What name is given to one of two identical parts of a duplicated chromosome?
How are these duplicates connected together?
1) Chromotid
2) Centromere
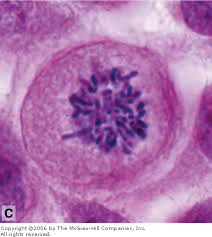
What phase is shown?
Prophase
In this phase, the microtubules shorten, pulling apart the sister chromatids.
Anaphase
G1, S, and G2 are collectively known as?
Interphase
This is an indentation or “pinched in” area on the surface of an animal cell; it will continue to pinch inward until two separate cells are formed.
Cleavage Furrow
What is the relationship between the mother cell and the 2 daughter cells?
They are exactly alike
What might happen to a cell that has undergone mitosis but not cytokinesis?
The cell would have two nuclei.
What phase is shown?

Anaphase
In this phase, the chromatids are lined up at the center of the cell.
Metaphase
What events occur in the G1 phase?
Cell doubles in size, enzymes and cell bound organelles double in number.
In plants, it is not possible for the cell to pinch inward because of the rigid cell wall. A _______ is produced between two dividing plant cells during telophase.
Cell Plate
In mitosis, 1 Mother Cell 🡪 ??
2 Identical daughter cells
What part of the cell organizes the building of the mitotic spindle?
Centriole
What phase is shown?
Telophase
In this phase, the cell cytoplasm is divided into two parts.
Telophase
What occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle?
DNA Replication
What is the end result of mitosis in a unicellular organism?
A new Organism (Asexual Reproduction)
There are two main reasons why cells divide rather than continuing to grow larger and larger. Name the two reasons
1) Large cells place to much demand on the DNA of the cell
2) Large cells have trouble getting enough nutrients across the cell membrane
What name is given to the framework to which the sister chromatids become attached?
What is this framework composed of?
1) Spindle Fibers
2) MicroTubles
What is next thing to happen?
Cytokinesis
In this phase, the nuclear membrane disappears, the nucleolus disappears, and the chromatids condense, shorten and thicken.
Prophase
What is the cell cycle?
It is the life of a cell from the time it is first formed from a dividing parent cell until its own division into two cells.
What is the result of mitosis in a multicellular organism?
Growth and Repair
What is mitosis?
What is cytokinesis?
1) Mitosis is the division of the nucleus
2) Cytokinesis is the division of the cell membrane and cytoplasm
What is the purpose of the spindle?
The microtubules of the spindle “push” the chromatids to the center of the cell during metaphase, and “pull” them apart during anaphase.
How did these chromosomes get lined up in the middle?
The Spindle fibers pushed and pulled them into position.
This is a phase in which the cell is not dividing, but carrying out its normal functions.
Interphase
What occurs during the G2 phase of the cell cycle?
What is an example of the structures created?
2)Centrioles, Microtubles
This results when there is runaway, uncontrollable cell division because the controls that keep cell division under control have failed to do their job.
Cancer Cells
As a cell grows, what is the relationship between the volume and the surface area?
The volume increases at a much greater rate than the surface area of the cell.