Common diagnostic test for osteoporosis, done routinely for postmenopausal women.
What is a DEXA scan?
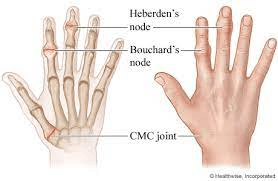
Clinical manifestations of osteoarthritis.
What are pain with activity initially (relieved by rest) and later stage pain worsening at rest, stiffness with inactivity, swelling/fluid accumulation, crepitus, and decreased ROM?
This type of disease consists of inflammation of the joints and deformity.
What is autoimmune disease (RA)?
Formations that occur throughout the white matter of the CNS.
What are plaques?
Predisposes people to fractures.
What is osteoporosis?
Three clinical manifestations of osteoporosis.
What are loss of height, change in posture (Dowager's hump), bones fracture easily (compression fractures), +/- pain.
This part of the joint deteriorates due to the process of OA.
What is cartilage (causing bone-on-bone friction and further damage)?
Vascular granulation tissue that forms in the synovial membranes of those with RA.
What is a pannus?
Most common type of MS.
What is relapsing-remitting?
Most common type of arthritis, progressive destruction of cartilage in synovial joints and vertebrae.
What is OA?
An increase in _______ activity and a decrease in osteoblast activity lead to an increased level of bone reabsorption.
What is osteoclast?
Idiopathic OA (intrinsic defects in cartilage with no identifiable cause) is seen in _____ _____ or _____.
What are old age and obesity?
Onset is considered _______ and is characterized by periods of remissions and exacerbations.
What is insidious?
Exacerbations of MS can be triggered by stress, illness, ______, or fatigue.
What is fever (or heat)?
Metabolic process characterized by decreased bone density and decreased bone mass.
What is osteoporosis?
Medication used to treat osteoporosis.
What is calcitonin?
Medication commonly used to treat OA.
What are cortiocosteroids?
Seventy to eighty percent of people with RA have this present in their blood.
What is rheumatoid factor?
One of the signs of MS; _________ of the muscles.
What is spasticity?
Risk factors for this disease include obesity, age, gender (equal after age 70), heredity.
What is osteoarthritis?
Modifiable risk factors for osteoporosis.
What are low calcium diet (we want to increase calcium, avoiding high sodium/protein, alcohol, and caffeine), sedentary lifestyle, medication use (avoid steroids, lithium, anticonvulsants, etc.)?
The type of proximal node that forms in interphalangeal joints.
What are Bouchard's nodes?
A type of systemic complication of RA.
What is vasculitis?
These types of cells are elevated in the CSF at the onset of MS.
What are helper T cells?
T lymphocytes sense the myelin as an antigen and attack it (macrophages demyelinate).
Risk factors for this disease include being female, middle age years (35-50), and possible genetic link.
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
MS has similar risk factors but usually, the age range for MS is younger (20-35).