This is an example of what?
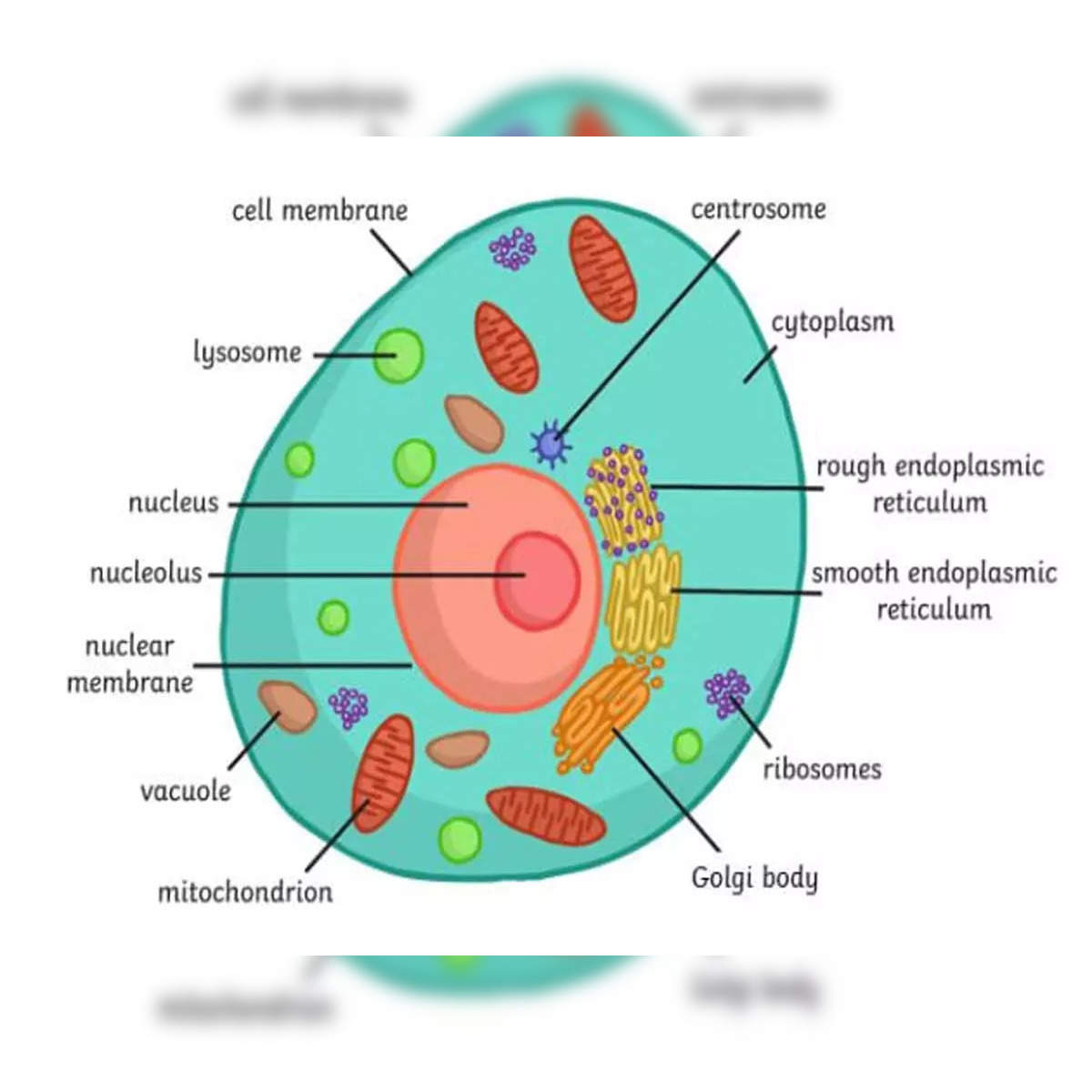
What is an Animal Cell?
This type of microscope uses light and lenses to magnify specimens and is commonly used in school laboratories.
What is a light microscope?
This cellular model describes how membrane components can move laterally within a phospholipid bilayer, explaining membrane flexibility and dynamic interactions.
What is the Fluid Mosaic Model?
This specific transport mechanism allows large or charged molecules to cross the cell membrane against their concentration gradient, requiring cellular energy.
What is active transport?
The hydrolysis of ATP releases energy by breaking these high-energy bonds, which are crucial for driving many cellular processes.
What are the phosphate bonds in ATP?
This cellular powerhouse generates most of the cell's ATP through respiration.
What are mitochondria?
These microscopic technologies allow scientists to examine cellular structures at nanoscale resolutions, revealing intricate details impossible with traditional light microscopy.
What are electron microscopes?
These polar regions of phospholipids interact readily with water molecules, creating the outer surfaces of the cell membrane.
What are the hydrophilic phosphate heads?
In diffusion, particles move from an area of ___ concentration to an area of ___ concentration.
What is high to low?
The overall equation for photosynthesis involves the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and this byproduct.
What is Oxygen?
This double-membraned organelle contains its own DNA and is responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells.
What are chloroplasts?
Label lines in biological diagrams should never have these at the ends.
What are arrows?
This molecule is scattered among phospholipids and helps to maintain membrane fluidity and stability.
What is cholesterol?
This type of passive transport uses protein channels to help large or charged particles cross the membrane.
What is facilitated diffusion?
The process of photosynthesis has two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and this stage, which does not require light.
What are light-independent reactions (The Calvin Cycle)?
This organelle contains digestive enzymes and breaks down cellular waste, damaged organelles, and foreign materials.
What are lysosomes?
In biological diagrams, this should be included if the drawing is not life-sized, so the viewer understands the size of the structures.
What is a scale?
These specialized membrane proteins span the entire phospholipid bilayer and can function as channels, carriers, or receptors for cellular communication.
What are transmembrane proteins?
This type of active transport involves the cell engulfing large particles or liquids by wrapping its membrane around them.
What is endocytosis?
This is the primary pigment responsible for absorbing light energy during photosynthesis.
What is Chlorophyll?
This organelle is a network of membranes without ribosomes, playing a key role in synthesising lipids and detoxifying harmful substances in the cell.
What is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
This part of a microscope adjusts the amount of light that reaches the specimen.
What is the diaphragm?
These membrane proteins are involved in cell recognition and often have carbohydrate chains attached.
What are glycoproteins?
Cells placed in a hypertonic solution will do this as water moves.
What is shrink/ shrivel?
This stage of cellular respiration produces the most ATP and occurs in the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
What is the Electron Transport Chain?