accumulate in the kidneys?
They are improperly glycosylated, they lack galactose.
A patient presents with acute flank pain. A biopsy shows this:
Additionally, pt has complaints of recurrent calcium oxalate kidney stones, chronic low back pain, fatigue, and pallor. What is the first blood test you would do to help diagnose the patients condition?
Patient has CRAB symptoms, so think MM. SPEP would be the first step
A patient with bladder cancer has a biopsy done to determine its staging. Biopsy shows that the neoplasm has grown into the lamina propria, but has not invaded the detrusor muscle. What would the appropriate therapy be?
TURBT + intravesicular therapy
A 53Yo female with RA presents to the clinic with cloudy urine. UA reveals WBCs, but no LE. Culture comes back negative. Renal US shows small, bumpy hyperechoic kidneys. Hx reveals that patient has been taking OTC analgesics for several years due to her joint pain. If the medications are responsible for her condition, which is known to cause calcifications of the medullary capillaries, what is best imaging choice needed to definitively diagnose the condition?
Condition is analgesic necrosis (long term med use, pyuria, bumpy kidneys). Best Dx'd with non-contrast CT
A patient presents with rapid onset of kidney pain and hematuria. Urine microscopy reveals crystals and monomorphic RBCs. The stones composition is determined to be struvite. What bacterial enzyme plays a key role in the pathogenesis of this type of stone?
urease
SGLT2 inhibitors decrease GFR by increasing the delivery of what substance to the macula densa?
Na+
A marathon runner presents to the ED with confusion. BMP reveals a hyponatremia. If you are giving fluid to help the patient, what type of fluid would you order and how much of it would you give?