Chapter 2 and 3
Chapter 2 and 3
Rounded structure within the center of the cell that is the control center for the cell which contains DNA and is the site for synthesis of RNA
What is the nucleus?
The patient has been assessed and an indention remains on the lower extremities when you pressed over the tibia area which would be documented as
What is pitting edema?
What is pH 7.35 - 7.45, CO2 35-45, HCO3 22-26?
Complication of a fracture that results in severe pain, numbness, tingling, and loss of circulation.
Decrease in cell size from lack of use or inability to use an extremity
What is atrophy?
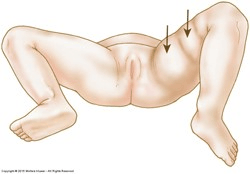 Disease or disorder indicated in the above picture
Disease or disorder indicated in the above picture
What is hip dysplasia?
Solution that will cause a cell to neither shrink nor swell.
What is Isotonic?
pH: 7.47
CO2: 52
HCO3: 35
What is partially compensated metabolic alkalosis?
ABG result:
pH: 7.35
CO2: 60
HCO3: 29
The site of ATP production in a cell
What is mitochondria?
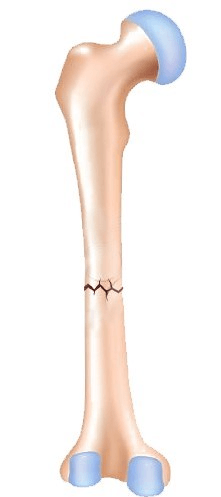
Fracture type caused by angular forces and is represented in the above picture.
What is transverse fracture?
What is hypertonic?
The client has the following symptoms fatigue, hypotension, bradycardia, and diminished deep tendon reflexes leading you to suspect this electrolyte abnormality
What is hypermagnesemia?
Lab Results Indicate:
Potassium: 4.9
Calcium: 10
Magnesium: 1.9
Phosphate: 3.0
Sodium: 155
What is hypernatremia?
Replacement of or change in the form of a cell to one that is better able to survive that result from such disease processes as GERD due to the exposure to chronic irritation from the gastric acid in the esophagus.
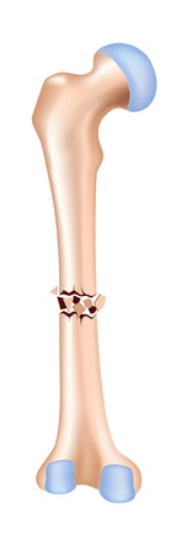 This fracture type has more than two pieces and is represented in the above image.
This fracture type has more than two pieces and is represented in the above image.
What is comminuted fracture?
This fluid contains 1/3 of the body's water, is what we are testing when we draw lab tests, and the primary cation is sodium
What is ECF (Extracellular Fluid)?
This diagnosis leads to failure of the negative feedback system that regulates the release and inhibition of ADH therefore leading to high levels of ADH with will cause low urine output and dilutional hyponatremia.
What is SIADH (syndrome of inappropriate diuretic hormone)?
Recommendations for osteoporosis includes what non pharmacological treatment
What is weight bearing exercise?
The transmission of information by neurotransmitters in the nervous system is this type of signaling
What is synaptic signaling?
This steroid hormone increases GI absorption of calcium.
This substance decreases renal excretion of calcium and increases absorption of calcium.
This substance will increase renal excretion of calcium and decrease calcium levels.
What is vitamin D?
What is PTH?
What is calcitonin?
The patient is dehydrated and therefore fluid volume is too low what hormone would attempt to correct this problem and would the hormone level increase or decrease?
What is ADH and what is increase?
The patient has been experiencing bone pain, numbness and tingling around the mouth, tetany, seizures, and has a positive trousseau and chvostek sign which indicates the most likely electrolyte disorder would be
What is hypocalcemia?
What disease process is complicated to diagnosis and will produce depression symptoms and the patient complaining of an extensive history of tiredness.
What is chronic fatigue?