This model tells us where to find an electron but can't tells us how they move.
What is the Wave Mechanical Model?
 The name for an orbital with this shape.
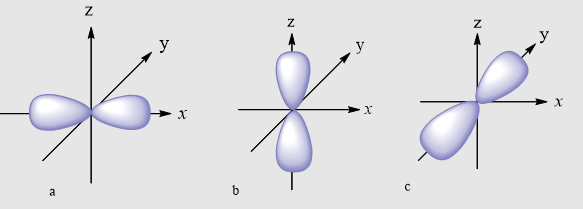
The name for an orbital with this shape.
What is the p orbital
The definition of electromagnetic radiation.
What is energy being transmitted from one place to another?
This type of elements tend to loose elections
What are metals?
The element with the electron configuration 1s1
What is Hydrogen?
The s in 1s2 tells us this type of information
What is the shape of the orbital?
This model does not tell us where to find an electron or how it moves.
What is Rutherford's atom
The name of an orbital with this shape.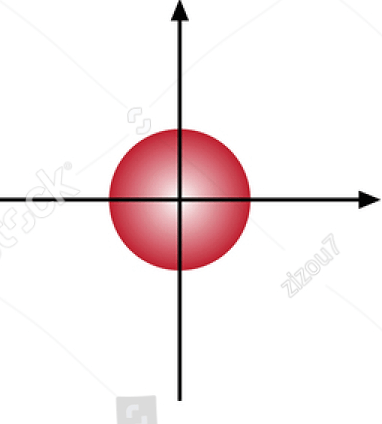
What is the s orbital?
When an electron goes in to a higher orbital.
What is it absorbs energy and becomes excited?
This number, commonly found on the periodic table, tells the number of valence elections those elements have.
What is the column number?
1s22s22p63s23p4
What is the electron configuration for S?
The max number of electrons every orbital can hold.
What is 2?
This model only works for Hydrogen, but is easy to draw.
What is Bohr's Model?
The p sub level contains this many orbitals and can hold a total of that many electrons.
What is 3 and 6?
The name commonly given to electromagnetic radiation's particle properties
What is a photon?
This property increases as you go down a column.
What is atomic size?
The number of valence electrons in chlorine.
What is 7?
What is the spin of the electrons?
This model used orbits.
What is Bohr's model
The name of an orbital with this shape.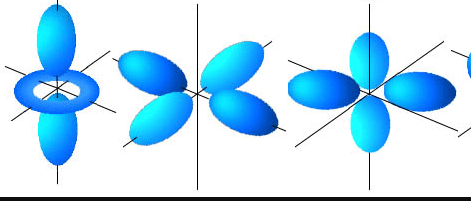
What is the d orbital?
Higher energies are carried by this type of wavelength.
What is shorter?
This property increases as you from the left to the right across a period.
This is where you would find the d orbitals on the periodic table
What is the transition metals?
The electrons in an elements highest principal energy level
What are the valence electrons?
This model is currently considered to be the only correct model.
What is the wave mechanical model?
The elements that have a 7s orbital.
What is all elements?
How we describe the energy levels emitted by atoms.
The reason atoms get smaller as you move across a period.
This orbital is filled after 4s
What is 3d?
We used this as an example of quantized levels.
What are stairs?
This model would explain a continuous emission spectrum of white light.
The d sub level contains this many orbitals and can hold a total of that many electrons.
What is 5 and 10?
The relationship between the amount of energy absorbed to move to an excited state and the amount of energy released to move to ground state.
What is identical?
The most reactive of these three elements: Ba, Ca, Ra.
What is Ra
The electron configuration for Silicon.
What is 1s22s22p63s23p2 ?
What happens to shapes of the orbitals in higher principal levels?
What is stay the same shape? or What is get larger?
The name for an area with a 90% certainty of finding an election.
What is an orbital?
The f sub level contains this many orbitals and can hold a total of that many electrons.
What is 7 and 14?
The reason each atom has a unique electromagnetic signature.
What is the unique spacing of their electrons and orbitals.
This number, commonly found on the periodic table, tells the highest principal energy level for its elements.
What is the period?
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d105p66s24f145d106p4
What is the electron configuration of Po
This principal tells us that electrons in the same orbital must have opposite spins
What is the Pauli Exclusion principal?