The diploid # of the organism above is this.
What is four?
This is the number of phases in meiosis II.
What is four?
A skin cell from an organism with 24 chromosomes will have this this many chromatids during G2.
What is 48?
Daughter cells in meiosis are not genetically identical due to crossing over that occurs during this phase.
What is Prophase I?
This is the false statement:
a. In meiosis, four daughter cells are produced; in mitosis, two daughter cells are produced
b. Crossing over is a phenomenon that creates genetic diversity during mitosis
c. In mitosis, cytokinesis occurs once; in meiosis, cytokinesis occurs twice
What is B?
If scientists studying cancer could help understand how to promote cell division in cells that do not ordinarily divide, this might help people with injuries involving these body parts.
Meiosis is used for just one purpose in the human body the production of what?
a. production of somatic (body cells)
b. production of germ cells --> gametes (reproductive) cells
b. germ cells --> gametes (reproductive) cells
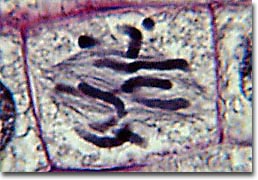
The stage of mitosis in which the chromosomes line up on a plane equidistant from the poles is this.
What is metaphase?
Genetic material is duplicated during this phase.
What is the S phase?
Asexual reproduction requires this many individuals; sexual reproduction requires this many.
What are 1 and 2?
This is how many haploid cells are created in mitosis..
What is 0 haploid cells (they are only created in meiosis - mitosis creates 2 diploid cells)
This is how many haploid cells are created in meiosis
What is 4 haploid cells?
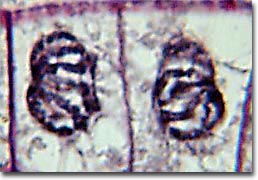
The stage of cell division that immediately follows the one seen above.
What is cytokinesis?
The process by which the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell divides to produce two cells is this.
What is cytokinesis?
Cancer is caused by uncontrolled this.
What is cell division?
You see a cell with several nuclei and know that something went wrong with cell division. This is the most likely explanation
What is... cytokinesis did not occur?
This is how many chromosomes each human gamete contains
What is 23?
A organism in which 2N = 60 will contain this many chromosomes, arranged in two nuclei, during this phase of the cell cycle.
What is 120 and telophase?
Animal cells grown in a petri dish typically stop dividing once they have formed a single, unbroken layer on the bottom of the dish. This arrest of cell division is an example of this.
What is density-dependent inhibition?
Two chromosomes in a nucleus that carry genes controlling the same inherited characteristics are called this.
What are homologous chromosomes?
You are asked to grow an unidentified sample of animal tissue and notice that the cells fail to exhibit density-dependent inhibition. The source of this tissue sample is most likely this.
What is a tumor? (cancerous tumor / cancer cell)
This statement correctly describes the behavior of a tetrad during anaphase I of meiosis.
a. it splits into two pairs of sister chromatids and one pair goes to each pole of the dividing cell
b. it travels intact to one pole of the dividing cell
c. it splits into two pairs of homologous, nonsister chromatids, and one pair goes to each pole of the dividing cell
d. it splits into four chromosomes, which distribute in random pairs to the two poles of the dividing cell
What is A?
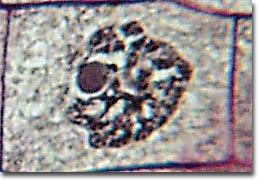
If this plant was N=54, this is how many pairs of sister chromatids would be in this cell at this stage
What is 108?
With the exception of identical twins, siblings with the same biological parents are likely to look similar because of this:
a. a similar but not identical combination of genes
b. identical genes but different chromosomes
c. the same combination of traits but different genes
What is A?
Of the following, this drug shows the most promise as a cancer chemotherapy agent:
a. a drug that prevents crossing over
b. a drug that prevents the mitotic spindle from forming
c. a drug that prevents tetrad formation
d. a drug that interferes with cellular respiration
What is B?
