This property of matter describes how compact a substance is.
What is density?
This is the true shape of Earth.
What is an oblate spheroid?
When writing latitude and longitude coordinates, this one always comes first.
What is latitude?
Feet above sea level.
What is elevation?
This is the thickest layer of Earth.
What is the mantle?
This force pulls objects toward Earth's center.
What is gravity?
Earth's equatorial diameter is _________________ than its polar diameter?
What is larger/bigger?
This star is used to find one's latitude in the northern hemisphere.
What is Polaris?
Lines connecting points of equal elevation are called this.
What are contour lines?
There are this many minutes in one degree of latitude or longitude.
What is 60?
A globe is considered this type of model.
What is physical?
The movement of Earth around the sun is called this.
What is revolution?
What is the Prime Meridian?
The equation change in elevation/distance is used to find this.
What is gradient?
The mathematician Eratosthenes accurately predicted this thing about Earth.
What is circumference?
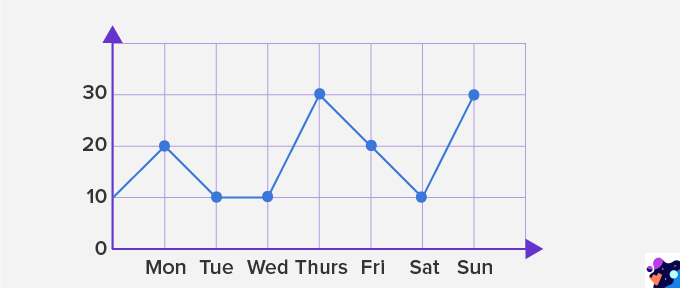 This is an example of a _______________ model.
This is an example of a _______________ model.
What is graphical?
What is 1 degree?
If it is 6:00 PM in New York, then it is this time in Los Angeles.
What is 3:00 PM?
Lines showing elevation on a contour map always bend this way when they meet a stream or river.
What is upstream?
Earth has distinct internal layers. The force of gravity causes the innermost layer to be more _________ than the outer layers.
What is dense?
These two things are needed to calculate density.
What are mass and volume?
This characteristic of a person becomes larger when they stand at the north or south pole compared to the equator.
What is weight?
This meridian separates one day from the next.
What is the International Date Line?
Hachure marks on a topographic map indicate this geographical feature.
What is a depression?
This is the difference between true north and magnetic north.
What is magnetic declination?